China Insight
CCTV Airs Program on Xinjiang’s ‘Vocational Training Centers’: Criticism & Weibo Responses
A noteworthy episode of CCTV “Focus Talk” marks the first time Chinese state media extensively reports on the existence of vocational education programs in Xinjiang. Weibo reactions are mixed.
Published
6 years agoon

A recent CCTV “Focus Talk” TV program themed around an “educational training center” in Xinjiang, along with other Chinese state media articles on ‘training facilities’ in northwest China, has triggered the attention of foreign media this week. Many reporters interpret the latest Xinjiang publicity as a way for the Chinese government to create a “new narrative” to defend its policies in the region.
On Tuesday, October 16 2018, the CCTV prime-time program ‘Focus Talk’ (焦点访谈) dedicated a 15-minute episode to the topic of Xinjiang’s ‘vocational skills educational training centers’ (职业技能教育培训中心), marking the first time for Chinese state media to extensively report on the existence of these controversial programs in Xinjiang.
‘Focus Talk’ is a renowned news program that has been aired by China’s state broadcaster since 1994. It is generally themed around various societal issues, and provides background analysis of various topics through interviews with officials and the public. The show’s official Weibo account has over 1,8 million fans.
Noteworthy is that the special Xinjiang-focused episode was aired hours after Xinjiang governor Shohrat Zakir (雪克来提·扎克尔) issued a statement to fend off international criticism on government-operated ‘Muslim internment camps,’ characterizing them as “people-oriented” facilities built to “fundamentally eliminate the environment and soil that breeds terrorism and religious extremism.”
Earlier this year, United Nations’ human rights experts said they had received credible reports that up to one million Muslim Uighurs may be held in extra-legal political detentions in Xinjiang, and called for them to be released.
Since 2014, China has implemented several measures to keep religious expressions to a minimum after a string of attacks allegedly committed by Chinese Muslim extremists. In March 2014, a knife attack at the Kunming railway station left 29 civilians dead. In May, 43 were killed when a Urumqi market was bombed. On June 22, attackers drove into a Kashgar police building and set off explosives. The list goes on.
The government responded to the increasing violence in 2014 with an ongoing crackdown that, at the time, resulted in more than 380 arrests within one month, and public controls on religious expression. In 2015, a ban on wearing burqa’s, or ‘face masking veils’ (面罩袍), was legally approved and went into effect on February 1st. In 2016, there were reports of local governments ordering restrictions on fasting during Ramadan. That same year also saw reports on the existence of “ideological training camps.”
This week’s efforts of Chinese media to highlight Xinjiang’s “educational centers” as a humane, positive, and constructive solution to defeat terrorism and extremism in the region (both in written state media and by state broadcaster CCTV) have made headlines in international media.
“China defends Xinjiang camps for Muslim citizens,” the Financial Times reported; “China admits to locking up Uyghurs, but defends Xinjiang crackdown,” CNN headlined; “China defends its ‘people-oriented’ Muslim reeducation program as job training,” Washington Post wrote.
On Twitter, New York Times reporter Chris Buckley tweeted about the CCTV episode, writing: “Dispelling any doubts that the Chinese government is trying to create a new narrative about its indoctrination camps in Xinjiang, CCTV on Tuesday broadcast a primetime program praising the camps.” Reporters from other newspapers also described the latest Xinjiang publicity as a “new narrative.”
The “Source Governance” Episode
On October 16, CCTV aired the episode in question. At the start of the program, the talk show host introduces the topic as follows:
“Terrorism and extremism are the public enemy of civilized society, and are the enemy of the international community. Since the 1990s, the ‘Three Evils’ of domestic and foreign ethnic separatist forces, religious extremist forces, and violent terrorist forces, have schemed and organized the execution of thousands of violent terrorist incidents in Xinjiang, victimizing a great number of innocent people, leading to the deaths of hundreds of public security forces, and causing incalculable damage.”

“The crackdown on terrorism and extremism is a global problem. To tackle this problem, Xinjiang has carried out the exploration of ‘source governance’ (源头治理) through the means of vocational skills educational training (职业技能教育培训), in accordance with the relevant laws and regulations. What is the result of this training? Let’s take a look.”
The show then shifts from the studio to the footage show in Xinjiang, with the voice-over saying:
“Recently, our reporters went to Xinjiang’s Hotan (和田市) to visit a vocational skills educational training center, just in time for the smooth graduation of some students.”
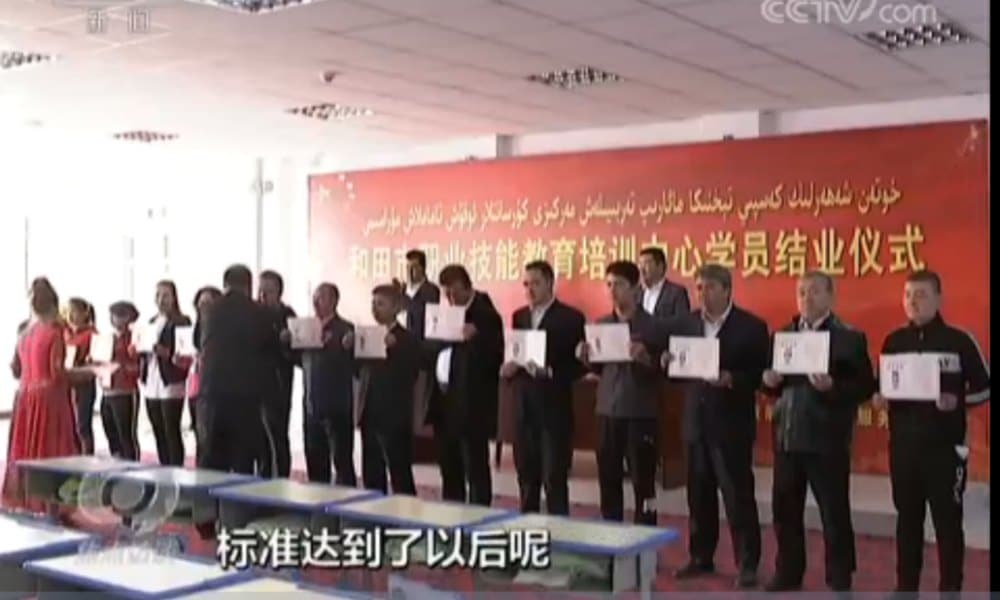

Mayor Alken Aili of the city of Hotan, a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, then talks to reporters, saying:
“There are criteria for our students to complete the course. Firstly, they need to reach the qualified standards in the spoken and written national common language. Then they need to qualify in legal and regulatory knowledge, and then in their training and employment ability. Once they reach the standard, and qualify for it, then they can complete the course.”

A student named Abdul then speaks to the reporter, saying:
“Through my studies, I’ve deeply realized my mistakes. I will continue to study hard once I’m back. I’ll be a good citizen, and influence the people around me.”
In the program, the mayor of Hotan then explains the main contents of the learning center as learning standard Chinese, studying various laws (including criminal law, national security law, anti-terrorism law, etc.), and then learning vocational skills.
A female student tells reporters:
“Before, I couldn’t understand the language and struggled to get by. Now, if I continue to study hard, I’ll be able to work and make money anywhere.”
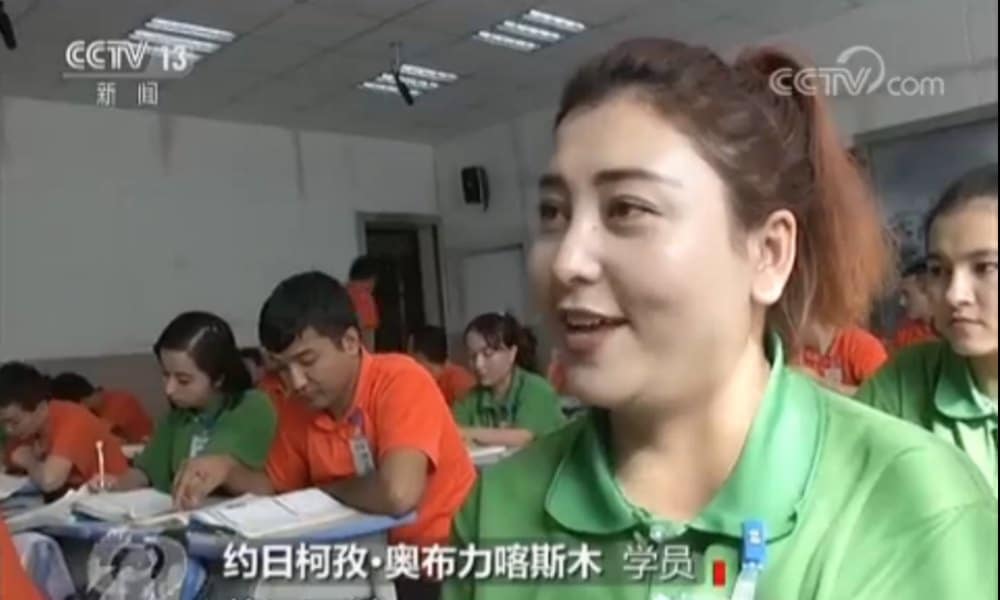

The voice-over continues to explain that many of the students at the Xinjiang training center do not master standard Chinese, have a “weak sense of the rule of law,” and face employment difficulties due to a lack of skills, leaving them extra vulnerable to turn to terrorism and extremism.

Another female student by the name of Turenisha Abdulla then says:
“If I wouldn’t have come here, I can’t imagine what would have happened. Perhaps I would have joined those religious extremists and take the criminal path. The Party and government have found me in time and saved me, giving me a chance to reform and start anew. I am very grateful.”
The voice-over explains that, looking at local needs and industrial development, the training center educates its students in various skills from beauty salon skills to food processing, and more “skills specific to ethnicity” (“民族特色的手工艺技能”), such as carpeting or making flatbread.
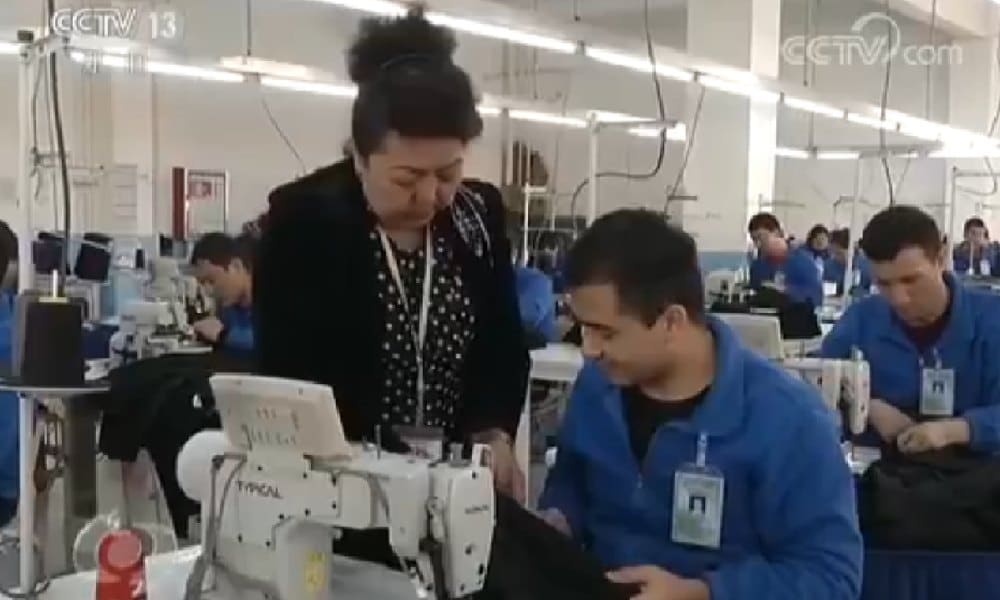

The program then further zooms in on the importance of education, and how teaching skills to students (of which some reportedly have been “eroded by religious extremism”) gives them better opportunities and a brighter future, and have “significantly improved the sense of security and happiness” in the region.

Throughout the episode, the CCTV voice-overs or commentators not once mention ‘Islam’ or ‘Muslims.’ They also do not label the educational center’s students as belonging to any particular religions. Instead, the program only mentions “terrorism” and “religious extremism.”
This is noteworthy because while foreign media have consistently reported about “Xinjiang camps for Muslim citizens” or “Uighur Muslims,” Chinese state media evade this issue by not mentioning any specific religion at all, but only mentioning the issue of extremism and terrorism.
Mixed Reactions on Weibo
The CCTV episode in question has triggered hundreds of comments on Chinese social media this week, which were quite mixed; many commenters expressed positive sentiments on the episode and its contents, but there were also others who were critical of the ‘educational centers.’
Comments in favor of the Xinjiang centers praised the government’s policies, with one micro-blogger writing: “Go and watch this episode of ‘Focus Talk’! It explains Xinjiang’s vocational education centers, which have been criticized as ‘transformation camps’ (转化营) by the West. They’re very real, very feasible, very effective, and very good.”
“Foreign journalists are distorting the facts,” others said: “I just came back from a business trip to Xinjiang, and it’s really much better there now than a few years before, so I need to support this.”
“We have to help a large number of Muslims to quit their Islam addiction,” another popular comment read: “It’s a quite frightening disease.”
“We can only adopt the correct extreme measures to combat the evil of extremism,” some in favor of the Xinjiang ‘education centers’ wrote in other threads discussing the program.
The negative comments often used sarcasm in their reactions, writing things as: “This is quite fantastic! Do they get winter- and summer holidays? When can they graduate? Can we visit there? And will we come out alive if we do?”
And: “What a great educational programme, we should implement it all across the country, so that we can all be treated this well!”
“But, isn’t this just exactly the same as a prison?”, one commenter said. “It’s really frightening, they all look like robots,” another person responded.
There are also Weibo users who simply want to know more about the ‘centers’, writing: “I want to know the reason for them to go there. And what if they do not qualify the standards [to complete], will they continue to stay there indefinitely?”
Some netizens indicate that what is happening in Xinjiang today might also happen in other provinces in China with a large Muslim population. Although Muslims live all over China, the majority lives in the northwestern regions of Xinjiang, Ningxia, Gansu and the Qinghai provinces.
“Xinjiang’s present-day is Ningxia’s tomorrow,” one Weibo user predicts.
Watch the full episode by CCTV here (no subtitles).
By Manya Koetse
Follow @whatsonweibo
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us.
©2018 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

You may like
China Insight
US-Russia Rapprochement and “Saint Zelensky”: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Shake-Up
From shifting sentiments on Zelensky to a renewed focus on Taiwan, recent geopolitical developments have sparked noteworthy takes from Chinese online commentators.
Published
2 weeks agoon
March 9, 2025
As the Russia-Ukraine war enters its fourth year, Chinese social media is once again flooded with discussions about the geopolitical shifts triggered by Trump’s policies. From the Oval Office clash to Trump’s ‘pivot’ to Russia, this article explores how Chinese netizens are interpreting the rapidly changing geopolitical landscape.
Three years ago, when the Russia-Ukraine war first broke out, one particular word went trending on Chinese social media: wūxīn gōngzuò (乌心工作). The term was a wordplay on the term wúxīn gōngzuò (无心工作), meaning not being in the mood to work, and it basically meant that people were too focused on Ukraine to concentrate on work.
Although that word has since faded from use online, recent geopolitical developments surrounding the Russia-Ukraine war have once again drawn considerable attention on Chinese social media, where trending word data tools show that “Trump” and “Zelensky” are among the hottest buzzwords of the moment.

Trump Zelensky, Ne Zha, Lei Jun; biggest words of interest on, among others, Weibo, on March 4, 2025.
Trump’s recent rhetoric toward Russia, his remarks about Ukraine, and his attitude toward NATO not only mark a shift from Biden and decades of US policy, but also reshuffle the geopolitical cards and raise questions about the future of the postwar international order.
Where does China stand in all this?
➜ Although China’s online environment is tightly controlled, particularly regarding political discussions, what stands out in conversations around the recent developments involving Trump, Putin, and Zelensky is a widespread sentiment that — at its core — it’s all about China.
Many believe that China’s rise on the global stage, and the resulting US-China rivalry, are key forces shaping US strategy toward Russia as well.
Woven into these discussions are US-China trade tensions, with Trump increasing tariffs by 10% on February 1, and then doubling the tariff on all Chinese imports to 20% from 10% on March 4. This immediately prompted China to retaliate with 10-15% tariffs on US agricultural products, effective March 10.
Currently, developments are unfolding so rapidly that one hashtag after another is appearing on Chinese social media. “It’s not that I don’t understand, it’s just that the world is changing so quickly,” one Weibo blogger commented, referencing a famous song by Cui Jian (“不是我不明白,是这世界变化快”).
Amid this whirlwind of events, let’s take a closer look at the current Chinese online discourse surrounding the Russia-Ukraine war, with a focus on shifting attitudes toward Zelensky and US-Russian relations.
THE OVAL OFFICE INCIDENT
“Saint Zelensky is a real man!”
One major moment in the recent developments has been the clash between Zelensky, Trump, and US Vice President JD Vance in the White House Oval Office on February 28.
Zelensky had come to the White House to discuss the US’s continued support against Russia and a potential deal involving Ukraine’s rare earth minerals, but it ended in a heated confrontation during which, among others, Zelensky questioned Vance’s notion of “diplomacy” with Putin, and Trump and Vance expressing frustration with what they perceived as Zelensky’s ingratitude for US support.
On Chinese social media, the clash between Zelensky, Trump, and Vance in the Oval Office seemingly caused a shift in public views towards Zelensky and the position of Ukraine. Some commentators who are known to usually take a pro-Russian stance were suddenly positive about Zelensky.
“Zelensky is really awesome, he had a confrontation with Putin’s two top negotiators in the Oval Office and still managed to hold his own,” historian Zhang Hongjie (@张宏杰) jokingly wrote on Weibo.
Others compared compared Trump and Vance to “two dogs barking” at Zelensky, and saw the meeting as one that was meant to humiliate Zelensky.
Nationalist blogging account “A Bad Potato” (一个坏土豆, 335k+ followers) admitted: “I’ll lay my cards on the table: I fully support Zelensky.”
He further wrote:
💬 “Let’s not make any illusions. Trump’s ultimate target is China. (..). He’s already added two rounds of 10% tariffs on China. Isn’t it obvious? Did you think he is pulling closer to Russia for some big China-Russia-America unification? Once he’s done dealing with his internal problems, he’ll inevitably come at China with full force. There are some people here who are hoping for Zelensky to kneel before the US, and I’d like to ask these people: Whose side are you on? Are you on the Russian or American side? When Zelensky’s firm towards the US, of course I’ll support him. His performance was so perfect that I’d like to call him Saint Zelensky!
(..) Some say Zelensky’s betraying his country. So what if he is? As long as he’s not selling out China, he can sell out the whole world for all I care. Just look at the stupid and bad Macron, or Starmer who’s full of sneaky tricks, they’re getting humiliated by Trump in all kinds of ways. Then look at Zelensky again and let me shout: Saint Zelensky is a real man! He’s a tough guy! Of course, I’m keeping it balanced here—I support Russia too. Both sides must make an effort.”
➜ Although there is some pragmatism in this ‘pro-Zelensky’ shift, which is Sino-centric and mostly based on which actors in the political game are considered antagonists of China, there is also another level of sympathy towards Zelensky as the underdog in this situation — facing a 2-against-1 dynamic on unfamiliar terrain, while speaking a language that is not his.
Weibo user “Uncle Bull” (@牛叔, 820k followers) wrote:
💬 “The arguing scene in the Oval Office should be a reminder for every politician that it doesn’t matter how well you speak English, when it’s a formal occasion, you should always speak your native language and have a translator with you— it helps avoid a lot of direct confrontations.”
In his analysis of the situation, well-known political commentator Chairman Rabbit (兔主席) took a far more critical stance towards Zelensky, suggesting that his confrontational attitude in the Oval Office was misplaced and driven by personal pride, and that his actions in the White House caused it to be “the most disastrous trip in history.”
Chairman Rabbit also commented:
💬 “There is an ancient Chinese saying: “A man of character can bow or stand tall as required [大丈夫能屈能伸].” When it comes to major issues like the survival of the nation, things like some dignity and righteousness and principles all are meaningless. When facing Trump, you just have to flatter and appease him. If Zelensky is unable to humble himself, then he’s probably not suited for this job. It’s just as the most pro-Ukraine Republican senator, Senator Lindsey Graham, said – he suggests that Zelensky should step down, and Ukraine should find someone else to negotiate.”
But there are many netizens who do not agree with him, like this popular comment saying: “Whatever you do, don’t kneel [to Trump] — you’re a spiritual totem (精神图腾) for so many people on Weibo.”
TRUMP’S ‘PIVOT’ TO RUSSIA
“The US-Russia honeymoon has begun”
When US and Russian delegates sat down in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, on February 18 to discuss improving Russia-US relations and ending the war in Ukraine—without Europe or Ukraine at the table—Chinese netizens pointed out that there were no plates on the table, joking that “Europe and Ukraine are what’s on the menu.”
They referred to a comment previously made by US Secretary of State Antony Blinken when replying to a question about US-China tensions leading to greater fragmentation: “If you’re not at the table in the international system, you’re going to be on the menu.”
The official Chinese response to the developments, as stated by Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Guo Jiakun (郭嘉昆), is that China is glad to see any efforts that contribute to peace, including any consensus reached between the US and Russia through negotiations (#中方回应俄美代表团举行会晤#).
Among social media users, there was banter about the sudden US-Russia rapprochement, after news came out that the two countries intend to cooperate on various matters concerning their shared geopolitical interests (#俄美决定未来将在多领域合作#).
“The US-Russian honeymoon has begun [美俄蜜月开始]!” some commenters concluded.
“It won’t last more than four years,” others predicted.
Some suggested it might be an opportunity for China and Europe to draw closer: “China and Europe will also cooperate on various matters.”
Regarding Putin agreeing to assist in US-Iran talks (#美媒爆普京同意协助美促成与伊朗核谈判#), reactions were cautiously optimistic: “It’s hard to find an American president seeking peace as much as Trump is,” one Weibo user wrote. Another added: “He might be pursuing ‘America First,’ but his efforts for peace deserve some acknowledgement. I hope it’s true.”
➜ Outside of China, analysts and commentators have argued that a US-Russia rapprochement could be bad for China, suggesting it might undermine the close strategic partnership between China and Russia. However, this sentiment seems less pronounced on Chinese social media, where many argue US-Russian relations are bound to be fickle, while others echo the official stance.
The official response to such concerns, as stated by Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson Lin Jian (林剑), is that the China-Russia bilateral relationship “will not be affected by any third party”:
💬 “Both China and Russia have long-term development strategies and foreign policies. No matter how the international landscape changes, our relationship will move forward at its own pace. The US attempt to sow discord between China and Russia is doomed to fail.”
Another perspective comes from Chinese political scientist and commentator Zheng Yongnian (郑永年), in a recent interview with Xiakedao (@侠客岛), a popular commentary account from People’s Daily Overseas Edition.
Zheng noted that the US-Russia shift is not surprising—considering, among other things, Trump’s previous comments about his good relationship with Putin—but that it places Ukraine and Europe in an unfavorable position.
➜ Like other commentators, Zheng suggests that Trump’s strategy to improve ties with Russia is also linked to gaining leverage over China. However, he does not necessarily view it as a direct revival of Kissinger’s famous Cold War-era strategy, which aimed to align with China to counter the Soviet Union. In this case, it would be reversed: allying with Russia to counter China (“联俄抗中”). In Trump’s view, Zheng argues, Europe doesn’t matter, and Ukraine is insignificant. Russia is the key to maximizing US interests.
➜ Like others—and in contrast to some foreign analyses—Zheng does not see the U.S.-Russia rapprochement as necessarily harmful to China. Instead, he suggests that right-wing, pragmatic partners may ultimately be more beneficial to China than left-wing ideological ones, stating:
💬 “When it comes to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the previous Biden administration continuously tried to frame China, attempting to shift the blame onto China. So now, after the US and Russian leaders spoke, the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs responded by saying they are ‘pleased to see all efforts working for peace, including Russia and the US coming to a common understanding that will lead to peace.’ China won’t meddle in another country’s internal affairs. No matter who’s in power, we will engage with them. China can indeed take a relatively neutral stance.
In the past, we said, ‘It’s easier to deal with the right-wing in the West.’ Why? Because the political right is less hypocritical; they value interests, and interests can be exchanged. Some Western left-wing factions, however, cling to ideological patterns, labeling and defining you, making exchange and interaction impossible.”
SHARPENED FOCUS ON TAIWAN
“Ever since Trump came to power and betrayed Ukraine, the rhetoric towards Taiwan has become increasingly tough”
Although there may be mixed views and different analyses, one thing is certain: Trump’s strategies are shaking things up from how they used to be.
➜ One thing that doesn’t change in rapidly changing times, is an overall anti-American sentiment on Chinese social media.
Even though some commenters appreciate Trump’s pragmatism or are entertained by the spectacle of US politics from the sidelines, there remains a strong belief that US strategies are ultimately aimed against China. This reinforces anti-American sentiments and fuels discussions about a potential US-China conflict.
This is especially tangible at a time when the US government has once again raised tariffs on Chinese imports.
“If war is what the U.S. wants—be it a tariff war, a trade war, or any other type of war—we’re ready to fight till the end,” China’s embassy in Washington posted on X, reiterating a government statement from Tuesday.
During the Two Sessions on March 7, Foreign Minister Wang Yi (王毅) also commented on US-China relations, stating:
💬 “No country should harbor the illusion that it can suppress and contain China on one hand while seeking to develop a good relationships with China on the other. Such two-faced behavior [两面人] is not only detrimental to the stability of bilateral relations and cannot build mutual trust.”
➜ Against this backdrop, the Taiwan issue has once again come into sharp focus.
This is partly driven by the two Two Sessions (March 5-11), China’s annual gathering of the National People’s Congress (NPC) and the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC). This is not just a major political event but also a key moment for propaganda and political messaging.
But it is mostly linked to the broader, rapidly changing geopolitical sphere and Trump’s shifting stance on Russia and Ukraine. The narrative of US power politics failing to change the course of a China-Taiwan “reunification” is surfacing again precisely because of Trump’s reshuffling of alliances.
Since the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, Chinese social media users have frequently drawn comparisons between Taiwan and Ukraine. The phrase “Today’s Ukraine, tomorrow’s Taiwan?” gained traction at the time, as online commenters saw Ukraine’s rapid invasion as a cautionary tale for Taiwan, highlighting how quickly the situation could change. A viral meme from that period depicted a pig labeled “Taiwan” watching another pig, “Ukraine,” being slaughtered.
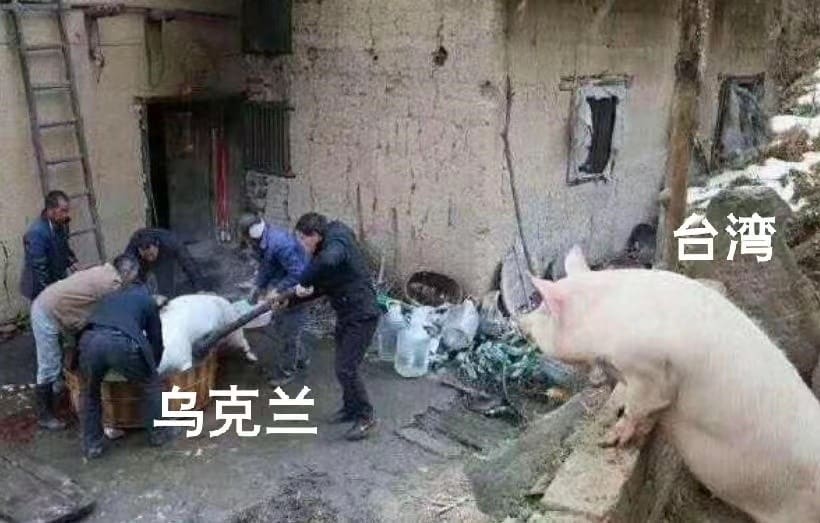

A meme circulating on social media in 2022 showing a pig “Taiwan” watching the slaughtering of another pig “Ukraine.”
This week, Chinese state media launched a large-scale social media propaganda campaign using strong language and clear visuals to reinforce the narrative that Taiwan is not a country, that it is part of China, and that reunification is inevitable.

Such rhetoric has appeared before, with similar peaks in Taiwan propaganda dating back to at least 2022. The topic of Taiwan has often been amplified during key political events, such as the 20th Party Congress and Xi Jinping’s speech in October 2022.
“Have you noticed?,” Weibo author Yangeisaibei (@雁归塞北) wrote: “Ever since Trump came to power and sold out Ukraine, the rhetoric towards Taiwan has become increasingly tough, the tones become more stern, and the words more straightforward.”
According to prominent Weibo blogger @前HR本人, who has over two million followers, the Taiwan issue is now more important than before.
💬 “When it comes to foreign struggles, resolving the Taiwan issue is China’s top priority. Judging from the Chinese Embassy in Washington declaring “We are not afraid of any kind of war with the US”, it seems we are already preparing to reunify Taiwan at any moment.”
Another Weibo blogger (@王江雨Law, 419k fans) wrote:
💬 “Now that all kinds of big and smaller developments are changing the [political] climate, especially if America’s strong territorial expansion claims turn into concrete actions, this could trigger synchronous reactions, greatly increasing the possibility of resolving the Taiwan issue within a few years. We need to rethink the previous view that the mainland is not in a hurry on this matter.”
What emerges from these discussions is that Chinese online discourse on the Russia-Ukraine war and US foreign policy is primarily centered around two key ideas:
🔸 The belief that China is ultimately at the core of US geopolitical strategies in its dealings with Russia.
🔸 A pragmatic, Sino-centric view in which support or opposition to leaders like Trump, Putin, or Zelensky shifts depending on what serves China’s interests best.
Rather than seeing the conflict in black-and-white terms, many Chinese netizens approach it as a dynamic political chess game, one in which China should play a smart and confident strategy.
Politics-focused blogger Mingshuzhatan (@明叔杂谈, 137k followers) wrote:
💬 “In the process of this game against US, we must respect them in tactics, and contempt them in strategy [战术上重视、战略上藐视] – stay patient and confident. Trump is currently going against the tide, he’s being destructive. But actually, this recklessness is damaging US credibility and its global influence, it will accelerate the decline of American hegemony. A silent majority of countries in the international community harbor growing resentment and disappointment toward the US, and when these sentiments reach a tipping point, America will truly experience the pain of “un unjust cause draws little support” [失道寡助]. China, on the other hand, although also facing some challenges, focuses on science and technological and industrial innovation. That’s the right path for China’s long-term stability, prosperity, and security. In the China-US competition, it is becoming increasingly evident that time is on China’s side.”
This perspective reflects a dominant theme across Chinese online discussions: No matter how intense the geopolitical shifts may be, or how much the US reshuffles its global strategy, China remains on its course and is playing the long game.🔚
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Digital
“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained
As American ‘TikTok Refugees’ flock to China’s Xiaohongshu (Rednote), their encounter with ‘Li Hua’ strikes a chord in divided times.
Published
2 months agoon
January 20, 2025
FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
China’s Xiaohongshu (Rednote) has seen an unprecedented influx of foreign “TikTok refugees” over the past week, giving rise to endless jokes. But behind this unexpected online migration lie some deeper themes—geopolitical tensions, a desire for cultural exchange, and the unexpected role of the fictional character Li Hua in bridging the divide.
Imagine you are Li Hua (李华), a Chinese senior high school student. You have a foreign friend, far away, in America. His name is John, and he has asked you for some insight into Chinese Spring Festival, for an upcoming essay has to write for the school newspaper. You need to write a reply to John, in which you explain more about the history of China’s New Year festival and the traditions surrounding its celebrations.
This is the kind of writing assignment many Chinese students have once encountered during their English writing exams in school during the Gaokao (高考), China’s National College Entrance Exams. The figure of ‘Li Hua’ has popped up on and off during these exams since at least 1995, when Li invited foreign friend ‘Peter’ to a picnic at Renmin Park.
Over the years, Li Hua has become somewhat of a cultural icon. A few months ago, Shangguan News (上观新闻) humorously speculated about his age, estimating that, since one exam mentioned his birth year as 1977, he should now be 47 years old—still a high school student, still helping foreign friends, and still introducing them to life in China.

Li Hua: the connector, the helper, the icon.
This week, however, Li Hua unexpectedly became a trending topic on social media—in a week that was already full of surprises.
With a TikTok ban looming in the US (delayed after briefly taking effect on Sunday), millions of American TikTok users began migrating to other platforms this month. The most notable one was the Chinese social media app Xiaohongshu (now also known as Rednote), which saw a massive influx of so-called “TikTok refugees” (Tiktok难民). The surge propelled Xiaohongshu to the #1 spot in app stores across the US and beyond.
This influx of some three million foreigners marked an unprecedented moment for a domestic Chinese app, and Xiaohongshu’s sudden international popularity has brought both challenges and beautiful moments. Beyond the geopolitical tension between the US and China, Chinese and American internet users spontaneously found common ground, creating unique connections and finding new friends.
While the TikTok/Xiaohongshu “honeymoon” may seem like just a humorous trend, it also reflects deeper, more complex themes.
✳️ National Security Threat or Anti-Chinese Witchhunt?
At its core, the “TikTok refugee” trend has sprung from geopolitical tensions, rivalry, and mutual distrust between the US and China.
TikTok is a wildly popular AI-powered short video app by Chinese company ByteDance, which also runs Douyin, the Chinese counterpart of the international TikTok app. TikTok has over 170 million users in the US alone.
A potential TikTok ban was first proposed in 2020, amid escalating US-China tensions. President Trump initiated the move, citing security and data concerns. In 2024, the debate resurfaced in global headlines when President Biden signed the “Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act,” giving ByteDance nine months to divest TikTok or face a US ban.
TikTok, however, has continuously insisted it is apolitical, does not accept political promotion, and has no political agenda. Its Singaporean CEO Shou Zi Chew maintains that ByteDance is a private business and “not an agent of China or any other country.”
🇺🇸 From Washington’s perspective, TikTok is viewed as a national and personal security threat. Officials fear the app could be used to spread propaganda or misinformation on behalf of the Chinese Communist Party.
🇨🇳 Beijing, meanwhile, criticizes the ban as an act of “bullying,” accusing the US of protectionism and attempting to undermine China’s most successful internet companies. They argue that the ban reflects America’s inability to compete with the success of Chinese digital products, labeling the scrutiny around TikTok as a “witch hunt.”

Political cartoon about the American “witchhunt” against TikTok, shared on Weibo in 2023, also published on Twitter by Lianhe Zaobao.
“This will eventually backfire on the US itself,” China’s Foreign Ministry spokesperson Wang Wenbin predicted in 2024.
Wang turned out to be quite right, in a way.
When it became clear in mid-January that the ban was likely to become a reality, American TikTok users grew increasingly frustrated and angry with their government. For many of these TikTok creators, the platform is not just a form of entertainment—it has become an essential part of their income. Some directly monetize their content through TikTok, while others use it to promote services or products, targeting audiences that other platforms like Facebook, Instagram, or X can no longer reach as effectively.
Initially, the mass migration of American users to Xiaohongshu was a symbolic protest against US policies. Users advocated for the right to choose their preferred social media, and voiced their frustration at how their favorite app had become a pawn in US-China geopolitical tensions. Rejecting the narrative that “data must be protected from the Chinese,” many pointed out that privacy concerns were equally valid for US-based platforms. As an act of playful political defiance, these users downloaded Xiaohongshu to demonstrate they didn’t fear the government’s warnings about Chinese data collection.
(If they had the option, by the way, they would have installed Douyin—the actual Chinese version of TikTok—but it is only available in Chinese app stores, whereas Xiaohongshu is accessible in international stores, so it was picked as ‘China’s version of TikTok.’)
Xiaohongshu is actually not the same as TikTok at all. Founded in 2013, Xiaohongshu (literal translation: Little Red Book) is a popular app with over 300 million users that combines lifestyle, travel, fashion, and cosmetics with e-commerce, user-generated content, and product reviews. Like TikTok, it offers personalized content recommendations and scrolling videos, but is otherwise different in types of engagement and being more text-based.
As a Chinese app primarily designed for a domestic audience, the sudden wave of foreign users caused significant disruption. Xiaohongshu must adhere to the guidelines of China’s Cyberspace Administration, which requires tight control over information flows. The unexpected influx of foreign users undoubtedly created challenges for the company, not only prompting them to implement translation tools but also recruiting English-speaking content moderators to manage the new streams of content. Foreigners addressing sensitive political issues soon found their accounts banned.
Of course, there is undeniable irony in Americans protesting government control by flocking to a Chinese app functioning within an internet system that is highly controlled by the government—a move that sparked quite some debate and criticism as well.
✳️ The Sino-American ‘Dear Li Hua’ Moment
While the initial hype around Xiaohongshu among TikTok users was political, the trend quickly shifted into a moment of cultural exchange. As American creators introduced themselves on the platform, Chinese users gave them a warm welcome, eager to practice their English and teach these foreign newcomers how to navigate the app.
Soon, discussions about language, culture, and societal differences between China and the US began to flourish. Before long, “TikTok refugees” and “Xiaohongshu natives” were collaborating on homework assignments, swapping recipes, and bonding through humor.
For instance, Chinese users jokingly asked the “TikTok refugees” to pay a “cat tax” for seeking refuge on their platform, which American users happily fulfilled by posting adorable cat photos. American users, in turn, joked about becoming best friends with their “Chinese spies,” playfully mocking their own government’s fears about Chinese data collection.

The newfound camaraderie sparked creativity, as users began generating humorous images celebrating the bond between American and Chinese netizens—like Ronald McDonald cooking with the Monkey King or the Terra Cotta Soldier embracing the Statue of Liberty. Later, some images even depicted the pair welcoming their first “baby.”

🇺🇸 At the same time, it became clear just how little Americans and Chinese truly know about each other. Many American users expressed surprise at the China they discovered through Xiaohongshu, which contrasted sharply with negative portrayals they’ve seen in the media. While some popular US narratives often paint Chinese citizens as “brainwashed” by their government, many TikTok users began to reflect on how their own perspectives had been shaped—or even “manipulated”—by their media and government.
🇨🇳 For Chinese users, the sudden interaction underscored their digital isolation. Over the past 15 years, China has developed its own tightly regulated digital ecosystem, with Western platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube inaccessible in the mainland. While this system offers political and economic advantages, it has left many young Chinese people culturally hungry for direct interaction with foreigners—especially after years of reduced exchange caused by the pandemic, trade tensions, and bilateral estrangement. (Today, only some 1,100 American students are reportedly studying in China.)
The enthusiasm and eagerness displayed by American and Chinese Xiaohongshu users this week actually underscores the vacuum in cultural exchange between the two nations.
As a result of the Xiaohongshu migration, language-learning platform Duolingo reported a 216% rise in new US users learning Mandarin—a clear sign of growing interest in bridging the US-China divide.
Mourning the lack of intercultural communication and celebrating this unexpected moment of connection, Xiaohongshu users began jokingly asking Americans if they had ever received their “Li Hua letters.”
What started as some lighthearted remarks evolved into something much bigger as Chinese users dug up their old Gaokao exam papers and shared the letters they had written to their imaginary foreign friends years ago. These letters, often carefully stored in drawers or organizers, were posted with captions like, “Why didn’t you reply?” suggesting that Chinese students had been trying to reach out for years.

Example letters on Xiaohongshu: ‘Li Hua’ writing to foreign friends.
The story of ‘Li Hua’ and the replies he never received struck a chord with American Tiktok users. One user, Debrah.71, commented:
“It was the opposite for us in the USA. When I was in grade school, we did the same thing—we had foreign pen pals. But they did respond to our letters.”
Then, something extraordinary happened: Americans started replying to Li Hua.
One user, Douglas (@neonhotel), posted a heartfelt video of him writing a letter to Li Hua:
📝”Dear Li Hua, I’m sorry I didn’t get your letters. I understand you’ve been writing me for a long time, but now I’m here to reply. Hello, from your American friend. I hope you’re well. Life here is pretty normal—we go to work, hit the gym, eat dinner, watch TV. What about you? Please write back. I’m sorry I didn’t reply before, but I’m here now. Your friend, Douglas.”
Another user, Tess (@TessSaidThat), wrote:
📝”Dear Li Hua, I hope this letter finds you well. I’m so sorry my response is so late. My government never delivered your letters. Instead, they told me you didn’t want to be my friend. Now I know the truth, and I can’t wait to visit. Which city should I visit first? With love, Tess.”
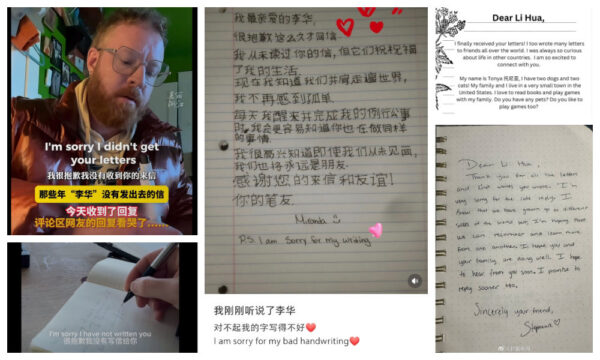
Examples of Dear Li Hua letters.
Other replies echoed similar sentiments:
📝”Dear Li Hua, I’m sorry the world kept us apart.”
📝”I know we don’t speak the same language, but I understand you clearly. Your warmth and genuine kindness transcend every barrier.”
📝”Did you achieve your dreams? Are you still practicing English? We’re older now, but wherever we are, happiness is what matters most.”
These exchanges left hundreds of users—both Chinese and American, young and old, male and female—teary-eyed. In a way, it’s the emotional weight of the distance—represented by millions of unanswered letters—that resonated deeply with both “TikTok refugees” and “Xiaohongshu natives.”
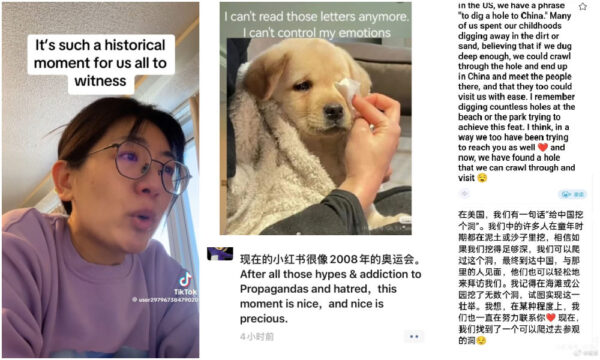
Emotional responses to the Li Hua letters.
The letters seemed to symbolize the gap that has long separated Chinese and American people, and the replies highlighted the unusual circumstances that brought these two online communities together. This moment of genuine cultural exchange made many realize how anti-Chinese, anti-American sentiments have dominated narratives for years, fostering misunderstandings.

Xiaohongshu commenter.
On the Chinese side, many people expressed how emotional it was to see Li Hua’s letters finally receiving replies. Writing these letters had been a collective experience for generations of Chinese students, creating messages to imaginary foreign friends they never expected to meet.
Receiving a reply wasn’t just about connection; it was about being truly seen at a time when Chinese people often feel underrepresented or mischaracterized in global contexts. Some users even called the replies to the Li Hua letters a “historical moment.”
✳️ Unity in a Time of Digital Divide
Alongside its political and cultural dimensions, the TikTok/Xiaohongshu “honeymoon” also reveals much about China and its digital environment. The fact that TikTok, a product of a Chinese company, has had such a profound impact on the American online landscape—and that American users are now flocking to another Chinese app—showcases the strength of Chinese digital products and the growing “de-westernization” of social media.
Of course, in Chinese official media discourse, this aspect of the story has been positively highlighted. Chinese state media portrays the migration of US TikTok users to Xiaohongshu as a victory for China: not only does it emphasize China’s role as a digital superpower and supposed geopolitical “connector” amidst US-China tensions, but it also serves as a way of mocking US authorities for the “witch hunt” against TikTok, suggesting that their actions have ultimately backfired—a win-win for China.
The Chinese Communist Party’s Publicity Department even made a tongue-in-cheek remark about Xiaohongshu’s sudden popularity among foreign users. The Weibo account of the propaganda app Study Xi, Strong Country, dedicated to promote Party history and Xi Jinping’s work, playfully suggested that if Americans are using a Chinese social media app today, they might be studying Xi Jinping Thought tomorrow, writing: “We warmly invite all friends, foreign and Chinese, new and old, to download the ‘Big Red Book’ app so we can study and make progress together!”
Perhaps the most positive takeaway from the TikTok/Xiaohongshu trend—regardless of how many American users remain on the app now that the TikTok ban has been delayed—is that it demonstrates the power of digital platforms to create new, transnational communities. It’s unfortunate that censorship, a TikTok ban, and the fragmentation of global social media triggered this moment, but it has opened a rare opportunity to build bridges across countries and platforms.
The “Dear Li Hua” letters are not just personal exchanges; they are part of a larger movement where digital tools are reshaping how people form relationships and challenge preconceived notions of others outside geopolitical contexts. Most importantly, it has shown Chinese and American social media users how confined they’ve been to their own bubbles, isolated on their own islands. An AI-powered social media app in the digital era became the unexpected medium for them to share kind words, have a laugh, exchange letters, and see each other for what they truly are: just humans.
As millions of Americans flock back to TikTok today, things will not be the same as before. They now know they have a friend in China called Li Hua.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
What’s on Weibo Chapters
Subscribe

Weibo Watch: The Great Squat vs Sitting Toilet Debate in China🧻
Chinese Netizens Turn to Tim Cook Over Battery Factory’s Illegal Overtime

Revisiting China’s Most Viral Resignation Letter: “The World Is So Big, I Want to Go and See It”

The 315 Gala: A Night of Scandals, A Year of Distrust

China Trending Week 11: The Yang Braised Chicken Scandal, Haidilao Pee Incident, Taiwan Tensions

Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Weibo Watch: Christmas in China Is Everywhere and Nowhere

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter
12-Year-Old Girl from Shandong Gets Infected with HPV: Viral Case Exposes Failures in Protecting Minors

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music12 months ago
China Music12 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment10 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment10 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments





