China Arts & Entertainment
Behind 8 Billion Streams: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in the Chinese Hit Song ‘Luocha Kingdom’?
What’s behind the Dao Lang hit song that has everyone talking these days?
Published
2 years agoon
By
Zilan Qian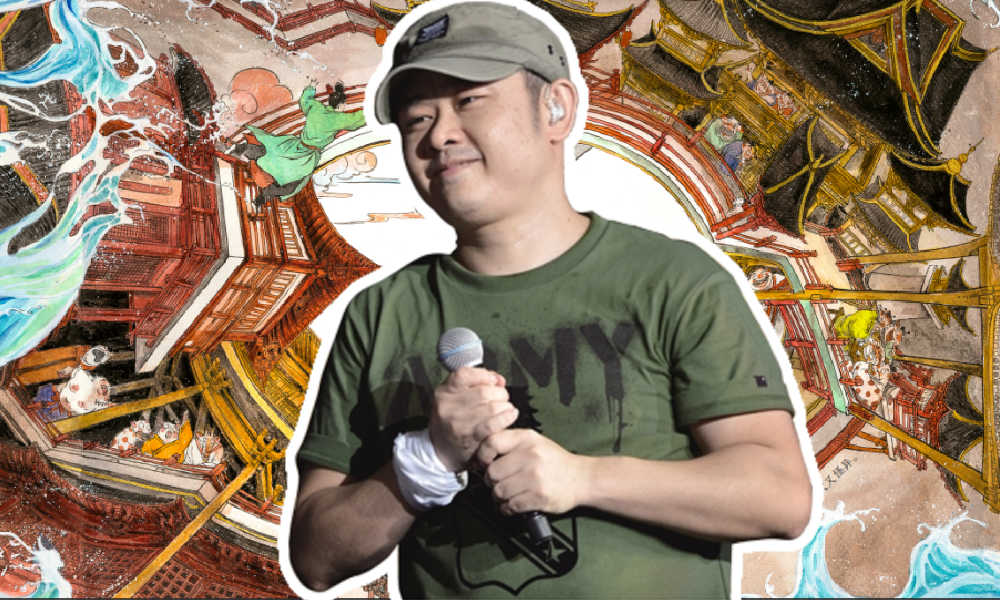
“Who is being mocked and cursed in this song?” This question has ignited a wildfire of speculation across the Chinese internet, as a recently released folk song by a relatively low-profile singer has amassed a staggering 8 billion plays, surpassing the success of previous hit songs.
A newly released Chinese song, composed and sung by a 52-year-old singer who was primarily active in the 2000s, has achieved an astounding milestone of 8 billion streams in less than two weeks since its release.
The song, titled “Luosha Haishi” (罗刹海市; “Raksha Sea Market” or “Luocha Kingdom”), has been widely acclaimed on various social media platforms, with many claiming that it has surpassed the Guinness World Record for the most streamed track worldwide, a record previously held by “Despacito” in 2017 with 5.5 billion plays. The official Weibo account of Guinness World Records recently stated that they haven’t received any application for a new record yet, and thus, no record has been officially confirmed broken at this time.
However, even 8 billion plays alone are enough to marvel at. The sudden surge in popularity of a song created by a low-profile singer, who has not participated in any major shows or held performances for the last few decades, has raised numerous questions: Who is the singer? What is in the song? And why has it become viral in China? We’ll answer some of these questions for you here.
Question 1: Who is Dao Lang?
Dao Lang (刀郎), whose real name is Luo Lin (罗林), embarked on his musical journey at a young age. Born in 1971, he made the decision to leave school at the age of 17 and fully immerse himself in learning keyboard instruments at a music hall in Neijiang. Over the next four years, he ventured to different locations such as Chengdu, Chongqing, Tibet, and Xi’an, where he gained experience and honed his musical skills. Throughout the 1990s, he actively participated in various music projects and bands, shaping his career in the music industry.
In 2004, Dao Lang’s album The First Snow of 2022 (2002年的第一场雪) was unexpectedly well-received, winning him nationwide popularity. After enjoying success with previous albums, Dao Lang diversified his musical endeavors, collaborating with other artists and exploring different genres, such as folk and ethnic music. Between 2010 and 2012, he participated in various performances and events, including appearing at Hong Kong singer Alan Tam’s concert and the Television Arts Evening Celebration for the 90th Anniversary of the Communist Party of China’s founding.

Dao Lang (Weibo).
Subsequently, Dao Lang appeared to withdraw from social media, only resurfacing with two albums in 2020 and 2021, which were released with minimal promotion. However, it is his latest album, titled There Are Few Folk Songs (山歌寥哉) that has brought him back into the public eye, primarily due to the “Luosha Haishi” song.
Question 2: What’s the Song About?
What makes a song so powerful that it has brought Dao Lang back into the public’s attention after almost 20 years?
The song carries strong folk and ethnic elements, and the lyrics are quite cryptic. The song itself has the same title as an ironic story in the famous Liaozhai Zhiyi (聊斋志异), or Strange Stories from a Chinese Studio, a collection of supernatural and ghostly tales written by Pu Songling (蒲松龄) during the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911).
The song’s sudden popularity is mainly attributed to the mocking implication embedded in the lyrics.
One particular verse, in particular, has sparked significant discussion:
那马户不知道他是一头驴
That Don Kee does not know that he is a donkey
那又鸟不知道他是一只鸡
That Scarlet does not know that she is a whore
勾栏从来扮高雅
Brothels have always pretended to be elegant
自古公公好威名
Since ancient times, eunuchs are fond of their mighty reputation
The terms “Mǎ Hù” (马户) and “Yòu Niǎo” (又鸟), translated here as ‘Don Kee’ and ‘Scarlet’ 1, are not commonly used terms in modern Chinese. Mǎ Hù (马户) is a combination of the characters 马 (mǎ), meaning “horse,” and 户 (hù), meaning “household” or “family.” If these two are combined as one character, you get “驴” (lü), meaning “donkey,” hence the ‘Don Kee’ translation to English.
Similarly, “Yòu Niǎo” (又鸟) is a made-up term consisting of two character components that, when put together, means “chicken” (“鸡”, jī).
Both ‘donkey’ and ‘chicken’ have been used as curses in China. People use phrases such as “as silly as a donkey” (“蠢得像头驴”) to describe foolish behavior. On the other hand, the term “chicken” (鸡) often implies prostitution when used in the singular form, but it can also take on the meaning of “trashy” (辣鸡, a phonetic adaptation of the word 垃圾, rubbish) or “weak” (菜鸡) when combined with other characters.
The term that is translated as “brothel” here is “gōulán” (勾栏), which refers to a type of performance venue for opera in urban areas during the Song and Yuan dynasties but is also used to refer to brothels.
The term “gōng gong” (公公) is used to address the father of one’s spouse, but is also has additional meanings and was historically used as an appellation for eunuchs, (castrated) male servants in the imperial court.
So we could say that the first two lines of these lyrics can be interpreted as mocking or cursing people who are unaware of their own silliness or weak status. When combined with the third and fourth lines, which describe things that are pretentious, we can deduce that these lyrics are meant to point out how some people perceive themselves as much more than they actually are, vainly focused on how they portray themselves to others and their status.
Question 3: Who is Dao Lang Cursing in This Song?
There are various online theories on what or who Dao Lang is actually referring to in this song.
◼︎ One trending theory is that it is about Na Ying (那英). Na Ying is a Chinese singer who rose to national fame after serving as a coach in the the popular television singing show The Voice of China in 2012.
Despite gaining recognition in 2004 for his album The First Snow of 2002 (2003), Dao Lang was not widely celebrated as an artist at that time. When Chinese media asked various artists about their thoughts on the ‘rising star’ Dao Lang, he was often criticized and belittled. Among those with the deepest grudge against Dao Lang, it is widely rumored that Na Ying was the one.
In 2010, during the selection of the “Top 10 Most Influential Singers of the Decade,” Na Ying, as the jury chairwoman, vehemently opposed Dao Lang’s inclusion. She allegedly believed that Dao Lang’s songs lacked aesthetic value, despite their high sales, and that music should not be solely judged based on sales volume.
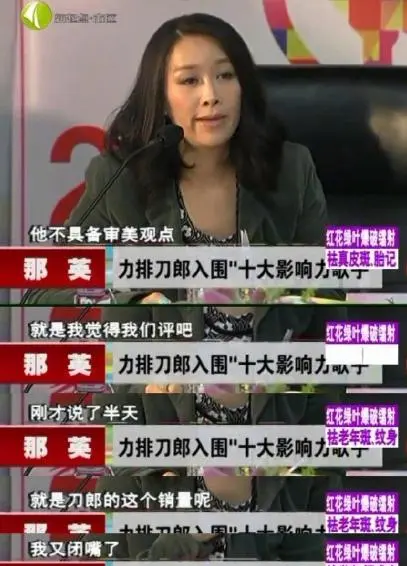
Na Ying commented that Dao Lang’s songs lack of aesthetic characteristic in the 2013’s show (source).
This publicly known clash with Na Ying has sparked widespread speculation that the person subtly mocked by Dao Lang in his song is actually her. Moreover, some interpret the repetition of the character “那” (nà, “that”) throughout the song as a reference to Na Ying’s surname.
Soon after the album’s release, Na Ying’s social media accounts were inundated with netizens convinced that the song was directed at her. Her follower count on Douyin (Chinese TikTok) surged from 770,000 to 1,800,000, and her recent video garnered millions of comments, with many referencing Dao Lang’s song and blaming her for belittling Dao Lang back in the day.
◼︎ Another trending theory is that Dao Lang is cursing the popular music talent show The Voice of China and its coaching panel. Besides Na Ying, singers Yang Kun and Wang Feng also received ten thousands of comments related to Dao Lang’s song on their social media accounts.
One of the reasons why people think the song refers to the show is because it contains the line “Before speaking, they turn around” (“未曾开言先转腚”), which reminds people of the show’s “chair turning moment” in which coaches, whose chairs are turned away from the blind audition stage, can press a button that turns their chair around to face the stage if they are impressed by the contestant’s voice and want to work with them.

In the 2015 season of “The Voice of China,” Wang Feng, Na Ying, and Yang Kun (from the second left to the right) participated as coaches (image source).
◼︎ A third trending theory suggests that the song’s meaning extends far beyond the music industry and carries geopolitical implications. Some netizens have let their imaginations run wild, arguing that the song is actually mocking the United States. The opening line “The land of Rakshasa extends 26,000 li to the east, crossing the Seven Gorges and the scorched Yellow Mud Land of three inches” (“罗刹国向东两万六千里,过七冲越焦海三寸的黄泥地”) is a point of focus.
Since 26,000 li is a traditional Chinese unit of distance, equivalent to half a kilometer, some believe it aligns precisely with China’s territory. Consequently, they speculate that the Rakshasa country, located 13,000 kilometers west of China, is a metaphor for the United States.
The Aftermath
Amidst the nationwide speculation on whom Dao Lang is targeting in his song, several “suspects” have responded to netizens’ guesses. Some chose to resolve the controversy humorously, while others indirectly expressed their distress over the online abuse stemming from these unfounded speculations. Recent reports indicate that Na Ying, in her latest debut, seemed to be greatly affected by the harsh comments made by netizens.
While the speculations surrounding the song have garnered significant attention for both the song and the singer, some discussions are not necessarily constructive. As some netizens point out, the song might not even aim to curse anyone.
It could also be that the song is simply inspired by one of the stories in the book Strange Stories from a Chinese Studio (聊斋志异), which is set in a place called Rakshasa Country, located 26,000 li west of China, resembling a bustling market. In this country, people have peculiar and bizarre appearances, and the more non-human they look, the more attention they receive, while those who appear human live at the bottom of society. Therefore, it is possible that the song aims to narrate these stories instead of attacking someone in particular.
Moreover, the extensive speculations surrounding the song’s intention have also seemingly transformed Dao Lang’s music from a source of enjoyment into a source of analysis, with netizens now meticulously scrutinizing every lyric line.
Among the billions of streams, it begs the question: how many listeners are genuinely enjoying Dao Lang’s music, and how many are just eager sleuths, searching for clues to support their theories about the song’s targets? This raises some curiosity about the true significance of the song’s popularity.
On the other hand, Dao Lang would likely not mind if the song eventually finds its place in the Guinness Book of Records, alongside a note that recognizes it as “the no 1 one most-played hit song that kept everyone guessing.”
By Zilan Qian
Follow @whatsonweibo
1. Part of the translation provided, namely the translation of ‘Ma Hu’ 马户 as ‘Don Kee’ and ‘You Niao’ 又鸟 as ‘the scarlet woman’ was created by Xiangdong Zhu & Ning Wan on Wenxuecity.com on August 1st 2023, although the original page has since been deleted.
This article has been edited for clarity by Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Part of featured image via Xigua Shipin.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Zilan Qian is a China-born undergraduate student at Barnard College majoring in Anthropology. She is interested in exploring different cultural phenomena, loves people-watching, and likes loitering in supermarkets and museums.

You may like
China Memes & Viral
How Ne Zha 2’s Shen Gongbao Became Known as the Ultimate “Small-Town Swot”
Published
3 weeks agoon
March 1, 2025
PART OF THIS TEXT COMES FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
Over the past few weeks, the Chinese blockbuster Ne Zha 2 has been trending on Weibo every single day. The movie, loosely based on Chinese mythology and the Chinese canonical novel Investiture of the Gods (封神演义), has triggered all kinds of memes and discussions on Chinese social media (read more here and here).
One of the most beloved characters is the leopard demon Shen Gongbao (申公豹). While Shen Gongbao was a more typical villain in the first film, the narrative of Ne Zha 2 adds more nuance and complexity to his character. By exploring his struggles, the film makes him more relatable and sympathetic.
In the movie, Shen is portrayed as a sometimes sinister and tragic villain with humorous and likeable traits. He has a stutter, and a deep desire to earn recognition. Unlike many celestial figures in the film, Shen Gongbao was not born into privilege and never became immortal. As a demon who ascended to the divine court, he remains at the lower rungs of the hierarchy in Chinese mythology. He is a hardworking overachiever who perhaps turned into a villain due to being treated unfairly.
Many viewers resonate with him because, despite his diligence, he will never be like the gods and immortals around him. Many Chinese netizens suggest that Shen Gongbao represents the experience of many “small-town swots” (xiǎozhèn zuòtíjiā 小镇做题家) in China.
“Small-town swot” is a buzzword that has appeared on Chinese social media over the past few years. According to Baike, it first popped up on a Douban forum dedicated to discussing the struggles of students from China’s top universities. Although the term has been part of social media language since 2020, it has recently come back into the spotlight due to Shen Gongbao.
“Small-town swot” refers to students from rural areas and small towns in China who put in immense effort to secure a place at a top university and move to bigger cities. While they may excel academically, even ranking as top scorers, they often find they lack the same social advantages, connections, and networking opportunities as their urban peers.
The idea that they remain at a disadvantage despite working so hard leads to frustration and anxiety—it seems they will never truly escape their background. In a way, it reflects a deeper aspect of China’s rural-urban divide.
Some people on Weibo, like Chinese documentary director and blogger Bianren Guowei (@汴人郭威), try to translate Shen Gongbao’s legendary narrative to a modern Chinese immigrant situation, and imagine that in today’s China, he’d be the guy who trusts in his hard work and intelligence to get into a prestigious school, pass the TOEFL, obtain a green card, and then work in Silicon Valley or on Wall Street. Meanwhile, as a filial son and good brother, he’d save up his “celestial pills” (US dollars) to send home to his family.
Another popular blogger (@痴史) wrote:
“I just finished watching Ne Zha and my wife asked me, why do so many people sympathize with Shen Gongbao? I said, I’ll give you an example to make you understand. Shen Gongbao spent years painstakingly accumulating just six immortal pills (xiāndān 仙丹), while the celestial beings could have 9,000 in their hand just like that.
It’s like saving up money from scatch for years just to buy a gold bracelet, only to realize that the trash bins of the rich people are made of gold, and even the wires in their homes are made of gold. It’s like working tirelessly for years to save up 60,000 yuan ($8230), while someone else can effortlessly pull out 90 million ($12.3 million).In the Heavenly Palace, a single meal costs more than an ordinary person’s lifetime earnings.
Shen Gongbao seems to be his father’s pride, he’s a role model to his little brother, and he’s the hope of his entire village. Yet, despite all his diligence and effort, in the celestial realm, he’s nothing more than a marginal figure. Shen Gongbao is not a villain, he is just the epitome of all of us ordinary people. It is because he represents the state of most of us normal people, that he receives so much empathy.”
In the end, in the eyes of many, Shen Gongbao is the ultimate small-town swot. As a result, he has temporarily become China’s most beloved villain.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Wendy Huang
Follow @whatsonweibo
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. Please note that your comment below will need to be manually approved if you’re a first-time poster here.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
China ACG Culture
Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?
The impact of Ne Zha 2 goes beyond box office figures—yet, in the end, it’s the numbers that matter most.
Published
4 weeks agoon
February 27, 2025
FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
These days, everybody is talking about Ne Zha 2 (哪吒2:魔童闹海), the recent hit film about one of China’s most legendary mythological heroes. With its spectacular visuals, epic battles, funny characters, dragons and deities, and moving scenes, the Chinese blockbuster animation is breaking all kinds of records and has gone from the major hit of this year’s Spring Festival film season to the 7th highest-grossing movie of all time and, with its 13.8 billion yuan ($1.90 billion USD) box office success, now also holds the title of the most successful animated film ever worldwide.
But there is so much more behind this movie than box office numbers alone. There is a collective online celebration surrounding the film, involving state media, brands, and netizens. On Weibo, a hashtag about the movie crossing the 10 billion yuan ($1.38 billion) milestone (#哪吒2破100亿#) has been viewed over a billion times. Social media timelines are filled with fan art, memes, industry discussions, and box office predictions.
The success of Ne Zha 2 is not just a win for China’s animation industry but for “Made in China” productions as a whole. Some argue that Ne Zha‘s triumph is not just cultural but also political, reinforcing China’s influence on the global stage and tying it to the ongoing US-China rivalry: after growing its power in military strength, technology, and AI, China is now making strides in cultural influence as well.
In a recent Weibo post, state broadcaster CCTV also suggested that Hollywood has lost its monopoly over the film industry and should no longer count on the Chinese market—the world’s second-largest movie market—for its box office dominance.

Various images from “Ne Zha 2” 哪吒2:魔童闹海
The success of Ne Zha 2 mainly resonates so deeply because of the past failures and struggles of Chinese animation (donghua 动画). For years, China’s animation industry struggled to compete with American animation studios and Japanese anime, while calls grew louder to find a uniquely Chinese recipe for success—to make donghua great again.
🔹 The Chinese Animation Dream
A year ago, another animated film was released in China—and you probably never heard of it. That film was Ba Jie (八戒之天蓬下界), a production that embraced Chinese mythology through the story of Zhu Bajie, the half-human, half-pig figure from the 16th-century classic Journey to the West (西游记). Ba Jie was a blend of traditional Chinese cultural elements with modern animation techniques, and was seen as a potential success for the 2024 Spring Festival box office race. It took eight years to go from script to screen.
But it flopped.
The film faced numerous setbacks, including significant production delays in the Covid years, limited showtime slots in cinemas, and, most importantly, a very cold reception from the public. On Douban, China’s biggest film review platform, many top comments criticized the movie’s unpolished animation and special effects, and complained that this film—like many before it—was yet another Chinese animation retelling a repetitive story from Journey to the West, one of the most popular works of fiction in China.
“Another mythological character, the same old story,” some wrote. “We’re not falling for low-quality films like this anymore.”
The frustration wasn’t just about Ba Jie—it was about China’s animation industry as a whole. Over the past decade, the quality of Chinese animation films has become a much-discussed topic on social media in China—sometimes sparked by flops, and other times by hits.
Besides Ba Jie, one of those flops was the 2018 The King of Football (足球王者), which took approximately 60 million yuan ($8.8 million) to make, but only made 1.8 million yuan ($267,000) at the box office.

Both Ba Jie, which took years to reach the screen, and King of Football, a high-budget animation, ended up as flops.
One of those successes was the 2019 first Ne Zha film (哪吒之魔童降世), which became China’s highest grossing animated film, or, of the same year, the fantasy animation White Snake (白蛇:缘起), a co-production between Warner Bros and Beijing-based Light Chaser Animation (also the company behind the Ne Zha films). These hits
showed the capabilities and appeal of made-in-China donghua, and sparked conversations about how big changes might be on the horizon for China’s animation industry.
“The only reason Chinese people don’t know we can do this kind of quality film is because we haven’t made any good stories or good films yet,” White Snake filmmaker Zhao Ji (赵霁) said at the time: “We have the power to make this kind of quality film, but we need more opportunities.”
More than just entertainment, China’s animated films—whether successes or failures—have come to symbolize the country’s creative capability. Over the years, and especially since the widespread propagation of the Chinese Dream (中国梦)—which emphasizes national rejuvenation and collective success—China’s ability to produce high-quality donghua with a strong cultural and artistic identity has become increasingly tied to narratives of national pride and soft power. A Chinese animation dream took shape.
🔹 The “Revival” of China’s Animation Industry
A key part of China’s animation dream is to create a 2.0 version of the “golden age” of Chinese animation.
This high-performing era, which took place between 1956 and 1965, was led by the Shanghai Animation Film Studio. While China’s leading animators were originally inspired by American animation (including Disney’s 1937 Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs), as well as German and Russian styles, they were committed to developing a distinctly Chinese animation style—one that incorporated classical Chinese literature, ink painting, symbolism, folk art, and even Peking opera.
Some of the most iconic films from this era include The Conceited General (骄傲的将军, 1956), Why Crows Are Black (乌鸦为什么是黑的, 1956), and most notably, Havoc in Heaven (大闹天宫, 1961 & 1964). Focusing on the legendary Monkey King, Sun Wukong (孙悟空), Havoc in Heaven remains one of China’s most celebrated animated films. On Douban, users have hailed it as “the pride of our domestic animation.”
One of China’s most renowned animation masters, Te Wei (特伟), once explained that the flourishing of China’s animation industry during this golden era was made possible by state support, a free creative atmosphere, a thriving production system, and multiple generations of animators working together at the studio.
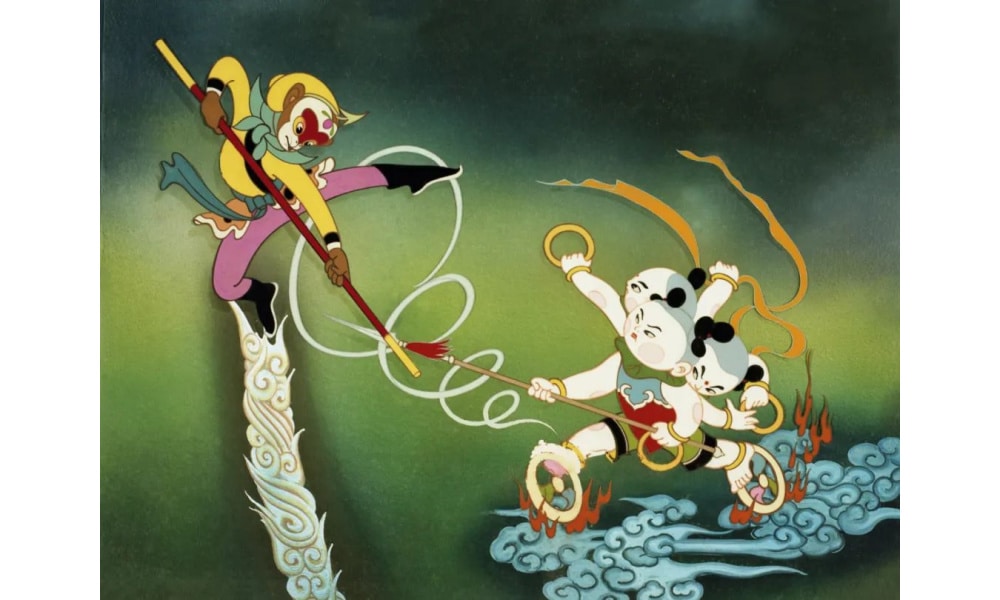

Still from Havoc in Heaven 大闹天宫 via The Paper.
➡️ So what happened to the golden days of Chinese animation?
The decline of this golden era was partly due to the political turmoil of the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976). While there was a second wave of successful productions in the late 1970s and 1980s, the industry lost much of its ‘magic touch’ in the 1990s and 2000s. During this period, Chinese animation studios were pressured to prioritize commercial value, adhere to strict content guidelines, and speed up production to serve the rising domestic TV market—while also taking on outsourcing work for overseas productions.
As the quality and originality of domestic productions lagged behind, the market came to be dominated by imported (often pirated) foreign animations. Japanese series like Astro Boy, Doraemon, and Chibi Maruko-chan became hugely influential among Chinese youth in the 1990s. The strong reaction in China to the 2024 death of Japanese manga artist Akira Toriyama, creator of Dragon Ball, also highlighted the profound impact of Japanese animation on the Chinese market.
This foreign influence also changed viewers’ preferences and aesthetic standards, and many Chinese animations adopted more Japanese or American styles in their creations.
However, this foreign ‘cultural invasion’ was not welcomed by Chinese authorities. As early as 1995, President Jiang Zemin reminded the Shanghai Animation Film Studio of the ideological importance of animation, emphasizing that China needed its “own animated heroes” to serve as “friends and examples” for Chinese youth.
By the early 2010s, the revitalization and protection of China’s animation industry became a national priority. This was implemented through various policies and incentives, including government funding, tax reductions and exemptions for Chinese animation companies, national animation awards, stipulations for the number of broadcasted animations that must be China-made. Additionally, there was an increased emphasis on animation as a tool for cultural diplomacy, focusing on how Chinese animation should reflect national values and history while maintaining global appeal.
It’s important to note that the so-called ‘rejuvenation’ of Chinese animation is not just a cultural and ideological project, there are economic motives at stake too: China’s animation industry is a multi-billion dollar industry.
🔹 “Are We Ne Zha or the Groundhogs?”
The huge success of Ne Zha 2 is seen as a new milestone for Chinese animation and as inspiration for audiences. The film took about five years to complete, reportedly involving 140 animation studios and over 4,000 staff members. The film was written and overseen by director Yang Yu (杨宇), better known as Jiaozi (饺子).
The story is all based on Chinese mythology, following the tumultuous journey of legendary figures Nezha (哪吒) and Ao Bing (敖丙), both characters from the 16th-century classic Chinese novel Investiture of the Gods (Fengshen Yanyi, 封神演义). Unlike Ba Jie or other similar films, the narrative is not considered repetitive or cliché, as Ne Zha 2 incorporates various original interpretations and detailed character designs, even showcasing multiple Chinese dialects, including Sichuan, Tianjin, and Shandong dialects.
One of the film’s unexpected highlights is its clan of comical groundhogs. In this particularly popular scene, Nezha engages in battle against a group of groundhogs (土拨鼠), led by their chief marmot (voiced by director Jiaozi himself). Amid the fierce conflict, most of the groundhogs are hilariously indifferent to the fight itself; instead, they are focused on protecting their soup bowls and continuing to eat—until they are ultimately hunted down and captured.
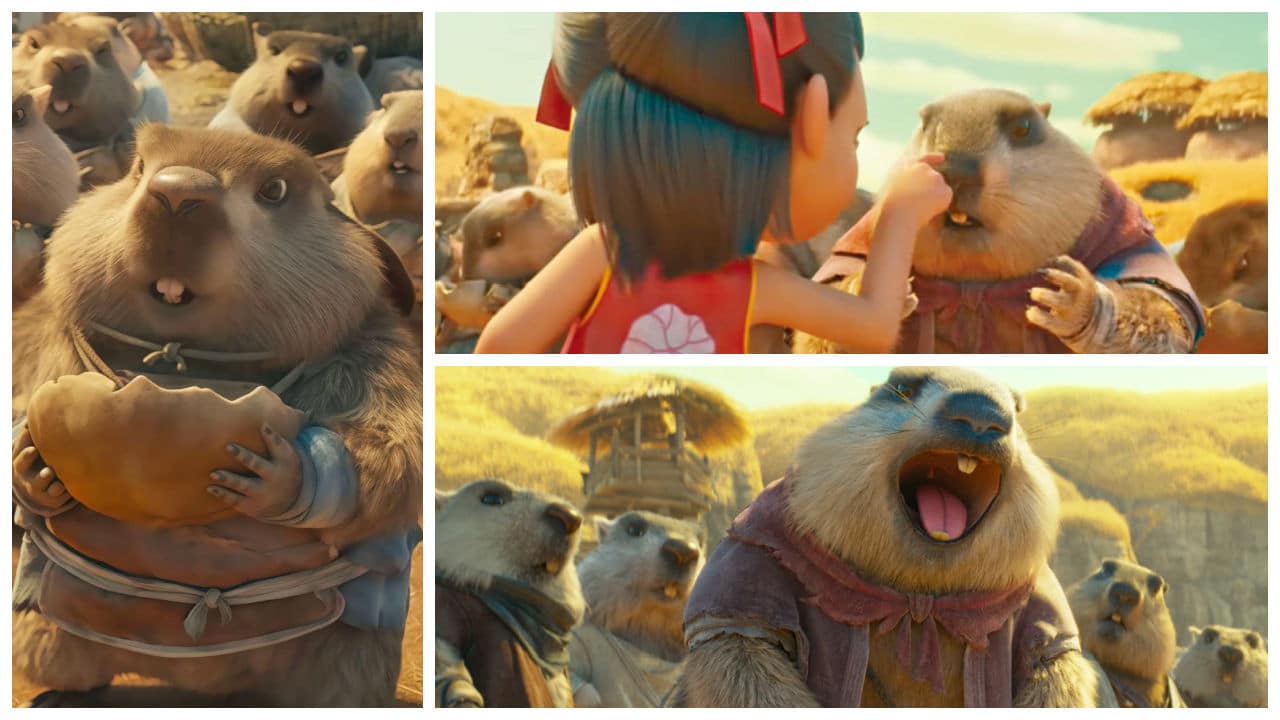

Nezha and the clan of groundhogs.
Besides fueling the social media meme machine, the groundhog scene actually also sparked discussions about social class and struggle. Some commentators began asking, “Are we Ne Zha or the groundhogs?”
Several blogs, including this one, argued that while many Chinese netizens like to identify with Nezha, they are actually more like the groundhogs; they don’t have powerful connections nor super talents. Instead, they are hardworking, ordinary beings, struggling to survive as background figures, positioned at the bottom of the hierarchy.
One comment from a film review captured this sentiment: “At first, I thought I was Nezha—turns out, I’m just a groundhog” (“开局我以为自己是哪咤,结果我是土拨鼠”).
The critical comparisons between Nezha and the groundhogs became politically sensitive when a now-censored article by the WeChat account Fifth Two-Six District (第五二六区) suggested that many Chinese people are so caught in their own information bubbles and mental frameworks that they fail to grasp how the rest of the world operates. The article said: “The greatest irony is that many people think they are Nezha—when in reality, they’re not even the groundhogs.”
While some see a parallel between Nezha’s struggles and their own hardships, others interpret the film’s success as a symbol of China’s rise on the global stage—particularly because the story is so deeply rooted in Chinese culture, literature, and mythology. This has led to an alternative perspective: rather than remaining powerless like the groundhogs, perhaps China—and its people—are transforming into the strong and rebellious Nezha, taking control of their destiny and rising as a global force.
Far-fetched or not, it’s an idea that continues to surface online, along with many other detailed analyses of the film. The nationalist Chinese social media blogger “A Bad Potato” (@一个坏土豆) recently wrote in a Weibo post:
“We were once the groundhog, but today, nobody can make us kneel!” (“我们曾经是土拨鼠,但是今天,没有任何人可以让我们跪下!”)
In another post, the blogger even dragged the Russia-Ukraine war into the discussion, arguing that caring too much about the powerless “groundhogs,” those struggling to survive, does not serve China’s interest. He wrote:
“(..) whether Russia is righteous or evil does not concern me at all. I only care about whether it benefits our great rejuvenation—whoever serves our interests, I support. Only the “traitors” speak hypocritically about love and justice. Speaking about freedom and democracy that we don’t even understand, they wish Russia collapses tomorrow but don’t care if that would lead to us being surrounded by NATO. So, in the end—are we Ne Zha, or are we the groundhog?”
One line from the film that has gained widespread popularity is: “If there is no path ahead, I will carve one out myself!” (“若前方无路,我就踏出一条路!”). Unlike the more controversial groundhog symbolism, this phrase resonates with many as a reflection not only of Nezha’s resilience but also of the determination that has been driving China’s animation industry forward.
The story of Ne Zha 2 goes beyond box office numbers—it represents the global success of Chinese animation, a revival of its golden era, and China’s growing cultural influence. Yet, paradoxically, it’s also all about the numbers. While the vast majority of its earnings come from the domestic market, Ne Zha 2 is still officially a global number-one hit. More than its actual reach worldwide, what truly matters in the eyes of many is that a Chinese animation has managed to surpass the US and Japan at the box office.
While the industry still has room to grow and many markets to conquer, this milestone proves that part of the Chinese animation dream has already come true. And with Ne Zha 3 set for release in 2028, the journey is far from over.
Want to read more on Ne Zha 2? Also check out the Ne Zha 2 buzz article by Wendy Huang here and our related Weibo word of the week here.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Some of the research referenced in this text can also be found in an article I published in 2019: The Chinese Animation Dream: Making Made-in-China ‘Donghua’ Great Again. For further reading, see:
►Du, Daisy Yan. 2019. Animated Encounters: Transnational Movements of Chinese Animation, 1940s-1970s. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
►Lent, John A. and Xu Ying. 2013. “Chinese Animation: A Historical and Contemporary Analysis.” Journal of Asian Pacific Communication 23(1): 19-40.
►Saito, Asako P. 2017. “Moe and Internet Memes: The Resistance and Accommodation of Japanese Popular Culture in China.” Cultural Studies Review 23(1), 136-150.
🌟 Attention!
For 11 years, What’s on Weibo has remained a fully independent platform, driven by my passion and the dedication of a small team to provide a window into China’s digital culture and online trends. In 2023, we introduced a soft paywall to ensure the site’s sustainability. I’m incredibly grateful to our loyal readers who have subscribed since then—your support has been invaluable.
But to keep What’s on Weibo thriving, we need more subscribers. If you appreciate our content and value independent China research, please consider subscribing. Your support makes all the difference.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
What’s on Weibo Chapters
Subscribe

Squat or Sit? China’s Great Toilet Debate and the Problem of Footprints on the Seat

Weibo Watch: The Great Squat vs Sitting Toilet Debate in China🧻
Chinese Netizens Turn to Tim Cook Over Battery Factory’s Illegal Overtime

Revisiting China’s Most Viral Resignation Letter: “The World Is So Big, I Want to Go and See It”

The 315 Gala: A Night of Scandals, A Year of Distrust

Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: Christmas in China Is Everywhere and Nowhere

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter
12-Year-Old Girl from Shandong Gets Infected with HPV: Viral Case Exposes Failures in Protecting Minors

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music12 months ago
China Music12 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment10 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment10 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments

