“China’s countermeasures are here” (#中方反制措施来了#). This hashtag, launched by Party newspaper People’s Daily, went top trending on Chinese social media on Friday, April 4, after President Trump announced steep new tariffs on Wednesday, including a universal 10 percent “minimum base tariff” on all imported goods and especially targeting China with an additional 34% reciprocal tariff as part of so-called “liberation day.”
Countermeasures were announced on Friday. China’s State Council Customs Tariff Commission Office (国务院关税税则委员会办公室) issued an announcement stating that, starting from April 10, an additional 34% tariff will be levied on all imported goods originating from the United States, on top of existing tariff rates.
Other countermeasures include immediate export restrictions on seven key medium to heavy rare earth elements, which are important for manufacturing critical products used in semiconductors, defense, aerospace, and green energy.
“This won’t make America great again”
The official response to the tariffs, both from state media and the government, has been twofold: on the one hand, it criticizes the U.S. for placing American interests above the good of the global community, arguing that the move only hurts the U.S., its people, and the world. On the other hand, the Chinese side stresses that although they do not believe tariff wars are the answer, China is not afraid of a trade war and will not sit idly by, but will respond with equal measures.
Chinese official media have condemned the new tariffs, which led to the largest single-day market drop in years. Describing the reactions of various experts, Xinhua News highlighted a comment by a Croatian professor, stating that the policy will only increase export prices and worsen inflation, ultimately hurting middle- and working-class Americans — and noting that the policy “won’t make America great again” (不会“让美国再次伟大”).
The official announcement by Chinese state media regarding China’s countermeasures received widespread support in its (highly controlled) comment sections, with both media outlets and netizens echoing the message that China will not be bullied by the U.S.
On Xiaohongshu, similar sentiments shnone through in popular posts, such as one person writing:
💬 “Congratulations to the U.S. on receiving a 34% tariff on all its goods! Luckily, very few of the things ordinary Chinese people eat or use come from the U.S. anyway.
#RMB purchasing power #China will inevitably be unified #Consumer confidence #Contemporary Chinese economy #Carrying forward the construction of a Beautiful China”

“Monday’s stock market will be a bloodbath,” another commenter wrote.
One Weibo blogger (@兰启昌) saw the recent developments as another sign of an ongoing trend of “de-globalization” (逆全球化).
But beyond global economics and geopolitics, many Chinese netizens — from Weibo to Xiaohongshu — seem more focused on how the new policies will affect everyday consumers.
Netizens have been actively discussing which goods will be hit hardest by the new tariffs. Based on 2023 trade data, here’s a breakdown of the top exports between China and the United States — and the sectors most likely to feel the impact.
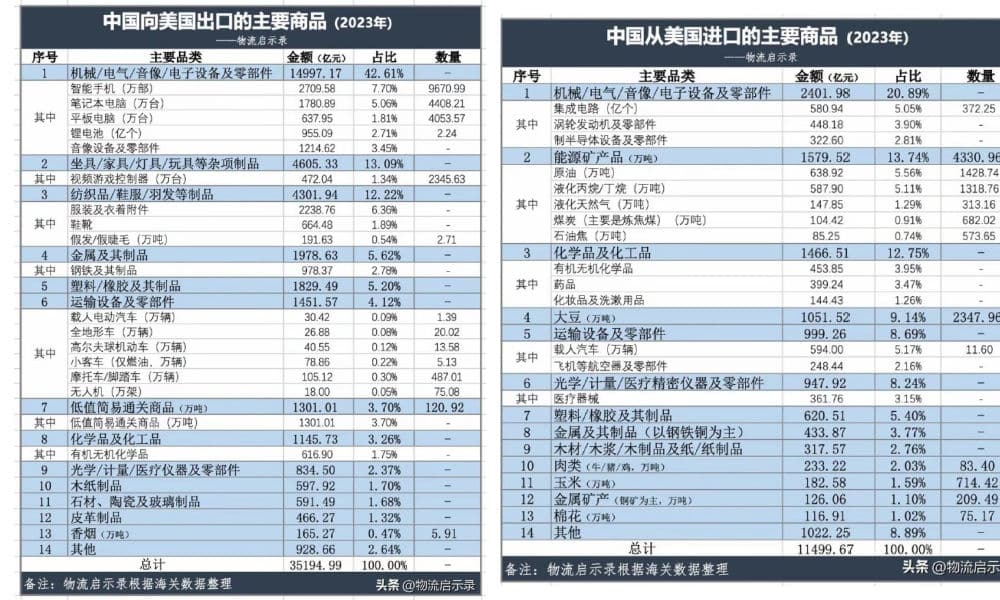
🔷🇺🇸🇨🇳Top 10 Chinese Exports to the U.S.
1. Electronics and Machinery
Includes smartphones, laptops, tablets, integrated circuits, and image processing equipment.
2. Furniture, Home Goods & Toys
Such as video game consoles, lamps, and much more.
3. Textiles and Apparel
Garments, footwear, and accessories like sunglasses.
4. Metals and Related Products
Especially steel and steel-based items.
5. Plastic and Rubber Products
Widely used in packaging, manufacturing, and consumer goods.
6. Transportation Equipment
Electric vehicles, passenger cars, motorcycles, scooters, and drones.
7. Low-Value Commodities
Bulk items used in general trade and low-cost manufacturing.
8. Chemicals
Industrial chemicals and related materials.
9. Medical and Optical Instruments
Includes medical devices and precision instruments.
10. Paper Products
Ranging from office supplies to industrial paper goods.
🔹🇨🇳🇺🇸Top 10 U.S. Exports to China
1. High-Tech Machinery and Electronics
Especially integrated circuits, turbine engine components, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
2. Energy Products
Crude oil, liquefied propane and butane, natural gas, and coking coal.
3. Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
Includes cosmetics, cleaning agents, and various medical drugs.
4. Soybeans
A key agricultural export widely used in food and animal feed in China.
5. Transportation Equipment
Such as automobiles and aircraft parts.
6. Medical and Optical Devices
Medical precision equipment, diagnostic tools, and lab instruments.
7. Plastic and Rubber Goods
Used in both consumer and industrial sectors.
8. Metal Products
Primarily iron and steel exports.
9. Wood and Pulp Products
Lumber, wood pulp, charcoal, and paper goods.
10. Meat
Including beef, pork, and poultry.
Those doing trade with the US, or otherwise involved in made-in-China products, like those working clothing and furniture factories, will inevitably be affected by the tariffs.
“Patriotism isn’t just a sentiment – it’s an action”
Much of the popular online conversation has focused on concrete examples of what kinds of things might get more expensive for Chinese consumers in their everyday lives.
Some bloggers noted that people might start to see price hikes in everyday groceries like dairy, meat, corn, and soybeans. With fewer soybeans coming in from the US, cooking oil prices may also rise.
China is the world’s largest consumer of soybeans, but because domestic production is relatively low, soybeans remain a key import.
Then there are popular American brands in the Chinese market that are expected to get pricier too — like beauty and health products, Starbucks coffee, or Häagen-Dazs ice cream.
Some also predicted a 30% to 40% increase in prices for iPhones and other Apple products.
Contrary to the earlier comment by the Xiaohongshu blogger, some netizens explain just how many American products are actually used by Chinese consumers, with many American companies operating in China — from McDonald’s and Coca-Cola, Walmart to Disney or Warner Brothers, Procter & Gamble to Colgate and Estée Lauder.
What’s noteworthy in these discussions, however, is a strong tendency to point to Chinese alternatives and encourage smart buying instead of following hypes (“理性替代,拒绝跟风”): No need to panic about soybeans — there are domestic alternatives, and China’s own soybean program is getting a boost. Who needs Starbucks when there’s Luckin Coffee? Why buy an iPhone when you can get a Huawei? Skip the Tesla, go for a BYD.
In these discussions, the ‘crisis’ is turned into an ‘opportunity’ for Chinese companies to focus even more on the Chinese market, and for Chinese consumers to, more than ever, actively embrace and celebrate local brands and made-in-China products.
One Chinese blogger (@O浅夏拾光O) wrote:
💬 “This moment is the time to reflect on our unity. If we can choose domestic alternatives, we should. For example, we can use rapeseed oil or peanut oil instead of imported soybean oil; we can buy cost-effective Chinese electronics instead of foreign brands. Support domestic products and respond to the nation’s call to expand domestic consumption.
We must have faith in our country. Only by uniting as one, young and old all together, the entire country working together, can we withstand all hazards. As Professor Ai Yuejin (艾跃进) once said, patriotism isn’t just a sentiment – it’s an action. As long as our core is stable and we are united in spirit, no hardship can defeat us.”
Despite the major happenings and the big words, some people just care about the small things: “As long as KFC and McDonald’s don’t raise their prices, it’s all fine by me.”
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Follow What’s on Weibo on


 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months ago
 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months ago
 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago






























