Newsletter
The 315 Gala: A Night of Scandals, A Year of Distrust
From sanitary pads to shrimp: these were 315 Gala’s biggest scandals. It’s business as usual.
Published
22 hours agoon

Dear Reader,
Since yesterday, China’s trending topic lists are all about recycled sanitary pads, unhygienic disposable underwear, and water-injected shrimp.
Why, you might wonder?
It has everything to do with the 35th edition of China’s consumer day show, ‘CCTV 3.15 Gala’ (3·15晚会). It aired on Saturday night, becoming one of the most-discussed topics on Chinese social media for exposing malpractices across various companies and industries.
The famous consumer rights show, which coincides with World Consumer Rights Day, is a joint collaboration between CCTV and government agencies. It has been broadcast live on March 15 since 1991.
Each year, the theme of the show varies slightly, but its core mission remains unchanged: to educate people on consumer rights and expose violations while holding companies accountable.
At the time of writing, topics exposed on the show are dominating trending & hot lists across multiple platforms, from Weibo to Douyin, and from Kuaishou to Toutiao.

Weibo’s hot trending list dominated by 315-related topics.
I’ll give you a quick walkthrough of three major stories that have sparked the most discussion online.
1️⃣🚨 “Recycled” Counterfeit Diapers & Sanitary Napkins

The first big story involves a company from Liangshan in Jining called Liangshan Xixi Paper Products (希希纸制品有限公司), which was exposed for selling so-called “refurbished” (翻新) sanitary pad and baby diapers.
The company’s owner, Mr. Liu (刘), bought up scraps and defective sanitary napkins and baby diapers from recognized brands for anything from 260 RMB ($36) to 1400 RMB ($193) per ton. He then repackaged and resold them to unsuspecting consumers, both online and offline, making significant profits.
The incident has a lot of impact. Some of the brands involved are big and reputable Chinese companies, including Freemore (自由点) and Sofy (苏菲), some of China’s most popular feminine hygiene brands.
On Saturday night, after the scandal was brought to light, virtually all of the brands involved halted their e-commerce livestreams. Behind the scenes, marketing crises teams gathered to create statements, which soon were published online.
Sofy responded by stating that the disposal of their non-conforming products is 100% handled within a closed-loop system, ensuring they cannot be resold or reused. They also denied manufacturing the products with their branding shown in the 315 Gala and pledged to fully cooperate with authorities to combat counterfeit and substandard goods (hashtag #苏菲发声明#, over 130 million views).
In response to this incident, the authorities in Jining have undertaken various actions. They have detained those responsible and launched a citywide campaign to oversee the production and sale of sanitary napkins and baby diapers.
In online comment sections, many Chinese netizens argue that the entire industry should be investigated to prevent similar violations from recurring, as this is not the first time such issues have come to light. How did products with defects end up for sale? How can people be sure that their diapers and sanitary pads aren’t counterfeit?
In 2024, there have been multiple online discussions about the safety of Chinese sanitary pads after an online film maker exposed how illegal factories are recycling used materials, including shredded pads and diapers, into new sanitary products. These contaminated pads, sold cheaply on e-commerce platforms, have been linked to pelvic inflammation and other gynecological problems.
2️⃣🚨 Disposable Underwear Sewn by Hand, Stored Next to Trash

The second major story revealed by the 315 Gala involves disposable underwear produced by local manufacturers in the city of Shangqiu. It was uncovered by investigative reporters that many of these manufacturers do not sterilize their disposable underwear products at all. They store them in unsanitary conditions, and use toxic chemicals. Additionally, they falsely advertise their products as 100% cotton when, in reality, they are made of polyester.
Disposable underwear has become more popular in China in recent years. This is not necessarily disposable incontinence underwear, or the kind you only see in hospitals, but it’s one-time wear underwear that is sold at Miniso or Watsons and promoted as a hygienic and convenient solution for workers or travelers, for use in hotels, spas, and beyond.
Among the various companies found to be violating production standards, one company (Mengyang Clothing 梦阳服饰) had a particularly chaotic production workshop. A reporter, going undercover as a potential buyer, entered the factory and saw how workers were sewing disposable underwear with bare hands, without any sterilization, and storing them right next to piles of garbage.
Among the brands involved are those regularly sold on platforms like Taobao, including Beiziyan (贝姿妍), Chuyisheng (初医生), and Langsha (浪莎). They’ve now been removed, and Shangqiu authorities have already established a joint task force to further tackle and investigate the situation.
A related hashtag (#一次性内裤爆雷#) has received over 310 million views by now on Weibo, showing just how concerned people are about the topic. Last year, one Douyin influencer (@黑犬酱·MO) also exposed a factory for the messy and chaotic circumstances under which they produce disposable underwear, after she ended up with a gynecological infection after wearing disposable underwear. Other people shared similar experiences.
3️⃣🚨 Shrimp, with an Extra Serving of Phosphates

The third big story exposed fraudulent practices in the seafood industry, where frozen shrimp suppliers were found illegally adding excessive amounts of phosphates as a water-retention agent.
Phosphates are widely used as food additives in seafood to preserve freshness and texture, but in this case, the process was exploited to artificially increase the weight of shrimp for profit.
One reporter uncovered a facility where shrimp were soaked in phosphates for over 10 hours, resulting in a phosphate content of 30%—far exceeding legal limits.
At another seafood facility, shrimp were rapidly frozen after chemical soaking, followed by an additional coating process to further increase weight. In some cases, only 30% of the final weight was actual shrimp after defrosting.
Beyond the deceptive nature of these practices, the overuse of phosphates poses serious health risks, including digestive issues, or increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
One worker at the seafood plant interviewed by one of the reporters admitted that they never eat the shrimp they process, saying: “Here on the coast, we only eat fresh shrimp.”
🔁🇨🇳 Business as Usual
These stories, along with other brands and fraudulent practices exposed by CCTV, have sparked anger among netizens. Many women voiced concerns about the safety of sanitary pads. Others wondered about the quality of their seafood. Some vowed never to buy disposable underwear again. Parents angrily asked why they had to question the safety of the diapers for their babies.
An old Dutch saying goes, “Trust arrives on foot and leaves on horseback.” It can take years to build a reputation, but a single bad incident can ruin people’s trust in an instant. This is especially true in China, where public trust in well-known brands has been repeatedly shaken by scandals. A single product crisis can not only severely damage a company’s reputation, but even lead to an erosion of trust in the entire industry.
➡️ The most infamous and devastating example, which left a deep scar on consumer trust, was the 2008 melamine scandal, in which dairy manufacturers deliberately added melamine, an industrial chemical—to diluted raw milk to falsely boost its protein content. Among the infants and children who consumed the tainted milk, over 250,000 cases of health problems were reported. 52,000 children were hospitalized, and six infants lost their lives.
Although the milk powder scandal became a turning point for food and product safety regulations in China, leading to stricter oversight and improved industry standards, it also fueled deep consumer distrust. Even as Chinese brands worked to enhance quality and adopt international safety standards, many consumers remained hesitant to trust them.
➡️ Last year’s cooking oil scandal, involving transport trucks and cargo ships being used to carry both cooking oil and toxic chemicals without proper cleaning procedures, again fueled many discussions about public safety and if people can trust the products they use on a daily basis. It raised public concern not just about unsafe food-handling practices, but also about a myriad of other problems, including a lack of enforcement, bureaucratic inefficiency, power plays, public deception, and especially a lack of transparent communication in the aftermath of such scandals.
🔹 Somewhat ironically, CCTV’s 315 Gala is tackling precisely this issue. By exposing unsafe products and illegal business practices, the show puts brand names, details, and investigations into the public eye. In doing so, they help shape an online discourse where state media, local authorities, and consumers unite in their fight against industry misconduct.
At the end of the day, both brands and consumers have become familiar with the playbook that follows such crises when they are exposed on the 315 Gala.
🔍 Today, an interesting blog by Market News (市场资讯) published on Sina Finance (“开了24年的315晚会 四大规律你懂么”), voiced a critique of the Consumer Day show, arguing that the show, instead of an actual solution for China’s food & product safety, has become more like an annual ritualistic spectacle for the people, a cathartic pressure valve for public frustration.
The author observes four patterns in relation to scandals exposed on the show.
📌 Businesses & consumers follow the same old script
The apologies are ready, the bows are rehearsed, and the damage control strategies are in place.
After so many years of getting exposed, Chinese companies no longer panic after being featured on the show. They have their response templates prepared and a crisis strategy to manage public outrage. Meanwhile, e-commerce platforms swiftly cut ties with implicated brands and showcase new quality control measures, while consumers are comforted with apology letters and discount coupons before getting distracted by the next headlines.
📌 Authorities/regulators also stick to their routine playbook
Similarly, Chinese regulators have a scripted response ready to demonstrate their proactiveness in handling the situation. They quickly issue official statements, ensuring to include phrases like “immediate shutdown,” “ongoing investigation,” and “fines will be imposed.”
📌 The dark side of the industry will still be there
Big businesses prioritize profit over ethics, and as long as the profits outweigh the fines, companies will continue to test regulatory boundaries. There will always be loopholes to exploit, ensuring that these scandals will happen again.
📌 Only small companies face real consequences
While major corporations have the capital and resources to weather a public relations crisis, it is only the small companies without strong investor backing that fail to recover after being exposed on the 315 Gala. This also means that these scandals often don’t actually lead to industry reform.
Scrolling through Chinese social media today, it’s evident that the combined force of social media and the CCTV 315 Gala show has an immense impact.
But public outrage has a short lifespan.
The more consumers grow accustomed to scandals, the more consumer tolerance increases, and the more corporate ethics degrade.
Public distrust remains. The anger is there. But the scandals continue.
The CCTV 315 Gala provides an opportunity for everyone to be angry about it for a day.🔚
There were even more consumer scandals this week, which you can read about below. Special thanks to Miranda Barnes for her input and contributions to this week’s newsletter—be sure to check out her podcast recommendation as well.
Best,
Manya Koetse
(@manyapan)
What’s Trending

What’s Behind the Headlines

Last week and into the beginning of this week, the Two Sessions—China’s annual parliamentary meetings—were trending on Weibo and other Chinese social media platforms. Chinese online media were filled with coverage, yet Western newspapers had surprisingly little to say about these meetings.
I listened to a well-known podcast by two British political commentators: The Rest Is Politics, hosted by Alastair Campbell and Rory Stewart. They talked about how little the Western world has been reporting about the Two Sessions in China.
This is how the podcast was started by Campbell:
“(..) Because most of our media hasn’t bothered with it, we should talk about the China National Congress they just had (..) The reason I wanted to talk about China is that we are in this world where we all tell each other that there are two superpowers in the world: the United States and China. And the United States, we cover and discuss every single aspect of everything that’s been happening inside Donald Trump’s White House—(..), we’re even talking about the woman who walks alongside Trump carrying his bags and knocking the dandruff off his suit and all that sorts of stuff. And yet China has just held its Two Sessions, which is the National Congress and the big advisory body, and it’s as if it never happened.
Over the past few days, I’ve been asking people if they’re aware of anything big happening in China recently, and nobody knows.
Now, I won’t put you on the spot, Rory, because it would be too cruel, but if I asked people to name the seven members of the Chinese Communist Party Politburo Standing Committee—probably the seven most powerful people in China—most of our listeners won’t know.
So, is this a language thing? Is it because Trump floods the zone with so much shit that we just find ourselves poking in the turds, deciding which piece to focus on before he drops the next one?
Or is it that we maybe haven’t fully caught up with just how important China is now in terms of our lives, as much as their own?”
In this podcast, the two hosts acknowledged that Trump, and, of course, the ongoing war, dominate media coverage in the West. But they made a very valid point in questioning how people could be ignoring such a major political event in China, emphasizing just how crucial China is on the world stage.
They argued that mainstream media editors simply don’t prioritize China—not because there aren’t great journalists covering it, but because it’s not seen as a pressing topic. They also suggested that this lack of coverage isn’t always due to disinterest (there’s no doubt the world is interested in China), but that language and cultural barriers might also play a role.
Yet, as pointed out in the podcast, here we are: the West, living under Trump’s influence, reacting from tweet to tweet, tantrum to tantrum, while practically disregarding Xi’s long-term vision—his roadmap for China from 2021 to 2035 and then from 2035 to 2050—which follows a methodical strategy that will inevitably shape the future.
You can watch or listen to the podcast here.
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

You may like
Newsletter
Five Trending Proposals at the Two Sessions 🔍
From noteworthy proposals at the Two Sessions to Chinese online reactions to Trump’s policy shifts on Ukraine and surprising Hu Xijin news.
Published
1 week agoon
March 9, 2025
PREMIUM NEWSLETTER | ISSUE #48
Dear Reader,
“It’s not that I don’t understand, it’s just that the world is changing so quickly,” one Weibo blogger commented this week, after yet another major news development hit the breaking news section.
Chinese social media has been flooded with discussions about the geopolitical shake-ups triggered by the Russia-Ukraine War and Trump’s policy shifts.
From the Oval Office clash to Trump’s ‘pivot’ to Russia, I’ve been monitoring the public sentiment on Chinese social media. You can read how Chinese netizens are interpreting the rapidly changing geopolitical landscape in our latest update here.
At the same time, the Two Sessions (liǎnghuì 两会), China’s largest annual parliamentary meetings, are also taking place. These meetings, which outline policy priorities, economic targets, and development plans for the upcoming year, commenced at the Great Hall of the People in Beijing on March 4 and will continue until March 11.
This includes the annual meeting of the National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC) advisory body and the meeting of the National People’s Congress (NPC), China’s legislative assembly—often described as a rubber-stamp parliament. This major political event is heavily propagated on Chinese social media, mainly on Weibo and Douyin.
Beyond providing insight into China’s strategic direction, the Two Sessions are also significant because they give delegates from across the country the opportunity to make their voices heard by China’s top leaders. These proposals and “suggestions” (建议)—essentially influential recommendations to government departments—often reflect public concerns and frequently go viral on Chinese social media.
For example, in previous years, a proposal to prohibit single women from freezing their eggs in an attempt to encourage marriage and childbirth sparked heated discussions on Weibo. Last year, another noteworthy proposal suggested that China’s online influencers—whether celebrities or e-commerce stars—should face harsher penalties than the general public for engaging in illegal activities, due to their influence on society.
This year, several new proposals have gained significant online attention. Here are five trending proposals from the past few days:
1. Integrating Sexual Assault Prevention into the School Curriculum
Hashtag: #建议将防性侵教育纳入义务教育课程体系#
🔹 In recent years, sexual assault against minors has become a frequently discussed topic in Chinese media. During this year’s Two Sessions, NPC delegate Fang Yan (方燕) is advocating for stronger protections for minors against sexual violence.
Among her key proposals, Fang suggests that school staff should be specifically screened for prior sexual assault offenses and calls for harsher penalties for those who commit such crimes. She also proposes that sexual assault prevention be integrated into the compulsory education curriculum through lesson plans and textbooks.
In the past, Chinese official media have launched awareness campaigns to help parents teach their children about sexual education and self-protection. However, these campaigns have also sparked online debate, with some arguing that sexual education should not be solely the parents’ responsibility—the education system should play a bigger role in addressing this issue.
2. Ban on Age Discrimination in Employment
Hashtag: 建议将禁止就业年龄歧视纳入法律
🔹 If you’re familiar with Chinese job advertisements, you’ll know how common it is to see age restrictions across different industries. Job listings often include requirements like “must be under 35”—or even physical requirements like “over 170 cm tall.”
This week, NPC delegate Meng Yuan (蒙媛) proposed officially banning age discrimination in hiring, aiming to tackle the “35+ job predicament” (“35岁+ 就业困境”) that many job seekers face. Although age discrimination is not yet officially recognized as employment discrimination in China, it remains widespread. Many companies prioritize younger workers for their lower salaries and perceived trainability, often overlooking the value of experience that older employees bring. In some industries, age discrimination starts as early as 30.
While there is strong online support for such a labor law, many doubt that it will effectively change hiring practices, as job seekers over 35 continue to face widespread discrimination in the Chinese job market.
3. Addressing “Involution” in Chinese Education
Hashtag: #建议破除教育内卷#
🔹 You might remember an image that went viral during flu season, showing Chinese schoolchildren doing homework while hooked up to an IV in a hospital. These images, in many ways, embodied the concept of nèijuǎn (内卷), or “involution”—a term representing the intense academic pressures in China.
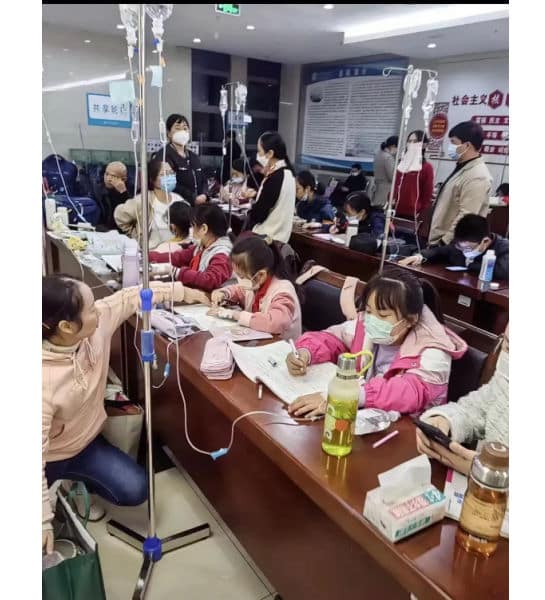

The image that went viral during flu season in winter of 2023.
This buzzword has been widely discussed on Chinese social media and reflects China’s highly competitive education system. One well-known cram school slogan summed up the rat race perfectly: “If you come to us, we will train your kids. If you don’t come to us, we will train the competitors of your kids.”
Now, “involution” has officially moved from online discussions to government reports, as the prevention of “involution-style” competition has been included in the Government Work Report. Delegate Yan Meirong (阎美蓉) also advocates for a better learning environment for children. Instead of focusing solely on numerical scores, he suggests introducing a grading evaluation system in classrooms and shifting the emphasis to critical thinking, innovation, practical skills, and emotional awareness.
Similarly, NPC delegate Liu Xiya (刘希娅) proposed shifting away from China’s “top-student selection” model and focusing more on children’s overall well-being, by emphasizing daily exercise and eliminating extra tutoring (#代表说0补课0月考孩子成绩都是A#).
4. The Impact of Short Videos on Children’s Attention Spans
Hashtag: #姚明建议开展未成年人息屏24小时行动#
🔹 Another noteworthy trending proposal comes from NPC delegate Yao Ming (姚明), China’s basketball icon. Yao wants to raise awareness about the impact of short videos on children’s attention spans, arguing that excessive screen time weakens deep-thinking abilities and makes it harder for kids to focus on reading long texts.
To tackle this issue, he proposed a “24-hour screen-free challenge”, endorsed by schools every semester, encouraging children to engage in alternative activities like music, sports, and the arts.
Another delegate, Bai Yansong (白岩松), suggested taking it even further, advocating for one screen-free day per month in all Chinese schools.
Some commenters jokingly suggested that it wouldn’t be a bad idea to implement this for adults, too.
5. Strengthening Governance Over AI Deepfakes and Voice Cloning
Hashtag: #雷军5个建议4个和汽车有关#
🔹 Lei Jun is the founder and CEO of Xiaomi, but made the news as a delegate submitting five proposals this week, which he also published on his public WeChat account.
Four of Lei Jun’s suggestions focus on the development of China’s automotive industry. He proposed creating a standardized system for AI-powered devices, as they play an important role in the future of AI in China. He believes China should lead the world in this industry by 2030, and to get there, stronger industrial collaboration, a clear standards system (since AI-enabled devices are rapidly emerging with different functions and qualities), and increased support from central and local authorities for R&D and everyday applications are needed.
He also proposed accelerating the commercialization of autonomous driving in China, improving the license plate design of New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) to better suit changing times (by, for example, adding smart features), and enhancing the overall NEV ecosystem.
But perhaps the proposal most popular with netizens was his call to strengthen governance over AI deepfakes and voice cloning to combat the illegal use of such technologies. Lately, there’ve been more stories involving fraudulent practices and scams that involve such technologies, and Chinese official channels have been trying to create more awareness on the abuse of such technologies.
🚀 There’ll be more Two Sessions news on the site soon, as Ruixin Zhang is currently working on an insightful piece about some noteworthy feminist issues related to the meetings.
I’ve sent this newsletter out through a new system integrated into my platform, so if there are any hiccups or you’re experiencing difficulties reading, opening links, etc., please let me know! If you receive this newsletter twice, my apologies in advance. Also, if you’re not receiving this newsletter in your inbox but should be, and are only reading it on the site, drop me a line and I’ll fix it asap.
As always, thanks for your support—every subscriber helps keep What’s on Weibo running. If you enjoy what we do, please recommend us to your friends. And if your colleagues would be interested in staying on top of the latest trends and deep dives into digital China, reach out—I offer discounted group subscriptions 🙌.
Warm greetings,
Manya Koetse
(@manyapan)
China’s Online Discourse on the Russia-Ukraine War

Why are some Weibo commentators calling Zelensky a ‘saint’? How are Trump’s policy shifts on Russia and Ukraine being received by Chinese netizens? And where does Taiwan fit into the bigger picture?
As the Russia-Ukraine war enters its third year, Chinese social media is once again flooded with discussions about the geopolitical shifts triggered by Trump’s policies. From the Oval Office clash to Trump’s ‘pivot’ to Russia, this article explores how Chinese netizens are interpreting the rapidly changing geopolitical landscape.
This article is part of the current focus topic for our What’s on Weibo Chapters: China’s Online Discourse on the Russia-Ukraine War.

A video has been making the rounds around the internet recently suggesting that Chinese nationals are fighting for Russia in the Donetsk region. The source is unknown, but some Chinese bloggers commented on the rumors.
➡️ Just because they speak Chinese doesn’t mean they’re Chinese nationals. There’s skepticism over the handwriting on the wall ( “Li Jingjing was here” “李晶晶到此一游”)—some argue the Chinese characters look poorly written, possibly by non-Chinese (such as Koreans).
➡️ Cosplay theory: Many believe it shows Chinese military fans or vloggers staging content, not real soldiers. There’s a lot of realistic military cosplay content on platforms like Kuaishou and Bilibili.
➡️ And then there are those wondering, “Who is Li Jingjing?!” Plus the Chinese blogger who jokingly pleaded: “Li Jingjing, come home—it’s not worth dying on the Russian battlefield.” Check out more on this below, including link to video:
What’s Trending

🎬 Ne Zha 2 Not in Taiwanese Cinemas
Ne Zha 2 continues to be a major topic of discussion on Chinese social media. Earlier this week, a top hashtag on Weibo (#哪吒2闯进全球前7却闯不进宝岛台湾#) highlighted the fact that Ne Zha 2 is not being released in Taiwanese cinemas. Taiwan enforces a strict quota of 10 mainland films per year, selected randomly by drawing lots—though exceptions are sometimes made. Despite the film becoming one of the highest-grossing animations worldwide, it remains absent from Taiwan’s screens. This has sparked some nationalistic responses, with many netizens suggesting that once Taiwan is “reunited with the motherland,” such quotas on mainland movies will no longer exist. Read more on Ne Zha 2 here.

🕯️ Death of Singer-songwriter Khalil Fong
Over the past week, Chinese netizens have been mourning Mandopop artist Khalil Fong (Fang Datong 方大同), who passed away at just 41. The American-born, Hong Kong–based R&B singer was widely seen as an inspiring figure who made a lasting impact on the mainland market by introducing fresh sounds. He won acclaim for his 2017 Journey to the West album and had only recently released a new album, despite battling illness for the past five years. The hashtag “Fang Datong Passed Away” (#方大同去世#) has garnered over 1.7 billion views on Weibo, where many are expressing their sadness over the loss of yet another young icon — with the death of Barbie Hsu still also being widely discussed.

🔪 Farewell to “Brother Knife”
Another beloved person who recently passed away is Li Kunpeng (李坤朋), better known as “Brother Knife” (菜刀哥) on the Chinese internet. During the devastating floods in Zhengzhou, Henan, in July 2021, Li became a local hero after a bystander’s video went viral showing him climbing onto the hood of a car that was being submerged in floodwaters, attempting to break the windshield with a kitchen knife, and calling on others to help. Thanks to his efforts, a grandfather and two children were successfully rescued from the sinking vehicle. Li, along with seven others, later received an award for their bravery—an act that stood out not only because of the tragic circumstances of the 2021 floods but also in a society where the “bystander effect” is a widely discussed phenomenon. Li passed away on March 3 at the age of just 39, after falling unexpectedly ill.

⭐ Xiaomi’s Lei Jun Shines at Two Sessions
Lei Jun (雷军), Xiaomi’s founder & CEO, isn’t just making headlines for his proposals at the Two Sessions this week—his cheerful presence and humble demeanor are also capturing public attention.
While speaking to the media at the “Deputies’ Corridor” before the opening of the third session of the 14th NPC on March 5, Lei Jun gave a speech highlighting Xiaomi’s commitment to contributing to “Chinese-style modernization” by pursuing high-end development strategies and continuing to innovate, applying the latest AI technologies.
More than the content of the speech—which largely follows the core ideas of China’s national AI plans—it’s Lei Jun’s delivery that’s popular with netizens. “It’s like I’m seeing a friend speaking,” some said. Social media users from Hubei, in particular, are expressing pride in Lei Jun (he was born in Xiantao, Hubei): “Aren’t we Hubei people particularly handsome?” “Who actually doesn’t like Lei Jun?” (“谁会不喜欢雷军呢”), another Weibo commenter wondered. Lei Jun’s popularity highlights how China’s tech entrepreneurs—at least some of them—are seen as modern idols, inspiring the public with their success stories.

🇨🇳 Tough Taiwan Language During Two Sessions
During the Two Sessions this week, Taiwan was a key topic, accompanied by a coordinated online propaganda campaign by Chinese official channels. The hashtag “Taiwan, Province of China” (#中国台湾省#) topped the trending list. CCTV posted an image on Weibo showing “China” in red with the text “Taiwan must return” below, stating: “Forward this! Taiwan Province, China—this is the only correct name for Taiwan! Taiwan has never been a country; it never was and never will be.” People’s Daily shared another version, declaring: “China will eventually achieve reunification; it is destined to be unified.”
The slogan “Taiwan was never a country” (“台湾从来不是一个国家”) has been ubiquitous across Chinese social media this week. It echoes a statement made by Foreign Minister Wang Yi during his March 7 press conference at the Two Sessions, where he stressed that the only official reference to Taiwan within the United Nations is “Taiwan, Province of China.” 📢 In our latest article, we provide more context.
What’s Noteworthy

We haven’t heard much from the well-known political and social commentator Hu Xijin lately. For those of you who’ve been following What’s on Weibo for a while, you might recall that I have often mentioned Hu Xijin’s perspectives in articles. With over 24 million followers on Weibo alone, the former editor-in-chief of the Global Times is one of those influential voices capable of shaping public opinion or sparking heated debates. He’s typically a daily presence on social media, always in the public eye.
However, since Hu Xijin abruptly went silent on Weibo in the fall of 2024 and stayed off social media for 100 days, his online presence seems to have lost some of its usual momentum.
The Weibo algorithms don’t appear to be boosting his posts as much anymore. He used to frequently dominate the trending hot lists, but I’m not seeing that happen lately.
Perhaps Hu himself sensed that things on Weibo weren’t going his way either, which might explain why he announced this week that he’s launching a new account on Xiaohongshu (also known as Rednote), the Chinese social app focused on lifestyle, fashion, and food—and not particularly on politics.
This shift to Xiaohongshu is funny for multiple reasons. This is the same man who, ahead of Pelosi’s controversial Taiwan visit, suggested it would be okay to shoot down her plane if Chinese fighter jets couldn’t stop it from landing in Taipei. He’s not exactly the kind of person you’d expect to see cheerfully talking about his favorite foods. Yet here he is, chatting about snacks, showing off his workout routine, and sharing his international experiences.
In his first video on the platform, Hu Xijin vowed not to discuss politics, but instead to focus on his everyday life. So far, he’s doing just that—and seems to be smiling a lot more. At the same time, Hu doesn’t seem too concerned—or perhaps just doesn’t care—whether Xiaohongshu’s typical user base (mostly young, educated female consumers) is thrilled about his presence on the platform. After his first video, he received plenty of sarcastic comments and jokes. “Gosh, this scared me,” some wrote, while others asked: “Who let their dog out?”
An image on Xiaohongshu mocking Hu Xijin.
In the end, some wonder whether ‘Old Hu’ is really on the app to share his lifestyle, or if he’s simply looking for an extra stream of monetization now that his career as a political commentator seems more vulnerable. He may be muted when it comes to talking about Beijing’s politics and economy—but when it comes to Beijing dumplings, he won’t be silenced anytime soon.
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
Newsletter
Ne Zha 2: Making Donghua Great Again
Explaining why the celebration of the success of “Ne Zha 2” goes beyond box office numbers and cinema screens.
Published
3 weeks agoon
February 27, 2025
PREMIUM NEWSLETTER | ISSUE #47
Dear Reader,
These days, everybody is talking about Ne Zha 2 (哪吒2:魔童闹海), the recent hit film about one of China’s most legendary mythological heroes. With its spectacular visuals, epic battles, funny characters, dragons and deities, and moving scenes, the Chinese blockbuster animation is breaking all kinds of records and has gone from the major hit of this year’s Spring Festival film season to the 7th highest-grossing movie of all time and, with its 13.8 billion yuan ($1.90 billion USD) box office success, now also holds the title of the most successful animated film ever worldwide.
But there is so much more behind this movie than box office numbers alone. There is a collective online celebration surrounding the film, involving state media, brands, and netizens. On Weibo, a hashtag about the movie crossing the 10 billion yuan ($1.38 billion) milestone (#哪吒2破100亿#) has been viewed over a billion times. Social media timelines are filled with fan art, memes, industry discussions, and box office predictions.
The success of Ne Zha 2 is not just a win for China’s animation industry but for “Made in China” productions as a whole. Some argue that Ne Zha‘s triumph is not just cultural but also political, reinforcing China’s influence on the global stage and tying it to the ongoing US-China rivalry: after growing its power in military strength, technology, and AI, China is now making strides in cultural influence as well.
In a recent Weibo post, state broadcaster CCTV also suggested that Hollywood has lost its monopoly over the film industry and should no longer count on the Chinese market—the world’s second-largest movie market—for its box office dominance.
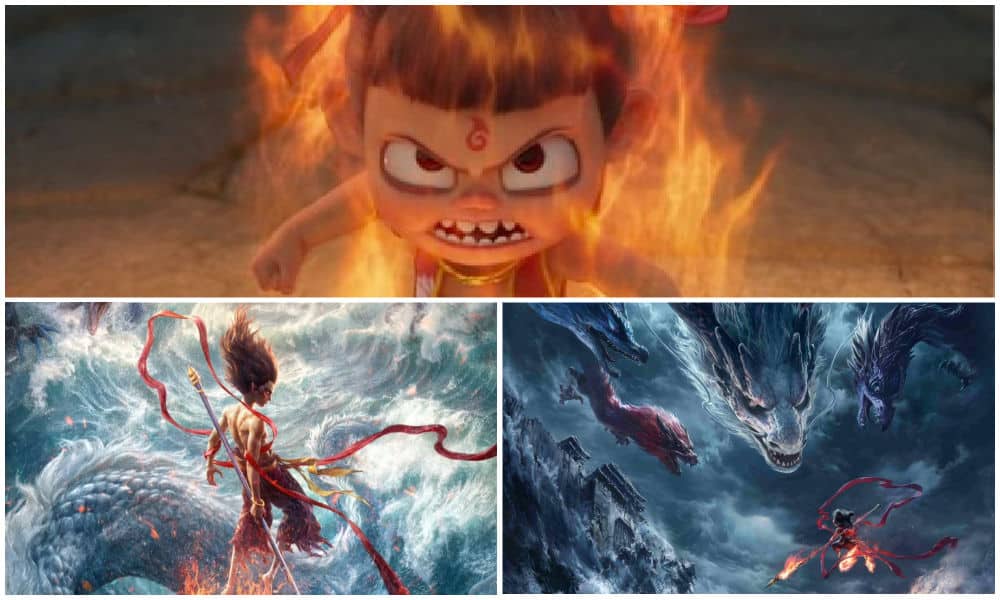

Various images from “Ne Zha 2” 哪吒2:魔童闹海
The success of Ne Zha 2 mainly resonates so deeply because of the past failures and struggles of Chinese animation (donghua 动画). For years, China’s animation industry struggled to compete with American animation studios and Japanese anime, while calls grew louder to find a uniquely Chinese recipe for success—to make donghua great again.
🔹 The Chinese Animation Dream
A year ago, another animated film was released in China—and you probably never heard of it. That film was Ba Jie (八戒之天蓬下界), a production that embraced Chinese mythology through the story of Zhu Bajie, the half-human, half-pig figure from the 16th-century classic Journey to the West (西游记). Ba Jie was a blend of traditional Chinese cultural elements with modern animation techniques, and was seen as a potential success for the 2024 Spring Festival box office race. It took eight years to go from script to screen.
But it flopped.
The film faced numerous setbacks, including significant production delays in the Covid years, limited showtime slots in cinemas, and, most importantly, a very cold reception from the public. On Douban, China’s biggest film review platform, many top comments criticized the movie’s unpolished animation and special effects, and complained that this film—like many before it—was yet another Chinese animation retelling a repetitive story from Journey to the West, one of the most popular works of fiction in China.
“Another mythological character, the same old story,” some wrote. “We’re not falling for low-quality films like this anymore.”
The frustration wasn’t just about Ba Jie—it was about China’s animation industry as a whole. Over the past decade, the quality of Chinese animation films has become a much-discussed topic on social media in China—sometimes sparked by flops, and other times by hits.
Besides Ba Jie, one of those flops was the 2018 The King of Football (足球王者), which took approximately 60 million yuan ($8.8 million) to make, but only made 1.8 million yuan ($267,000) at the box office.

Both Ba Jie, which took years to reach the screen, and King of Football, a high-budget animation, ended up as flops.
One of those successes was the 2019 first Ne Zha film (哪吒之魔童降世), which became China’s highest grossing animated film, or, of the same year, the fantasy animation White Snake (白蛇:缘起), a co-production between Warner Bros and Beijing-based Light Chaser Animation (also the company behind the Ne Zha films). These hits
showed the capabilities and appeal of made-in-China donghua, and sparked conversations about how big changes might be on the horizon for China’s animation industry.
“The only reason Chinese people don’t know we can do this kind of quality film is because we haven’t made any good stories or good films yet,” White Snake filmmaker Zhao Ji (赵霁) said at the time: “We have the power to make this kind of quality film, but we need more opportunities.”
More than just entertainment, China’s animated films—whether successes or failures—have come to symbolize the country’s creative capability. Over the years, and especially since the widespread propagation of the Chinese Dream (中国梦)—which emphasizes national rejuvenation and collective success—China’s ability to produce high-quality donghua with a strong cultural and artistic identity has become increasingly tied to narratives of national pride and soft power. A Chinese animation dream took shape.
🔹 The “Revival” of China’s Animation Industry
A key part of China’s animation dream is to create a 2.0 version of the “golden age” of Chinese animation.
This high-performing era, which took place between 1956 and 1965, was led by the Shanghai Animation Film Studio. While China’s leading animators were originally inspired by American animation (including Disney’s 1937 Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs), as well as German and Russian styles, they were committed to developing a distinctly Chinese animation style—one that incorporated classical Chinese literature, ink painting, symbolism, folk art, and even Peking opera.
Some of the most iconic films from this era include The Conceited General (骄傲的将军, 1956), Why Crows Are Black (乌鸦为什么是黑的, 1956), and most notably, Havoc in Heaven (大闹天宫, 1961 & 1964). Focusing on the legendary Monkey King, Sun Wukong (孙悟空), Havoc in Heaven remains one of China’s most celebrated animated films. On Douban, users have hailed it as “the pride of our domestic animation.”
One of China’s most renowned animation masters, Te Wei (特伟), once explained that the flourishing of China’s animation industry during this golden era was made possible by state support, a free creative atmosphere, a thriving production system, and multiple generations of animators working together at the studio.
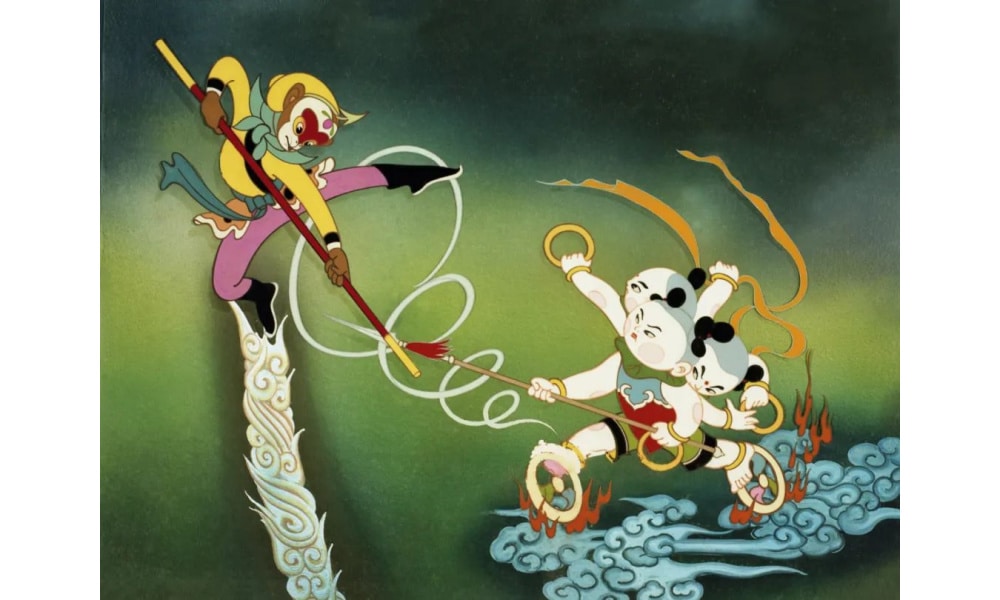

Still from Havoc in Heaven 大闹天宫 via The Paper.
➡️ So what happened to the golden days of Chinese animation?
The decline of this golden era was partly due to the political turmoil of the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976). While there was a second wave of successful productions in the late 1970s and 1980s, the industry lost much of its ‘magic touch’ in the 1990s and 2000s. During this period, Chinese animation studios were pressured to prioritize commercial value, adhere to strict content guidelines, and speed up production to serve the rising domestic TV market—while also taking on outsourcing work for overseas productions.
As the quality and originality of domestic productions lagged behind, the market came to be dominated by imported (often pirated) foreign animations. Japanese series like Astro Boy, Doraemon, and Chibi Maruko-chan became hugely influential among Chinese youth in the 1990s. The strong reaction in China to the 2024 death of Japanese manga artist Akira Toriyama, creator of Dragon Ball, also highlighted the profound impact of Japanese animation on the Chinese market.
This foreign influence also changed viewers’ preferences and aesthetic standards, and many Chinese animations adopted more Japanese or American styles in their creations.
However, this foreign ‘cultural invasion’ was not welcomed by Chinese authorities. As early as 1995, President Jiang Zemin reminded the Shanghai Animation Film Studio of the ideological importance of animation, emphasizing that China needed its “own animated heroes” to serve as “friends and examples” for Chinese youth.
By the early 2010s, the revitalization and protection of China’s animation industry became a national priority. This was implemented through various policies and incentives, including government funding, tax reductions and exemptions for Chinese animation companies, national animation awards, stipulations for the number of broadcasted animations that must be China-made. Additionally, there was an increased emphasis on animation as a tool for cultural diplomacy, focusing on how Chinese animation should reflect national values and history while maintaining global appeal.
It’s important to note that the so-called ‘rejuvenation’ of Chinese animation is not just a cultural and ideological project, there are economic motives at stake too: China’s animation industry is a multi-billion dollar industry.
🔹 “Are We Ne Zha or the Groundhogs?”
The huge success of Ne Zha 2 is seen as a new milestone for Chinese animation and as inspiration for audiences. The film took about five years to complete, reportedly involving 140 animation studios and over 4,000 staff members. The film was written and overseen by director Yang Yu (杨宇), better known as Jiaozi (饺子).
The story is all based on Chinese mythology, following the tumultuous journey of legendary figures Nezha (哪吒) and Ao Bing (敖丙), both characters from the 16th-century classic Chinese novel Investiture of the Gods (Fengshen Yanyi, 封神演义). Unlike Ba Jie or other similar films, the narrative is not considered repetitive or cliché, as Ne Zha 2 incorporates various original interpretations and detailed character designs, even showcasing multiple Chinese dialects, including Sichuan, Tianjin, and Shandong dialects.
One of the film’s unexpected highlights is its clan of comical groundhogs. In this particularly popular scene, Nezha engages in battle against a group of groundhogs (土拨鼠), led by their chief marmot (voiced by director Jiaozi himself). Amid the fierce conflict, most of the groundhogs are hilariously indifferent to the fight itself; instead, they are focused on protecting their soup bowls and continuing to eat—until they are ultimately hunted down and captured.
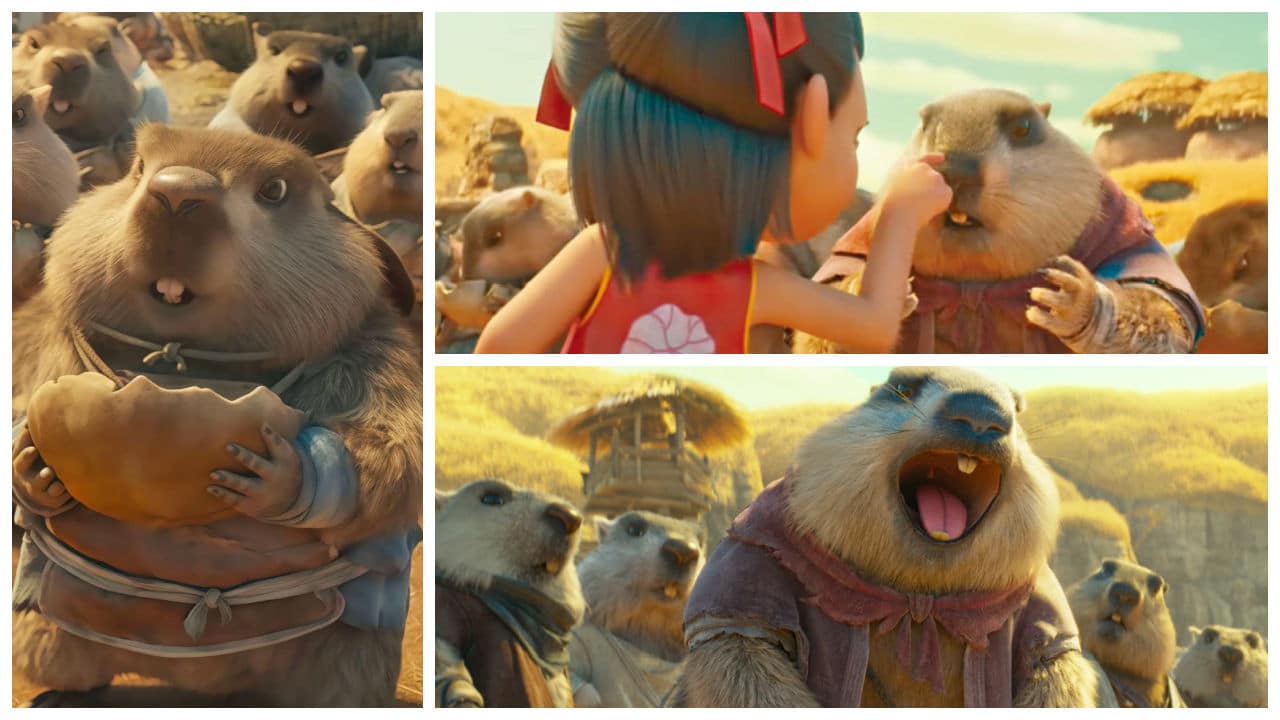

Nezha and the clan of groundhogs.
Besides fueling the social media meme machine, the groundhog scene actually also sparked discussions about social class and struggle. Some commentators began asking, “Are we Ne Zha or the groundhogs?”
Several blogs, including this one, argued that while many Chinese netizens like to identify with Nezha, they are actually more like the groundhogs; they don’t have powerful connections nor super talents. Instead, they are hardworking, ordinary beings, struggling to survive as background figures, positioned at the bottom of the hierarchy.
One comment from a film review captured this sentiment: “At first, I thought I was Nezha—turns out, I’m just a groundhog” (“开局我以为自己是哪咤,结果我是土拨鼠”).
The critical comparisons between Nezha and the groundhogs became politically sensitive when a now-censored article by the WeChat account Fifth Two-Six District (第五二六区) suggested that many Chinese people are so caught in their own information bubbles and mental frameworks that they fail to grasp how the rest of the world operates. The article said: “The greatest irony is that many people think they are Nezha—when in reality, they’re not even the groundhogs.”
While some see a parallel between Nezha’s struggles and their own hardships, others interpret the film’s success as a symbol of China’s rise on the global stage—particularly because the story is so deeply rooted in Chinese culture, literature, and mythology. This has led to an alternative perspective: rather than remaining powerless like the groundhogs, perhaps China—and its people—are transforming into the strong and rebellious Nezha, taking control of their destiny and rising as a global force.
Far-fetched or not, it’s an idea that continues to surface online, along with many other detailed analyses of the film. The nationalist Chinese social media blogger “A Bad Potato” (@一个坏土豆) recently wrote in a Weibo post:
“We were once the groundhog, but today, nobody can make us kneel!” (“我们曾经是土拨鼠,但是今天,没有任何人可以让我们跪下!”)
In another post, the blogger even dragged the Russia-Ukraine war into the discussion, arguing that caring too much about the powerless “groundhogs,” those struggling to survive, does not serve China’s interest. He wrote:
“(..) whether Russia is righteous or evil does not concern me at all. I only care about whether it benefits our great rejuvenation—whoever serves our interests, I support. Only the “traitors” speak hypocritically about love and justice. Speaking about freedom and democracy that we don’t even understand, they wish Russia collapses tomorrow but don’t care if that would lead to us being surrounded by NATO. So, in the end—are we Ne Zha, or are we the groundhog?”
One line from the film that has gained widespread popularity is: “If there is no path ahead, I will carve one out myself!” (“若前方无路,我就踏出一条路!”). Unlike the more controversial groundhog symbolism, this phrase resonates with many as a reflection not only of Nezha’s resilience but also of the determination that has been driving China’s animation industry forward.
The story of Ne Zha 2 goes beyond box office numbers—it represents the global success of Chinese animation, a revival of its golden era, and China’s growing cultural influence. Yet, paradoxically, it’s also all about the numbers. While the vast majority of its earnings come from the domestic market, Ne Zha 2 is still officially a global number-one hit. More than its actual reach worldwide, what truly matters in the eyes of many is that a Chinese animation has managed to surpass the US and Japan at the box office.
While the industry still has room to grow and many markets to conquer, this milestone proves that part of the Chinese animation dream has already come true. And with Ne Zha 3 set for release in 2028, the journey is far from over.
Best,
Manya
(@manyapan)
Some of the research referenced in this text can also be found in an article I published in 2019: The Chinese Animation Dream: Making Made-in-China ‘Donghua’ Great Again. For further reading, see:
►Du, Daisy Yan. 2019. Animated Encounters: Transnational Movements of Chinese Animation, 1940s-1970s. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
►Lent, John A. and Xu Ying. 2013. “Chinese Animation: A Historical and Contemporary Analysis.” Journal of Asian Pacific Communication 23(1): 19-40.
►Saito, Asako P. 2017. “Moe and Internet Memes: The Resistance and Accommodation of Japanese Popular Culture in China.” Cultural Studies Review 23(1), 136-150.
What’s on Weibo Chapters

🚀 In 2025, international media are more focused on Chinese social media apps than ever, especially after January’s “TikTok refugee” phenomenon, where waves of American TikTok users migrated to China’s Xiaohongshu app. This foreign focus on China’s online landscape also highlights some lingering misconceptions, with major media outlets still trying to label Chinese apps as “the Chinese Instagram,” “the Chinese Facebook,” and so on.
Some of these comparisons actually made sense around 2010, when Chinese companies were indeed building domestic versions of Twitter or Pinterest. But since then, these apps have evolved into something far bigger.
China’s online ecosystem is constantly shifting, and some of its biggest social apps are already 15, 20, or even 25 (!) years old. Their secret? It’s not about copying Western platforms anymore—it’s about rejecting a one-size-fits-all approach and embracing change. As Xiaohongshu’s Charlwin Mao (毛文超) puts it:
🗣️”We don’t ask ourselves if we’re a social or commerce company—we ask, what does the consumer want?”
📌 Xiaohongshu is not the “Chinese Instagram.” It also didn’t start as a shopping site that added reviews—it was a review site that added shopping, flipping the traditional e-commerce model on its head.
📌 One of China’s leading livestreaming platforms, Kuaishou, didn’t even begin as a livestreaming app. It started as a GIF-making tool, built its user base through other platforms, then evolved into a short-video app before skyrocketing during the livestreaming boom. Today, Kuaishou is a major player in generative AI, with its Sora competitor, Kling, emerging from this same adaptability.
💡 Chinese social media apps have grown into superapps by thinking outside the box, breaking free from labels, and evolving like chameleons—constantly adapting to user needs.
📱 In such a rapidly changing digital landscape, it’s high time for a short guide to understanding Chinese social media (especially since some subscribers have been requesting one for a while). This overview breaks down the top 10 Chinese social media platforms, their key functions, and what makes them unique. Whether you’re navigating China’s digital space for the first time or keeping up with its evolution, this list should offer a useful snapshot:
What’s Popular

The major box office success of Ne Zha 2 has sparked all kinds of memes and discussions across Chinese social media. In this article, Wendy Huang provides an overview of the hashtags and trends surrounding the film—from the evolution of Nezha to the popularity of the ‘Stone Diva’ character and the booming ‘Ne Zha economy’ that has taken off in the wake of the movie’s success.
What’s Memorable

For this week’s pick from the archive, we revisit how the big Chinese production Creation of the Gods I, despite initial lackluster performance, became a box office hit thanks to the collaborative efforts of the production team and a dedicated group of fans who volunteered to promote the film online, a phenomenon referred to as zìláishuǐ (自来水).
Zìláishuǐ (自来水) literally means ‘tap water’ but it is a label for those netizens who spontaneously promote a film or artist without getting paid for it. Article by Wendy Huang 👇
Weibo Word of the Week

Small-town Swot | Our Weibo phrase of the week is 小镇做题家 (xiǎozhèn zuòtíjiā), which translates to ‘small-town swot.’
“Small-town swot” is a buzzword that has appeared on Chinese social media over the past few years. According to Baike, it first popped up on a Douban forum dedicated to discussing the struggles of students from China’s top universities. Although the term has been part of social media language since 2020, it has recently come back into the spotlight due to a popular character in Ne Zha 2.
“Small-town swot” refers to students from rural areas and small towns in China who put in immense effort to secure a place at a top university and move to bigger cities. While they may excel academically, even ranking as top scorers, they often find they lack the same social advantages, connections, and networking opportunities as their urban peers. The idea that they remain at a disadvantage despite working so hard leads to frustration and anxiety—it seems they will never truly escape their background. In a way, it reflects a deeper aspect of China’s rural-urban divide.
Among Ne Zha 2 fans, one of their most beloved characters is the leopard demon Shen Gongbao (申公豹). He was a villain in the first film, but Ne Zha 2 adds more nuance to his character. By exploring his struggles, the film makes him a more relatable and sympathetic figure.
Unlike many celestial figures in the film, Shen Gongbao was not born into privilege and never became immortal. As a demon who ascended to the divine court, he remains at the lower rungs of the hierarchy in Chinese mythology. He is a hardworking overachiever with a stutter, who perhaps turned into a villain due to being treated unfairly—yet the film also highlights his good qualities. Many viewers resonate with him because, despite his diligence, he will never be like the gods and immortals around him.
Many Chinese netizens suggest that Shen Gongbao represents the experience of many “small-town swots” (xiǎozhèn zuòtíjiā 小镇做题家) in China, making him, in a way, the ultimate small-town swot. As a result, Shen Gongbao has temporarily become China’s most beloved villain.
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
What’s on Weibo Chapters
Subscribe

The 315 Gala: A Night of Scandals, A Year of Distrust

China Trending Week 11: The Yang Braised Chicken Scandal, Haidilao Pee Incident, Taiwan Tensions

Five Trending Proposals at the Two Sessions 🔍

US-Russia Rapprochement and “Saint Zelensky”: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Shake-Up

“Li Jingjing Was Here”: Chinese Netizens React to Rumors of “Chinese Soldiers” in Russian Army

Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Why Chinese Hit Movie “Her Story” is ‘Good Stuff’: Stirring Controversy and Celebrating Female Perspectives
12-Year-Old Girl from Shandong Gets Infected with HPV: Viral Case Exposes Failures in Protecting Minors

Weibo Watch: Christmas in China Is Everywhere and Nowhere

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Story of Chinese Female MA Graduate Going Missing for 13 Years Sparks Online Storm

Weibo Watch: China’s Online Feminism Is Everywhere

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight10 months ago
China Insight10 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music12 months ago
China Music12 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital9 months ago
China Digital9 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment10 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment10 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments






