China Society
Chinese Netizens Voice Concerns over Molly the Elephant, Call for Animal Performance Boycott
Molly the elephant has become a powerful symbol for hundreds of other performing elephants in China.
Published
3 years agoon
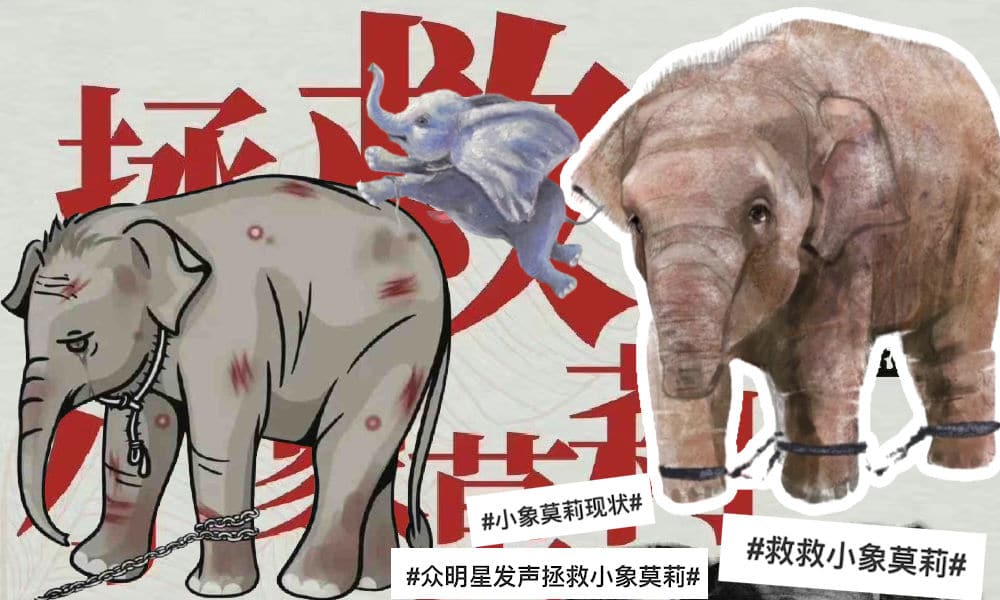

The fate of Molly, an elephant born in the Kunming Zoo and separated from its mother at the age of 2, has become a topic of public debate in China. As viral photos show the elephant being forced to perform tricks, calls for an animal performance ban in China are growing louder.
A little elephant named Molly is a big topic of discussion on Chinese social media this week. There are various hashtags about Molly on Weibo, where the elephant also has several fan forums (‘supertopics’) dedicated to her.
There are Molly artworks, Molly videos, Molly gifs, Molly cartoons, but most of all, there are the calls from netizens to ‘rescue Molly the little elephant’ (#救救小象莫莉#).
Molly’s Chinese name is Mòlì (莫莉), an Asian elephant born on March 20 in 2016 in the Kunming Zoo in Yunnan. The baby elephant was initially nicknamed “Little Princess” (小公主). When she turned one year old, the Kunming Zoo invited the public to help come up with a name for her.
On her first birthday, the popular ‘Little Princess’ received her official name and a special big elephant birthday cake. The celebration was covered by local media at the time.
Although Kunming Zoo initially seemed to take pride in their baby Molly, they separated her from her mother at the age of two in April of 2018. Molly was then transferred from Kunming Zoo to Qinyang, Jiaozuo, in Henan in exchange for another elephant.
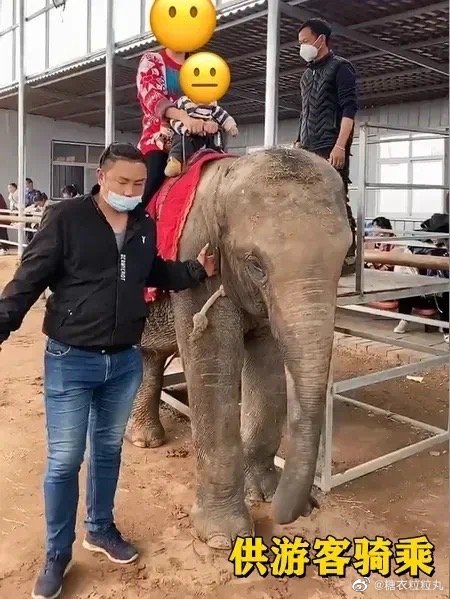
Over the past few years, Molly the elephant has allegedly been trained to do tricks and performances and to carry around tourists on her back at the Qinyang Swan Lake Ecological Garden (沁阳天鹅湖生态园), the Qinyang Hesheng Forest Zoo (沁阳和生森林动物园), the Jiaozuo Forestry Zoo (焦作森林动物园), and the Zhoukou Safari Park (周口野生动物世界).
Netizens started raising the alarm about Molly’s welfare when they spotted her chained up and seemingly unhappy, forced to do handstands or play harmonica, with Molly’s handlers using iron hooks to coerce her into performing.


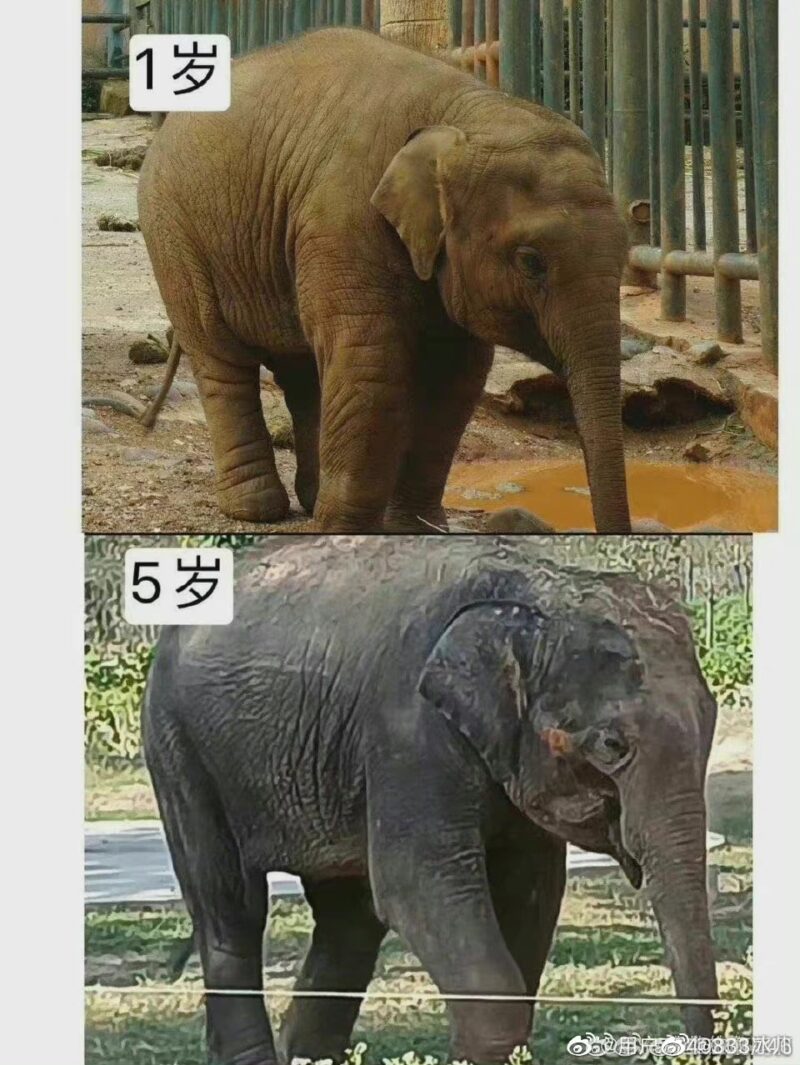
Posts about Molly being abused started to gain more online attention in the summer of 2021, and photos showing the stark difference between Molly at the age of one and at the age of five years old circulated online.

After so many netizens expressed concerns about the elephant’s mistreatment, the local zoo and authorities issued a statement in September of 2021 saying Molly was not being maltreated. But because no further clarification was given, netizens kept pushing for the elephant to be rescued and reunited with its mother in Kunming.

One of the reasons why Molly became a big topic on social media again this week is because her case was pushed forward on the social media platform Xiaohongshu, after which it also gained renewed attention on Weibo due to various big accounts posting about ‘Save Molly’ and calling for an elephant performance ban in China.
One of these influentiual people expressing concerns over the elephant is Taiwanese actress Chen Qiao’en (陈乔恩), who posted about Molly on Weibo on April 24, using the #SaveMollytheElephant hashtag:
“It’s heartbreaking to see Molly covered in wounds. She shouldn’t be treated like this. Please reject animal performances, please don’t abuse animals, please save Molly the elephant.”
Chen’s post received over 90,000 likes and a lot of attention, leading to more netizens voicing their concerns about the elephant and joining online groups about Molly’s case.

As voices speaking up for Molly grew louder, some of the groups and hashtags related to the ‘Save Molly’ movement were taken offline by Weibo censors.
“There are many ‘Molly’s’ in this world, the more you try to silence us, the louder we will get,” one Weibo commenter wrote.
A Maze of Conflicting Regulations
Beyond Molly’s situation, there is a somewhat confusing web of laws, regulations, and standards about wildlife protection and animal performances in China.
China’s Wildlife Protection Law (WPL), the national legislation for animal protection, was enacted in 1989. Throughout the decades, the law was widely criticized for not doing enough to actually protect animals and promoting the use of wildlife for human benefit. Although the law was revised in 2015, it still facilitated the commercial use of wildlife and there is no anti-cruelty legislation that might penalize cruelty to animals in zoos, wildlife parks, or other venues where wild animals are kept in captivity (Li 2021, p. 227).
When it comes to China’s zoos and safari parks, there are two regulatory bodies that play an important role: China’s Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (住房城乡建设部, MHURD), and the Chinese State Forestry and Grassland Administration (国家林业和草原局, SFGA).
The Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (MHURD) is the relevant organ overseeing Chinese zoos, which are usually owned and managed by municipal or regional governments. The MHURD also hosts the Chinese Association of Zoological Gardens (中国动物园协会, CAZG), which is an organization that most of China’s larger zoos are members of.
China’s Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development banned animal performances in China over a decade ago in 2011, although the rule excluded performances at aquariums and did not specify penalties (China Daily 2012). In 2013, the MHURD also issued the “National Zoo Development Outline” (“全国动物园发展纲要“) which strictly prohibited all animal performances in zoos.
Nevertheless, many zoos and wildlife parks have still continued shows featuring cycling bears, jumping tigers, and dancing elephants since then – and not necessarily illegally.
One of the reasons why there are conflicting regulatory regimes is because “zoos” and “wild animal parks” fall under different jurisdictions in China.
The MHURD 2011 administrative national ban on animal performance was unable to stop animal performances at China’s privately-owned wild animal parks, safari parks, or circuses, since they are administered by the Chinese State Forestry and Grassland Administration (SFGA), which also regulates the holding of all exotic species, including those in city zoos. The SFGA, however, does not consider the welfare of these animals its responsibility (see Arcus Foundation 2021, p. 99; Li 2021, p. 227).
City zoos can theoretically still subcontract animal performances to private companies within special areas of the zoo as long as their contract was signed before 2011, and can also still sell or trade animals with these parks. Dozens of zoos with performance programs have therefore continued animal performances, sometimes also in violation of policies in place (Arcus Foundation 2021, p. 99; Li 2021, p. 19).
In line with the WPL, the SFGA is able to provide permits that allow animal parks to hold animal “exhibition and performances.” The Qinyang Swan Lake Ecological Garden, where Molly is, also has a permit to “showcase wildlife” (展演野生动物), basically giving them a green light to put on performances.
Beyond Molly
On April 27, the Kunming Zoo responded to the online storm over Molly, claiming that the elephant is in good condition and that the zoo in question has since long stopped animal performances.
Chinese media outlet Phoenix News also published an article about Molly on April 30, aimed to uncover the truth about the conditions in which Molly is currently being kept at the Qinyang Hesheng Forest Zoo.
The report concluded that Molly was kept in good living conditions, and that the elephants at the park were not participating in any (circus) performances. The person in charge of the Qinyang Hesheng Forest Zoo, Shi Baodong (史保东) reportedly claims the park has stopped all animal performance activities as of April 2019, with Shi denying all claims of animal abuse taking place.
Staff members also said that some of the footage and images circulating online in relation to the Molly incident are not of Molly at all, instead showing elephant training in Thailand, India and other countries.
But many Chinese netizens believe the zoo is not speaking the truth, since social media users said they still saw Molly performing and carrying zoo visitors on her back in 2021. Even if Molly is not performing at this moment, many still think that media reports and statements cover up the truth of how the elephant is really doing.
For others, the ‘Save Molly’ hashtag is not just about Molly anymore, as the elephant has come to represent hundreds of other elephants who are living in captivity in China and are forced to perform. They hope the government can prohibit elephant performances entirely and introduce better laws and regulations to prohibit animal performances and mistreatment.
“One person doesn’t have a lot of power, but as a group we have more power,” the description for one Molly supertopic on Weibo says (小吉象莫莉).
Underneath one of the Weibo threads about Molly’s current situation, a top commenter replies: “This is not just about Molly anymore, we want to protect all of the ‘Molly’s’ out there.”


“Reject animal performances, don’t turn suffering into entertainment.”
This is not the first time netizens come into action to get justice for zoo animals that are suffering. In 2017, visitor photos of a mouth-foaming, lethargic-looking panda at Lanzhou Zoo also caused outrage on Weibo. In 2016, netizens also jumped to the aid of a polar bear by the name of Pizza after he was found living in deplorable conditions at an aquarium in the Grandview Mall in Guangzhou. He was later removed from the mall.
UPDATE MAY 17 2022: MOLLY RETURNS TO KUNMING ZOO
To follow more updates regarding Molly, check out Twitter user ‘Diving Paddler’ here. We thank them for their contributions to this article.
To read more about zoos and wildlife parks causing online commotion in China, check our articles here.
By Manya Koetse
References (other sources linked to within text)
Arcus Foundation (Ed.). 2021. State of the Apes: Killing, Capture, Trade and Ape Conservation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
China Daily. 2012. “Animal Rights Groups Seek Performance Ban.” China Daily, April 16 http://www.china.org.cn/environment/2012-04/16/content_25152066.htm [Accessed May 1 2022].
Li, Peter J. 2021. Animal Welfare in China: Culture, Politics and Crisis. Sydney: Sydney University Press.
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our weekly newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2022 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China Insight
Squat or Sit? China’s Great Toilet Debate and the Problem of Footprints on the Seat
From squatting to standing on seats: the messy reality of sitting toilets in Beijing malls.
Published
2 weeks agoon
March 25, 2025
FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
Shoe prints on top of the toilet seat are never a pretty sight. To prevent people from squatting over Western-style sitting toilets, there are some places that will place stickers above the toilet, reminding people that standing on the seat is strictly forbidden.

For years, this problem has sparked debate. Initially, these discussions would mostly take place outside of China, in places with a large number of Chinese tourists. In Switzerland, for example, the famous Rigi Railways caused controversy for introducing separate trains with special signs explaining to tourists, especially from China, how (not) to use the toilet.
Squat toilets are common across public areas in China, especially in rural regions, for a mix of historical, cultural, and practical reasons. There is also a long-held belief — backed by studies (like here or here) — that the squatting position is healthier for bowel movements (for more about the history of squat toilets in China, see Sixth Tone’s insightful article here).

Public squatting toilets in Beijing, images via Xiaohongshu.
Without access to the ground-level squat toilets they are used to — and feel more comfortable with — some people will climb on top of sitting toilets to use them in the way they’re accustomed to, seeing squatting as the more natural and hygienic method.

Not only does this make the toilet seat all messy and muddy, it is also quite a dangerous stunt to pull, can break the toilet, and lead to pee and poo going into all kinds of unintended directions. Quite shitty.
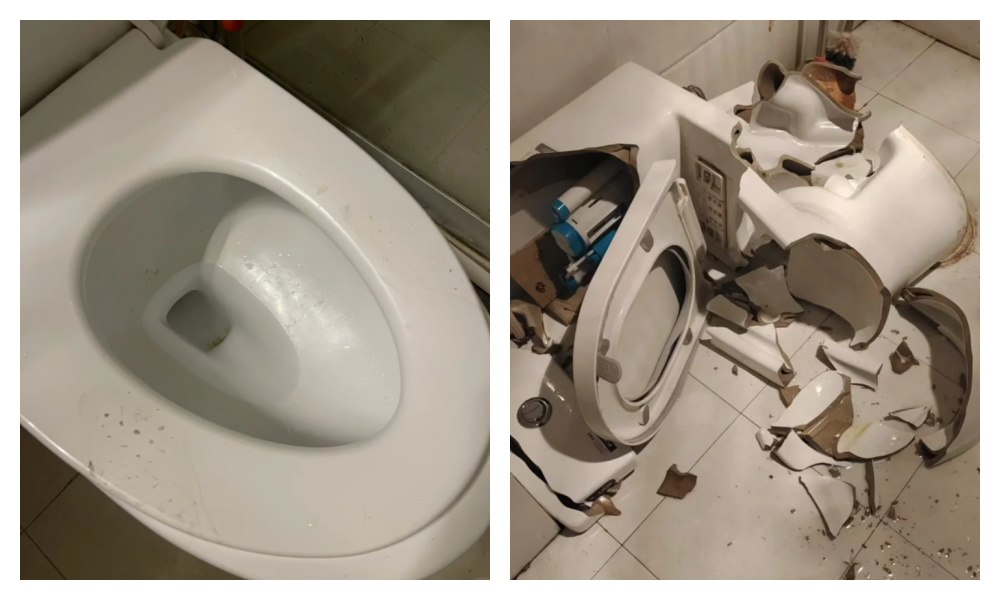

Squatting on toilets makes the seat dirty and can even break the toilet.
Along with the rapid modernization of Chinese public facilities and the country’s “Toilet Revolution” over the past decade, sitting toilets have become more common in urban areas, and thus the sitting-toilet-used-as-squat-toilet problem is increasingly becoming topic of public debate within China.
The Toilet Committee and Preference for Sitting Toilets
Is China slowly shifting to sitting toilets? Especially in modern malls in cities like Beijing, or even at airports, you see an increasing number of Western-style sitting toilets (坐厕) rather than squatting toilets (蹲厕).
This shift is due to several factors:
🚽📌 First, one major reason for the rise in sitting toilets in Chinese public places is to accommodate (foreign) tourists.
In 2015, China Daily reported that one of the most common complaints among international visitors was the poor condition of public toilets — a serious issue considering tourists are estimated to use public restrooms over 27 billion times per year.
That same year, China’s so-called “Toilet Revolution” (厕所革命) began gaining momentum. While not a centralized campaign, it marked a nationwide push to upgrade toilets across the country and improve sanitation systems to make them cleaner, safer, and more modern.
This movement was largely led by the tourism sector, with the needs of both domestic and international travelers in mind. These efforts, and the buzzword “Toilet Revolution,” especially gained attention when Xi Jinping publicly endorsed the campaign and connected it to promoting civilized tourism.
In that sense, China’s toilet revolution is also a “tourism toilet revolution” (旅游厕所革命), part of improving not just hygiene, but the national image presented to the world (Cheng et al. 2018; Li 2015).
🚽📌 Second, the growing number of sitting toilets in malls and other (semi)public spaces in Beijing relates to the idea that Western-style toilets are more sanitary.
Although various studies comparing the benefits of squatting and sitting toilets show mixed outcomes, sitting toilets — especially in shared restrooms — are generally considered more hygienic as they release fewer airborne germs after flushing and reduce the risk of infection (Ali 2022).
There are additional reasons why sitting toilets are favored in new toilet designs. According to Liang Ji (梁骥), vice-secretary of the Toilet Committee of the China Urban Environmental Sanitation Association (中国城市环境卫生协会厕所专业委员会), sitting toilets are also increasingly being introduced in public spaces due to practical concerns.
🚽📌 Squatting is not always easy, and can pose a safety risk, particularly for the elderly, pregnant women, and people with disabilities.
🚽📌 Then there are economic reasons: building squat toilets in malls (or elsewhere) requires a deeper floor design due to the sunken space needed below the fixture, which increases both construction time and cost.
🚽📌 Liang also points to an aesthetic factor: sitting toilets simply look more “high-end” and are easier to clean, which is why many consumer-oriented spaces prefer to install Western-style toilets.
So although there are plenty of reasons why sitting toilets are becoming a norm in newly built public spaces and trendy malls, they also lead to footprints on toilet seats — and all the problems that come with it.
The Catch 22 of Sitting vs Squad Toilets
This week, the issue became a trending topic on Weibo after Beijing News published an investigative report on it. The report suggested that most shopping malls in Beijing now have restrooms with sitting toilets, which should, in theory, be cleaner than the squat toilets of the past — but in reality, they’re often dirtier because people stand on them. This issue is more common in women’s restrooms, as men’s restrooms typically include urinals.
In researching the issue, a reporter visited several Beijing malls. In one women’s restroom, the reporter observed 23 people entering within five minutes. Although the restroom had only three squat toilets versus seven sitting ones, around 70% of the users opted for the squat toilets.
Upon inspection, most of the seven sitting toilets were dirty — despite being equipped with disposable seat covers — showing clear signs of urine stains and footprints. They found that sitting toilets being used as squat toilets is extremely common.
It’s a bit of a Catch-22. People generally prefer clean toilets, and there’s also a widespread preference for squat toilets. This leads to sitting toilets being used as squat toilets, which makes them dirty — reinforcing the preference for squat toilets, since the sitting toilets, though meant to be cleaner, end up dirtier.
In interviews with 20 women, nearly 80% said they either hover in a squat or directly squat on the toilet seat. One woman said, “I won’t sit unless I absolutely have to.” While some of those quoted in the article said that sitting toilets are more comfortable, especially for elderly people, they are still not preferred when the seats are not clean.
In the Beijing News article, the Toilet Committee’s Liang Ji suggested that while a balanced ratio of squat and sitting toilets is necessary, a gradual shift toward sitting toilets is likely the future for public restrooms in China.

How NOT to use the sitting toilet. Sign photographed by Xiaohongshu user @FREAK.00.com.
Liang also highlighted the importance of correct toilet use and the need to consider public habits in toilet design.
In Squatting We Trust
On Chinese social media, however, the majority of commenters support squatting toilets. One popular comment said:
💬 “Please make all public toilets squat toilets, with just one sitting toilet reserved for people with disabilities.”

Squatting toilets in a public toilet in a Beijing hutong area, image by Xiaohongshu user @00后饭桶.
The preference for squatting, however, doesn’t always come down to bowel movements or tradition. Many cite a lack of trust in how others use public toilets:
💬 “When it comes to things for public use, it’s best to reduce touching them directly. Honestly, I don’t trust other people…”
💬 “Squatting is the most hygienic. At least I don’t have to worry about touching something others touched with their skin.”
💬 “I hate it when all the toilets in the women’s restroom at the mall are sitting toilets. I’m almost mastering the art of doing the martial-arts squat (蹲马步).”
Others view the gradual shift toward sitting toilets as a result of Westernization:
💬 “Sitting toilets are a product of widespread ‘Westernization’ back in the day — the further south you go, the worse it gets.”
But some come to the defense of sitting toilets:
💬 “Are there really still people who think squat toilets are cleaner? The chances of stepping in poop with squat toilets are way higher than with sitting ones. Sitting toilet seats can be wiped with disinfectant or covered with paper. Some people only care about keeping themselves ‘clean’ without thinking about whether the next person might end up stepping in their mess.”
💬 One reply bluntly said: “I don’t use sitting toilets. If that’s all there is, I’ll just squat on top of it. Not even gonna bother wiping it.”
It’s clear this debate is far from over, and the issue of people standing on toilet seats isn’t going away anytime soon. As China’s toilet revolution continues, various Toilet Committees across the country may need to rethink their strategies — especially if they continue leaning toward installing more sitting toilets in public spaces.
As always, Taobao has a solution. For just 50 RMB (~$6.70), you can order an anti-slip sitting-to-squatting toilet aid through the popular e-commerce platform.
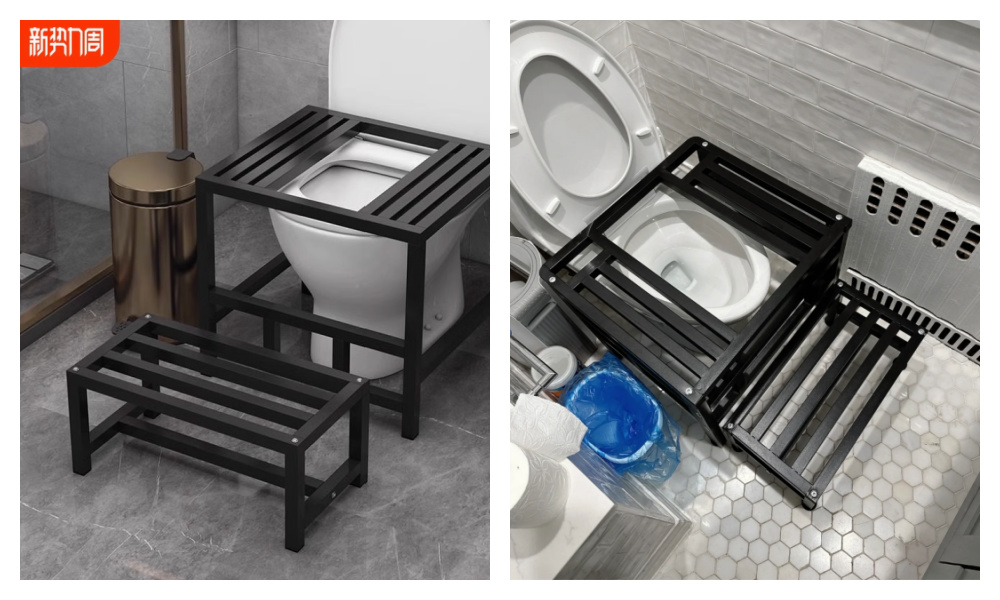

The Taobao solution.
For Chinese malls, offering these might be cheaper than dealing with broken toilets and the never-ending battle against footprints on toilet seats…
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
References:
Ali, Wajid, Dong-zi An, Ya-fei Yang, Bei-bei Cui, Jia-xin Ma, Hao Zhu, Ming Li, Xiao-Jun Ai, and Cheng Yan. 2022. “Comparing Bioaerosol Emission after Flushing in Squat and Bidet Toilets: Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment for Defecation and Hand Washing Postures.” Building and Environment 221: 109284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109284.
Bhattacharya, Sudip, Vijay Kumar Chattu, and Amarjeet Singh. 2019. “Health Promotion and Prevention of Bowel Disorders Through Toilet Designs: A Myth or Reality?” Journal of Education and Health Promotion 8 (40). https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_198_18.
Cao, Jingrui 曹晶瑞, and Tian Jiexiong 田杰雄. 2025. “城市微调查|商场女卫生间,坐厕为何频频变“蹲坑”? [In Shopping Mall Women’s Restrooms, Why Do Sitting Toilets Frequently Turn into ‘Squat Toilets’?]” Beijing News, March 20. https://weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309405146044773302810. Accessed March 19, 2025.
Cheng, Shikun, Zifu Li, Sayed Mohammad Nazim Uddin, Heinz-Peter Mang, Xiaoqin Zhou, Jian Zhang, Lei Zheng, and Lingling Zhang. 2018. “Toilet Revolution in China.” Journal of Environmental Management 216: 347–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.043.
Dai, Wangyun. 2018. “Seats, Squats, and Leaves: A Brief History of Chinese Toilets.” Sixth Tone, January 13. https://www.sixthtone.com/news/1001550. Accessed March 22, 2025.
Li, Jinzao. 2015. “Toilet Revolution for Tourism Evolution.” China Daily, April 7. https://europe.chinadaily.com.cn/opinion/2015-04/07/content_20012249_2.htm. Accessed March 22, 2025.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Food & Drinks
China Trending Week 11: The Yang Braised Chicken Scandal, Haidilao Pee Incident, Taiwan Tensions
What’s been trending on Weibo and beyond? I doomscrolled Chinese social media so you don’t have to.
Published
4 weeks agoon
March 13, 2025
Here’s the latest roundup of the three top trends and most noteworthy discussions on Chinese social media this week.
🍚🤢Yang’s Braised Chicken Rice Scandal

The popular Chinese franchise Yang’s Braised Chicken Rice (杨铭宇黄焖鸡米饭) is at the center of attention this week—for all the wrong reasons. The company, which opened its first restaurant in 2011 and has since franchised more than 2500 locations across China, was exposed by Beijing News for reusing expired ingredients and reselling leftover food in at least three of its restaurants in Zhengzhou and Shangqiu (Henan). Cooks were smoking in the kitchen and even going as far as dyeing spoiled, darkened beef with food coloring to make it appear fresh.
The issue has sparked widespread concern on Chinese social media—not only because Yang’s Braised Chicken Rice is a well-known restaurant chain, but also because food safety and kitchen hygiene remain ongoing concerns in China. The timing of this news is particularly significant, as it was published in the lead-up to March 15—China’s National Consumer Rights Day, an annual event that highlights consumer protection issues.
China’s State Council Food Safety Commission Office has now ordered authorities in Henan and Shandong, where Yang’s Braised Chicken is headquartered, to thoroughly investigate the case. The affected stores will reportedly be closed permanently, but the impact extends far beyond these locations—most netizens discussing the scandal have made it clear they won’t be ordering from Yang’s Braised Chicken Rice anytime soon.
Can the company win back consumer trust? Even though general management has been apologizing and pledged to personally oversee kitchen standards, this is not the first time the company is in hot water. In 2024, a customer in Chengdu allegedly ordered Yang’s Braised Chicken Rice via takeout and discovered a fully cooked dead rat in their meal (picture here not for the faint of heart).
🇹🇼⚔️Beijing Angrily Responds to Lai Ching-te’s Speech: “Pushing Taiwan Towards the Danger of War”

While tough language on Taiwan was already trending last week during China’s Two Sessions, another wave of discussions on Taiwan has emerged this week. This follows a high-level national security meeting held on Thursday by Taiwanese President Lai Ching-te (赖清德), after which he addressed the media and proposed more aggressive strategies to counter Beijing’s so-called ‘united front’ efforts within Taiwan.
On Friday, Beijing responded with stern remarks. Chen Binhua (陈斌华), spokesperson for the Taiwan Affairs Office of the State Council, called Lai Ching-te a “destroyer of cross-strait peace” (“两岸和平破坏者”) and a “creator of crises in the Taiwan Strait” (“台海危机制造者”) who is “pushing Taiwan towards the dangerous situation of war” (“把台湾推向兵凶战危险境”).
Chen also reiterated Beijing’s stance that reunification with Taiwan is inevitable. This message was further amplified on Chinese social media platforms such as Weibo and Douyin through the hashtag “Inevitable Reunification with the Motherland” (#祖国必然统一#).
🔥🚽Haidilao’s “Pissgate”

Last week, on March 6, a peculiar news item went viral on Chinese social media, and I tweeted out the viral video here. The footage shows a young man standing on a table in a private dining room at a Haidilao restaurant, seemingly urinating into the hotpot. The incident was later confirmed to have taken place at the popular chain’s Bund location in Shanghai on the night of February 24.
Just when you thought the world couldn’t get any crazier… someone stands up and pisses in the Haidilao hotpot. Blasphemy! Hotpot treason!
Anyway, Haidilao reported the guy to the police, and I’m pretty sure he won’t be welcome back anytime soon. pic.twitter.com/3ytLhGdYjX
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) March 6, 2025
Honestly, the video seemed staged (the “pee” looked more like water), but understandably, Haidilao was very pissed about the negative impact on its reputation. In case you’re not familiar: Haidilao is one of China’s most popular hotpot chains, known for its excellent service and food quality (read here).
The company immediately launched an investigation into the video’s origins and reported the two men—the one urinating and the one filming—to the police.
This week, the incident gained even more traction (even the BBC covered it) after it was revealed that Haidilao had reimbursed 4,109 customers who dined at the restaurant between February 24, when the incident occurred, and March 8, when all tableware was discarded and the entire restaurant was disinfected.
Not only did Haidilao reimburse customers, but they also compensated them tenfold.
This compensation strategy sparked all kinds of discussions on Chinese social media. While many agreed with Haidilao’s solution to prevent a marketing crisis, some customers and netizens raised ethical questions, such as:
💰If you paid for your meal with coupons and only spent a couple of cents in cash, is it fair that some customers only received 9 RMB ($1.25) in compensation?
💰If you paid for an entire group of friends, meaning you originally spent around $140 on a meal but now received $1,400 in reimbursement, should you split the compensation with your friends?
💰How should cases be handled where a third party made the reservation and ends up claiming part of the compensation?
By now, the incident has become about much more than just pissing in soup.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

No Quiet Qingming: From High-Tech Tomb-Sweeping to IShowSpeed & the Seven China Streams

From Trade Crisis to Patriotic Push: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Tariffs

China Trending Week 14: Gucci Fake Lipstick, Xiaomi SU7 Crash, Yoon’s Impeachment

Strange Encounter During IShowSpeed’s Chengdu Livestream

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?

Squat or Sit? China’s Great Toilet Debate and the Problem of Footprints on the Seat
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng