China Arts & Entertainment
Let’s Plant: China’s Variety Show “Become a Farmer” Is Harvesting Success Online
As iQIYI’s ‘Become a Farmer’ gains momentum, it highlights China’s growing trend of embracing rural themes in mainstream entertainment.
Published
2 years agoon

With its focus on hard farm work and meeting actual targets, Become a Farmer is a fresh breeze of air for China’s variety show business, especially among young Chinese viewers who appreciate the show’s authenticity and the calmness of the rural scenes that pose a stark contrast with stressful urban life.
The Chinese variety show Become A Farmer has achieved tremendous popularity in China recently through the iQIYI platform, which is often hailed as the Chinese equivalent of Netflix. Become A Farmer recently gained over 4.6 billion (!) views on Weibo through the hashtag #种地吧# (Zhǒng dì ba), which translates to “Let’s Plant” or “Let’s Farm” in English and also happens to be the show’s name in Chinese.
Produced by iQIYI and Blue Sky Media Group (BSMG), Become A Farmer (Young Men edition) is a documentary-style interactive reality show that revolves around the theme of farming, with actual farm work as its central focus.
The show handpicked ten young men out of 300 candidates to assemble a “farming team.” With unwavering dedication, they toiled for over 190 days, diligently cultivating 142.8 mu (approximately 95,200 square meters) of land. They actively engaged in every aspect of farm work, starting from planting a single seed and guiding the audience through the complete journey of rice germination, growth, flowering, and ultimately reaping the harvest.
Chinese netizens have drawn comparisons between the show and the British television documentary series Clarkson’s Farm. Playfully, they remarked that if Clarkson’s Farm were to be introduced in the Chinese market, it could aptly be renamed “Become A Farmer (Old Men Edition).”
Become A Farmer released its first episode on February 4 of this year, initially receiving limited attention. However, as subsequent episodes were released, the show started garnering increased interest, with the audience discovering the genuine dedication of the ten young men towards their farming endeavors – and that it was not just for show.
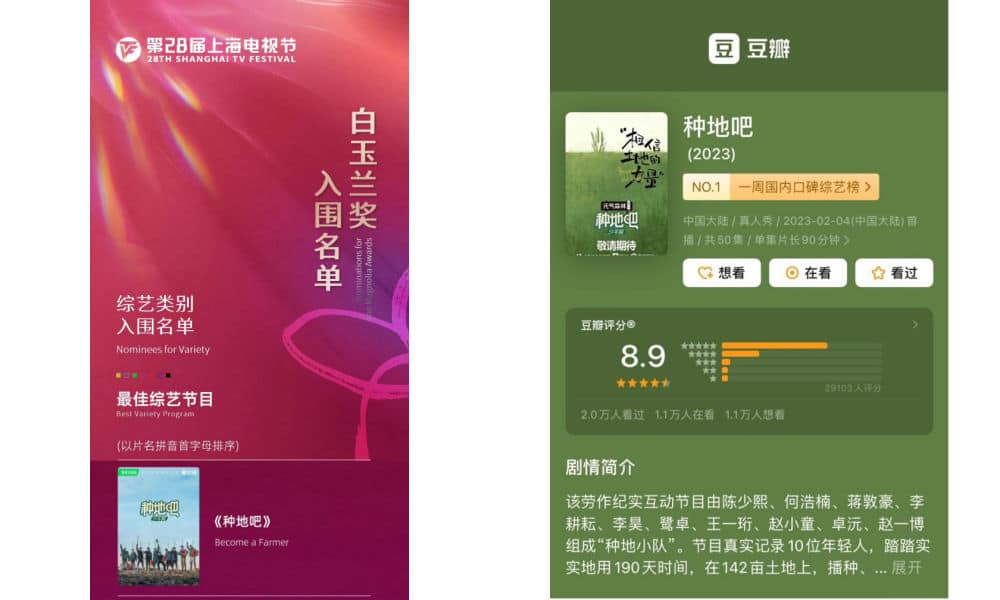
The show’s nomination for the Shanghai TV Festival, and its current rating on Douban.
Its rating on Douban, China’s IMDB, has climbed up to 8.9 out of 10. Meanwhile, the series has been nominated for the prestigious Magnolia Award for Best Variety Program at the 28th Shanghai TV Festival.
A Fresh Take on Chinese Idol Survival Shows
Become A Farmer initially caught the attention of many Chinese netizens through the humorous jokes of veteran comedian Pang Bo during the fifth season of the stand-up comedy competition Rock & Roast.
At that time, the show had not yet been aired but its format had already been introduced during a media conference, and Pang Bo (庞博) had heard about it.
In Pang’s joke, he compared the show to a farmer version of idol survival shows, proposing that the four individuals who made the greatest contributions to the final harvest could come together as a group, forming a new generation of F4 (referring to the popular Asian boy band), playfully dubbed “Farmer 4.”

Pang Bo joking about the upcoming show.
While Chinese netizens were initially amused by this joke, little did they realize that iQIYI was actually turning it into a reality, albeit without the comedic intent.
“Food is not something we can take lightly with jokes and banter, especially considering the size of our farmland, which spans approximately 140 mu and has the potential to provide sustenance for many people. This is a matter of responsibility and morality,” stated Yang Changling (杨长岭), the show’s director.
Normally, Chinese entertainers are compensated for their involvement in reality or variety shows, as they play a crucial role in generating engaging content. Such shows often seek out celebrities with a large online fan base to ensure a favorable viewership.
But Become A Farmer is different. Among the ten young men, no one is a typical celebrity that has a huge fan base online. Moreover, they are not paid for filming the show but have to earn from the land rented from local farmers through their own hard work.
To legally sell the products grown on their farmland, the ten young men took the step of registering an official company. This registration allowed Chinese netizens to verify the company’s information on the government website, providing evidence of the project’s authenticity. As the information about the company circulated, the related hashtag (#种地吧 开公司#) gained traction on Weibo, eventually trending when the ten young men received their official company certificate.
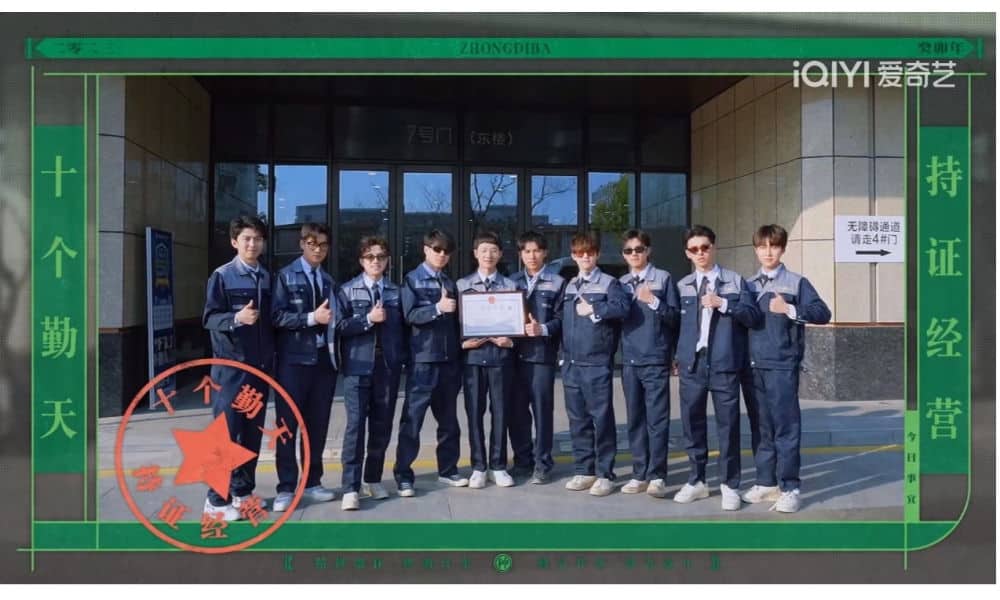

(Snapshot from the show /The ten young men received the certificate of their company)
Become A Farmer leans more towards being a documentary rather than a traditional entertainment program. To underscore its authenticity, a novel approach has been adopted in China’s variety show landscape. It airs live for one hour every day, beginning at 9:30 am, synchronizing with the young men’s start of work. This timing allows netizens, who typically commence their own workday around that time, to actively participate as ‘online supervisors,’ overseeing the ten young men’s daily tasks while starting on their own tasks of the day.
Through livestreaming on both Weibo and Douyin (the Chinese version of TikTok), the show creates a natural teaser for the edited reality series while embodying its interactive nature.
As an additional element, the ten young men occasionally share vlogs on Weibo and Douyin during the filming process. This unique combination of long-form reality show footage + livestreaming + vlogs allows the audience to closely follow and stay updated on the progress of the ten young men’s work over the span of more than 190 days.
The show’s concept of gathering relatively unknown young men aspiring to make a breakthrough in the entertainment industry bears resemblance to popular shows like Youth With You, also produced by iQIYI. However, Youth With You‘s third season was suspended in 2021 for wasting large amounts of milk amid the China’s strengthened efforts in eradicating wasting food; viewers were ecouraged to buy bottled Mengniu milk and scan QR codes inside the caps to vote for their favorite trainees, which led to fans buying tons of bottles only to vote and getting rid of the milk.
Clearly, iQIYI has learned from the past and taken a different approach with Become A Farmer. In this show, there are no milk-wasting competitions or cutthroat rivalries. Instead, the ten young men are united in their goal to complete the farm work together and to run the company and get rid of its debt.
Focus on Vital China Topics: Empowering Youth, Food Security, and Rural Revitalization
Various topics that are relevant in today’s China come together in Become a Farmer. The show also explicitly addressed its objectives in producing this diverse variety show and released a pre-episode to emphasize the importance of food security and shed light on the challenges faced by Chinese youth upon entering the workforce.
In recent years, China has placed significant emphasis on food security, with leaders repeatedly stressing the need to ensure that “the Chinese rice bowl is firmly held in our own hands.”
The China Agricultural Outlook Report (2023-2032), released on April 20, outlined the ongoing consolidation of China’s food security foundation for the next decade. Notably, all 103 million hectares of permanent farmland will be transformed into high-standard farmland. The report also highlighted plans to diversify import channels for agricultural products, improve the trade structure, and reduce grain imports by 19.7 percent over the next decade.
During the pre-episode of the show, an expert who provided training courses to ten young men emphasized the need to address the aging agricultural workforce in China’s agricultural development.
Simultaneously, in 2023, China witnessed a record-breaking number of graduates, reaching 11.58 million.
Given the increasing digitalization in agriculture, encouraging young people to pursue farming careers emerges as a viable solution. By becoming New Era Farmers (新农人) and actively participating in the nine tasks outlined in China’s “No. 1 central document” for 2023, which promotes rural vitalization comprehensively, young talent can contribute to the development of rural areas instead of solely pursuing white-collar jobs in urban areas.
A Rural Trend in Chinese Entertainment
The increasing appeal of rural life among young people in China is reflected in a survey conducted by the Social Survey Center of China Youth Daily (中国青年报社社会调查中心) in September 2022. The survey revealed that 70.9% of the respondents believed that the countryside has become more attractive to young individuals. Factors such as a slower pace of life, lower pressure, and reduced costs were cited as the main reasons why young people find rural areas appealing.
As transportation and internet connectivity have gradually improved, rural life in China is no longer seen as isolated and cut off from the rest of the world. This transformation has sparked a growing interest in living in the countryside, particularly among young people. The countryside’s allure lies in its simplicity, natural beauty, and the chance to escape the fast-paced and hectic city life.
This growing interest in rural life may explain the popularity of shows like Become a Farmer. The commitment demonstrated by the ten young men to their farm work has garnered applause from Chinese netizens. Overcoming challenges such as working in adverse weather conditions, assisting with difficult births for animals, and engaging in physically demanding tasks have showcased their dedication and hard work. These aspects have resonated with the audience and contributed to the show’s success.

(The ten young men are diligently digging drainage ditches in the farmland during chilly weather, working hard to ensure they meet the planting season deadline.)
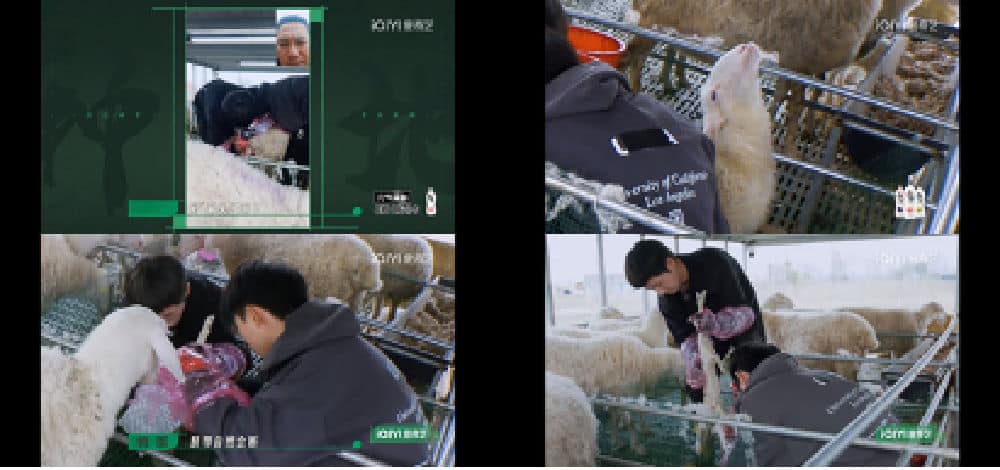

Snapshot from the show: Jiang Dunhao, the oldest among the ten young men and chairman of the company, joins forces with He Haonan to support in the challenging task of aiding the delivery of difficult births for ewes. Together, they strive to save the life of a premature lamb, seeking guidance from a professional veterinarian through online assistance.
Originally planned to conclude after 39 episodes, the show’s production team has decided to extend it to 50 episodes due to the abundance of material gathered from over 190 days of farm work and the increasing interest and positive feedback from viewers. This extended episode count goes beyond the typical duration for a variety show, highlighting its exceptional popularity.
It is evident that iQIYI, the broadcasting platform behind the show, is keen on fulfilling its alleged social responsibility to promote the importance of food security and sustainable food production, farming, and showing that young individuals that they can thrive in rural areas.
Capitalizing on the success of the reality show, iQIYI has also released a teaser for an upcoming drama called Romance on the Farm (田耕纪), which also revolves around farming. This drama portrays a contemporary woman unexpectedly finding herself in the countryside during the Song Dynasty and embarking on a journey of farming, prosperity, and love alongside the enigmatic Shen Nuo.
In the last couple of years, there were several countryside-themed dramas that showcased China’s rural revitalization efforts and highlighted the involvement of younger generations in supporting their rural hometowns, such as On The Way to Hope (在希望的田野上) or The Story of Xing Fu (幸福到万家) which starred the renowned Chinese actress Zhao Liying.
The success of Become a Farmer, the upcoming Romance on the Farm, and the overwhelming enthusiasm among Chinese viewers for these shows suggest that farming has become the latest ‘hip’ trend in China’s entertainment industry. It seems that plowing fields and tending to crops have now found their place in the limelight. With the growing interest and excitement surrounding these shows, it’s safe to say that we can expect a blooming harvest of more Chinese productions focused on farm work and rural life in the near future.
Watch “Become a Farmer” on Youtube here (including English subtitles).
By Wendy Huang
Follow @whatsonweibo
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. Please note that your comment below will need to be manually approved if you’re a first-time poster here.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
Wendy Huang is a China-based Beijing Language and Culture University graduate who currently works for a Public Relations & Media software company. She believes that, despite the many obstacles, Chinese social media sites such as Weibo can help Chinese internet users to become more informed and open-minded regarding various social issues in present-day China.

China Arts & Entertainment
How K-pop Fans and the 13-Year-Old Daughter of Baidu VP Sparked a Debate on Online Privacy
What began as K-pop fan outrage targeting a snarky commenter quickly escalated into a Baidu-linked scandal and a broader conversation about data privacy on Chinese social media.
Published
3 weeks agoon
March 26, 2025By
Ruixin Zhang
For an ordinary person with just a few followers, a Weibo account can sometimes be like a refuge from real life—almost like a private space on a public platform—where, along with millions of others, they can express dissatisfaction about daily annoyances or vent frustration about personal life situations.
But over recent years, even the most ordinary social media users could become victims of “opening the box” (开盒 kāihé)—the Chinese internet term for doxxing, meaning the deliberate leaking of personal information to expose or harass someone online.
A K-pop Fan-Led Online Witch Hunt
On March 12, a Chinese social media account focusing on K-pop content, Yuanqi Taopu Xuanshou (@元气桃浦选手), posted about Jang Wonyoung, a popular member of the Korean girl group IVE. As the South Korean singer and model attended Paris Fashion Week and then flew back the same day, the account suggested she was on a “crazy schedule.”
In the comment section, one female Weibo user nicknamed “Charihe” replied:
💬 “It’s a 12-hour flight and it’s not like she’s flying the plane herself. Isn’t sleeping in business class considered resting? Who says she can’t rest? What are you actually talking about by calling this a ‘crazy schedule’..”

Although the comment may have come across as a bit snarky, it was generally lighthearted and harmless. Yet unexpectedly, it brought disaster upon her.
That very evening, the woman nicknamed Charihe was bombarded with direct messages filled with insults from fans of Jang Wonyoung and IVE.
Ironically, Charihe’s profile showed she was anything but a hater of the pop star—her Weibo page included multiple posts praising Wonyoung’s beauty and charm. But that context was ignored by overzealous fans, who combed through her social media accounts looking for other posts to criticize, framing her as a terrible person.
After discovering through Charihe’s account that she was pregnant, Jang Wonyoung’s fans escalated their attacks by targeting her unborn child with insults.
The harassment did not stop there. Around midnight, fans doxxed Charihe, exposing her personal information, workplace, and the contact details of her family and friends. Her friends were flooded with messages, and some were even targeted at their workplaces.
Then, they tracked down Charihe’s husband’s WeChat account, sent him screenshots of her posts, and encouraged him to “physically punish” her.
The extremity of the online harassment finally drew backlash from netizens, who expressed concern for this ordinary pregnant woman’s situation:
💬 “Her entire life was exposed to people she never wanted to know about.”
💬 “Suffering this kind of attack during pregnancy is truly an undeserved disaster.”
Despite condemnation of the hate, some extreme self-proclaimed “fans” remained relentless in the online witch hunt against Charihe.
Baidu Takes a Hit After VP’s 13-Year-Old Daughter Is Exposed
One female fan, nicknamed “YourEyes” (@你的眼眸是世界上最小的湖泊), soon started doxxing commenters who had defended her. The speed and efficiency of these attacks left many stunned at just how easy it apparently is to trace social media users and doxx them.
Digging into old Weibo posts from the “YourEyes” account, people found she had repeatedly doxxed people on social media since last year, using various alt accounts.
She had previously also shared information claiming to study in Canada and boasted about her father’s monthly salary of 220,000 RMB (approx. $30.3K), along with a photo of a confirmation document.
Piecing together the clues, online sleuths finally identified her as the daughter of Xie Guangjun (谢广军), Vice President of Baidu.
From an online hate campaign against an innocent, snarky commenter, the case then became a headline in Chinese state media, and even made international headlines, after it was confirmed that the user “YourEyes”—who had been so quick to dig up others’ personal details—was in fact the 13-year-old daughter of Xie Guangjun, vice president at one of China’s biggest tech giants.
On March 17, Xie Guangjun posted the following apology to his WeChat Moments:

💬 “Recently, my 13-year-old daughter got into an online dispute. Losing control of her emotions, she published other people’s private information from overseas social platforms onto her own account. This led to her own personal information also getting exposed, triggering widespread negative discussion.
As her father, I failed to detect the problem in time and failed to guide her in how to properly handle the situation. I did not teach her the importance of respecting and protecting the privacy of others and of herself, for which I feel deep regret.
In response to this incident, I have communicated with my daughter and sternly criticized her actions. I hereby sincerely apologize to all friends affected.
As a minor, my daughter’s emotional and cognitive maturity is still developing. In a moment of impulsiveness, she made a wrong decision that hurt others and, at the same time, found herself caught in a storm of controversy that has subjected her to pressure and distress far beyond her age.
Here, I respectfully ask everyone to stop spreading related content and to give her the opportunity to correct her mistakes and grow.
Once again, I extend my apologies, and I sincerely thank everyone for your understanding and kindness.”
The public response to Xie’s apology has been largely negative. Many criticized the fact that it was posted privately on WeChat Moments rather than shared on a public platform like Weibo. Some dismissed the statement as an attempt to pacify Baidu shareholders and colleagues rather than take real accountability.
Netizens also pointed out that the apology avoided addressing the core issue of doxxing. Concerns were raised about whether Xie’s position at Baidu—and potential access to sensitive information—may have helped his daughter acquire the data she used to doxx others.
Adding fuel to the speculation were past conversations allegedly involving one of @YourEyes’ alt accounts. In one exchange, when asked “Who are you doxxing next?” she replied, “My parents provided the info,” with a friend adding, “The Baidu database can doxx your entire family.”
Following an internal investigation, Baidu’s head of security, Chen Yang (陈洋), stated on the company’s internal forum that Xie Guangjun’s daughter did not obtain data from Baidu but from “overseas sources.”
However, this clarification did little to reassure the public—and Baidu’s reputation has taken a hit. The company has faced prior scandals, most notably a the 2016 controversy over profiting from misleading medical advertisements.
Online Vulnerability
Beyond Baidu’s involvement, the incident reignited wider concerns about online privacy in China. “Even if it didn’t come from Baidu,” one user wrote, “the fact that a 13-year-old can access such personal information about strangers is terrifying.”
Using the hashtag “Reporter buys own confidential data” (#记者买到了自己的秘密#), Chinese media outlet Southern Metropolis Daily (@南方都市报) recently reported that China’s gray market for personal data has grown significantly. For just 300 RMB ($41), their journalist was able to purchase their own household registration data.
Further investigation uncovered underground networks that claim to cooperate with police, offering a “70-30 profit split” on data transactions.
These illegal data practices are not just connected to doxxing but also to widespread online fraud.
In response, some netizens have begun sharing guides on how to protect oneself from doxxing. For example, they recommend people disable phone number search on apps like WeChat and Alipay, hide their real name in settings, and avoid adding strangers, especially if they are active in fan communities.
Amid the chaos, K-pop fan wars continue to rage online. But some voices—such as influencer Jingzai (@一个特别虚荣的人)—have pointed out that the real issue isn’t fandom, but the deeper problem of data security.
💬 “You should question Baidu, question the telecom giants, question the government, and only then, fight over which fan group started this.”
As for ‘Charihe,’ whose comment sparked it all—her account is now gone. Her username has become a hashtag. For some, it’s still a target for online abuse. For others, it is a reminder of just how vulnerable every user is in a world where digital privacy is far from guaranteed.
By Ruixin Zhang
Independently covering digital China for over a decade. Like what we do? Support us and get the story behind the hashtag by subscribing:
edited for clarity by Manya Koetse
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Memes & Viral
How Ne Zha 2’s Shen Gongbao Became Known as the Ultimate “Small-Town Swot”
Published
2 months agoon
March 1, 2025
PART OF THIS TEXT COMES FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
Over the past few weeks, the Chinese blockbuster Ne Zha 2 has been trending on Weibo every single day. The movie, loosely based on Chinese mythology and the Chinese canonical novel Investiture of the Gods (封神演义), has triggered all kinds of memes and discussions on Chinese social media (read more here and here).
One of the most beloved characters is the leopard demon Shen Gongbao (申公豹). While Shen Gongbao was a more typical villain in the first film, the narrative of Ne Zha 2 adds more nuance and complexity to his character. By exploring his struggles, the film makes him more relatable and sympathetic.
In the movie, Shen is portrayed as a sometimes sinister and tragic villain with humorous and likeable traits. He has a stutter, and a deep desire to earn recognition. Unlike many celestial figures in the film, Shen Gongbao was not born into privilege and never became immortal. As a demon who ascended to the divine court, he remains at the lower rungs of the hierarchy in Chinese mythology. He is a hardworking overachiever who perhaps turned into a villain due to being treated unfairly.
Many viewers resonate with him because, despite his diligence, he will never be like the gods and immortals around him. Many Chinese netizens suggest that Shen Gongbao represents the experience of many “small-town swots” (xiǎozhèn zuòtíjiā 小镇做题家) in China.
“Small-town swot” is a buzzword that has appeared on Chinese social media over the past few years. According to Baike, it first popped up on a Douban forum dedicated to discussing the struggles of students from China’s top universities. Although the term has been part of social media language since 2020, it has recently come back into the spotlight due to Shen Gongbao.
“Small-town swot” refers to students from rural areas and small towns in China who put in immense effort to secure a place at a top university and move to bigger cities. While they may excel academically, even ranking as top scorers, they often find they lack the same social advantages, connections, and networking opportunities as their urban peers.
The idea that they remain at a disadvantage despite working so hard leads to frustration and anxiety—it seems they will never truly escape their background. In a way, it reflects a deeper aspect of China’s rural-urban divide.
Some people on Weibo, like Chinese documentary director and blogger Bianren Guowei (@汴人郭威), try to translate Shen Gongbao’s legendary narrative to a modern Chinese immigrant situation, and imagine that in today’s China, he’d be the guy who trusts in his hard work and intelligence to get into a prestigious school, pass the TOEFL, obtain a green card, and then work in Silicon Valley or on Wall Street. Meanwhile, as a filial son and good brother, he’d save up his “celestial pills” (US dollars) to send home to his family.
Another popular blogger (@痴史) wrote:
“I just finished watching Ne Zha and my wife asked me, why do so many people sympathize with Shen Gongbao? I said, I’ll give you an example to make you understand. Shen Gongbao spent years painstakingly accumulating just six immortal pills (xiāndān 仙丹), while the celestial beings could have 9,000 in their hand just like that.
It’s like saving up money from scatch for years just to buy a gold bracelet, only to realize that the trash bins of the rich people are made of gold, and even the wires in their homes are made of gold. It’s like working tirelessly for years to save up 60,000 yuan ($8230), while someone else can effortlessly pull out 90 million ($12.3 million).In the Heavenly Palace, a single meal costs more than an ordinary person’s lifetime earnings.
Shen Gongbao seems to be his father’s pride, he’s a role model to his little brother, and he’s the hope of his entire village. Yet, despite all his diligence and effort, in the celestial realm, he’s nothing more than a marginal figure. Shen Gongbao is not a villain, he is just the epitome of all of us ordinary people. It is because he represents the state of most of us normal people, that he receives so much empathy.”
In the end, in the eyes of many, Shen Gongbao is the ultimate small-town swot. As a result, he has temporarily become China’s most beloved villain.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Wendy Huang
Follow @whatsonweibo
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. Please note that your comment below will need to be manually approved if you’re a first-time poster here.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
Subscribe
China Trending Week 15/16: Maozi & Meigui Fallout

China Reacts: 3 Trending Hashtags Shaping the Tariff War Narrative

No Quiet Qingming: From High-Tech Tomb-Sweeping to IShowSpeed & the Seven China Streams

From Trade Crisis to Patriotic Push: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Tariffs

China Trending Week 14: Gucci Fake Lipstick, Xiaomi SU7 Crash, Yoon’s Impeachment

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

US-Russia Rapprochement and “Saint Zelensky”: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Shake-Up

“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng





