China Insight
More Than Gold: The Success of ‘Made-in-China’ at the Olympics
Chinese products and techniques have gained worldwide attention during the Rio Olympics. From made-in-China Olympic helmets and mosquito nets to its traditional cupping therapy – China gained more from the Rio Olympics than gold alone.
Published
9 years agoon
By
Yanling Xu
Chinese products and techniques have gained worldwide attention during the Rio Olympics. From made-in-China Olympic helmets and mosquito nets to its traditional cupping therapy – China gained more from the Rio Olympics than gold alone.
The Rio Olympics have done much good for the international image of ‘made in China’. Chinese news site Economic Daily recently reported that a variety of Chinese products have been used in this year’s Rio Olympics, ranging from eco-friendly tableware to air-conditioners. Even this year’s Olympic mascot was manufactured in China. “Made in China is everywhere”, CCTV reported.
According to Economic Daily (@经济日报), the prevalence of China-made products demonstrates China’s rise and its overall competitiveness in the global market. It is also said to give the world a more positive view of China’s image.
Chinese audiences on Sina Weibo praised the heightened presence of China-made products in the international arena: “Made in China! As a Chinese, I feel proud [of my country]! Good job, China!” one Weibo netizen wrote.
[rp4wp]
Last week, the made in China design of the helmets of China’s gold-winning cycling track team made headlines. According to Chinese media, the special helmets were a good promotion of China’s design and cultural heritage.

Besides the cycling helmets, two other made-in-China products also sparked international interest: Chinese mosquito nets and cupping sets.
Mosquito nets: China’s answer to Zika
Mosquito nets played an important role at the Rio Olympics since the Zika virus became a major concern to the Olympic Games and its athletes.
Mosquitoes are the primary transmitters of the Zika virus, which has infected hundreds of thousands of people across Latin America, especially in Brazil. Many athletes, such as Australian golfer Jason Day, even withdrew from the Rio Olympics due to concerns over Zika. The virus is known to be especially harmful to pregnant women, as infection can result in severe brain malformations in the fetus and other birth defects.
Chinese mosquito nets, that have since long been used in households across China, became trending Olympic news in and outside the PRC when pictures of Chinese athletes under their efficient tents made its rounds across the internet.
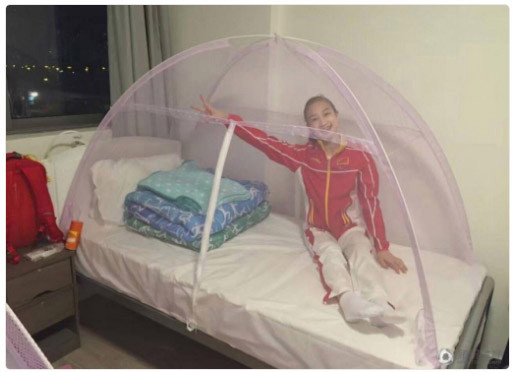
Chinese gymnast Feng Zhe said on Weibo that a foreigner even came to him to buy a mosquito net. On Twitter, Australian female basketball player Elizabeth Cambage shared pictures of herself with a made-in-China mosquito net. China’s e-commerce sites now even promote their mosquito nets as “2016 Olympic mosquito nets”.
After China’s completely mosquito-proof tents became popular in Rio, Chinese netizens started to list items that are widely used among Chinese households and yet less known to people in other regions.

One of these products is Liushen Hua Lu Shui (or Liushen Florida Water, 六神花露水), another effective product against mosquitoes. This product has recently also been introduced to markets outside of China, where it has been well-received.
Chinese cupping therapy goes global
Interest in China’s traditional cupping therapy has also grown since US swimmer Michael Phelps won the Olympic medal with deep-purple, circular bruise-like patterns on his back, which drew international attention.
Phelps’s marks came from cupping, a Chinese technique that involves placing heated cups on the back that create skin suction. In traditional Chinese practice, cupping is used to reduce pain, loose muscles, and prevent skin inflammation.
In an interview with Sohu TV, Phelps touted the benefits of cupping and said: “For me, cupping works great. It releases some of the tensions I have on my shoulders, my back, and legs – I love it.”
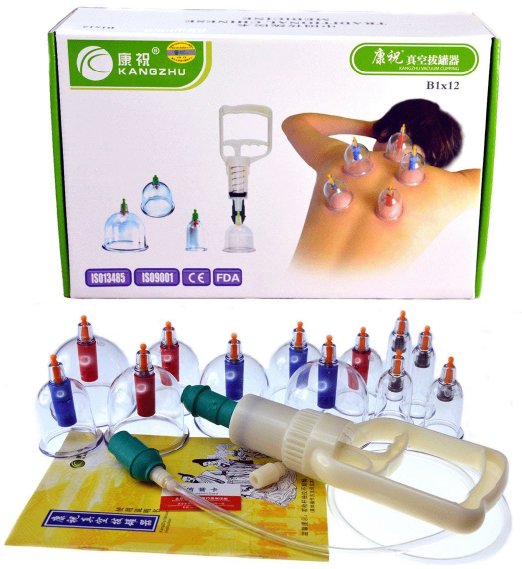
Phelps’s Olympic success and media coverage on the treatment preceding his race have led to an increase in the sales of cupping sets both in and outside China. On Taobao, the sales in cupping sets have almost doubled this month.
The 2025 vision of ‘Made-in-China’
The increased presence of Chinese products abroad is consistent with China’s first high-level 2025 vision that focuses in upgrading China’s international manufacturing.
In making this plan, Chinese leaders emphasize the importance of innovation and quality over quantity in the Chinese manufacturing industry, hoping to move ‘made in China’ up the value chain by 2025. In accordance with this 2025 vision, more and more China-made products will appear in international events like the Olympics and beyond.
But the image of ‘made in China’ is still not all sunshine and roses. As Chinese products and techniques are getting more popular across the world, there are also more discussions on effectiveness and safety. The recent hype around Chinese cupping, for example, also raised discussions on whether or not the therapy works and how safe it is.
Earlier this summer, shocking images of a man being severely burnt through cupping were shared across the internet. Guokr.com, a website that seeks to popularize science in China, points out that cupping is still a rare and little-studied practice. Due to the potential risks associated with cupping therapy, such as burns and skin infections, Guokr does not recommend people try cupping on their own.
The growing interest for Chinese products indicates an increasing international acceptance of Chinese culture and ‘made in China’. Especially athletes and celebrities play an important role in the promotion of these products. But the existing negative connotations of ‘made in China’, that is often associated with low quality and safety hazards, is not likely to change overnight.
There are still nine years to go before the China’s “2025 Vision”. That means that after Rio, there will be four more Olympics that can serve as a platform for Chinese products to prove they’re golden. Who knows, made-in-China bobsleighs might just become all the rage in Pyeongchang 2018.
– By Yanling Xu and Manya Koetse
Follow @WhatsOnWeibo
©2016 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Yanling Xu is a freelance writer and recent college graduate. Originally from Xiamen, China, she studied in the U.S. and received her Bachelor degree in Political Science and East Asian Studies from Grinnell College. Yanling currently resides in Chicago.

China Insight
Squat or Sit? China’s Great Toilet Debate and the Problem of Footprints on the Seat
From squatting to standing on seats: the messy reality of sitting toilets in Beijing malls.
Published
4 days agoon
March 25, 2025
FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
Shoe prints on top of the toilet seat are never a pretty sight. To prevent people from squatting over Western-style sitting toilets, there are some places that will place stickers above the toilet, reminding people that standing on the seat is strictly forbidden.

For years, this problem has sparked debate. Initially, these discussions would mostly take place outside of China, in places with a large number of Chinese tourists. In Switzerland, for example, the famous Rigi Railways caused controversy for introducing separate trains with special signs explaining to tourists, especially from China, how (not) to use the toilet.
Squat toilets are common across public areas in China, especially in rural regions, for a mix of historical, cultural, and practical reasons. There is also a long-held belief — backed by studies (like here or here) — that the squatting position is healthier for bowel movements (for more about the history of squat toilets in China, see Sixth Tone’s insightful article here).

Public squatting toilets in Beijing, images via Xiaohongshu.
Without access to the ground-level squat toilets they are used to — and feel more comfortable with — some people will climb on top of sitting toilets to use them in the way they’re accustomed to, seeing squatting as the more natural and hygienic method.

Not only does this make the toilet seat all messy and muddy, it is also quite a dangerous stunt to pull, can break the toilet, and lead to pee and poo going into all kinds of unintended directions. Quite shitty.
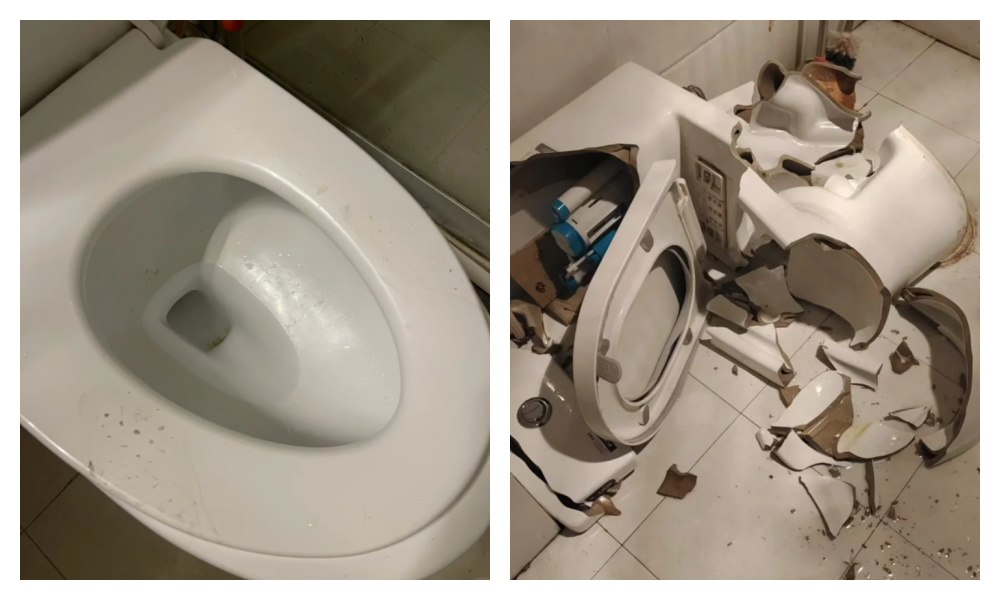

Squatting on toilets makes the seat dirty and can even break the toilet.
Along with the rapid modernization of Chinese public facilities and the country’s “Toilet Revolution” over the past decade, sitting toilets have become more common in urban areas, and thus the sitting-toilet-used-as-squat-toilet problem is increasingly becoming topic of public debate within China.
The Toilet Committee and Preference for Sitting Toilets
Is China slowly shifting to sitting toilets? Especially in modern malls in cities like Beijing, or even at airports, you see an increasing number of Western-style sitting toilets (坐厕) rather than squatting toilets (蹲厕).
This shift is due to several factors:
🚽📌 First, one major reason for the rise in sitting toilets in Chinese public places is to accommodate (foreign) tourists.
In 2015, China Daily reported that one of the most common complaints among international visitors was the poor condition of public toilets — a serious issue considering tourists are estimated to use public restrooms over 27 billion times per year.
That same year, China’s so-called “Toilet Revolution” (厕所革命) began gaining momentum. While not a centralized campaign, it marked a nationwide push to upgrade toilets across the country and improve sanitation systems to make them cleaner, safer, and more modern.
This movement was largely led by the tourism sector, with the needs of both domestic and international travelers in mind. These efforts, and the buzzword “Toilet Revolution,” especially gained attention when Xi Jinping publicly endorsed the campaign and connected it to promoting civilized tourism.
In that sense, China’s toilet revolution is also a “tourism toilet revolution” (旅游厕所革命), part of improving not just hygiene, but the national image presented to the world (Cheng et al. 2018; Li 2015).
🚽📌 Second, the growing number of sitting toilets in malls and other (semi)public spaces in Beijing relates to the idea that Western-style toilets are more sanitary.
Although various studies comparing the benefits of squatting and sitting toilets show mixed outcomes, sitting toilets — especially in shared restrooms — are generally considered more hygienic as they release fewer airborne germs after flushing and reduce the risk of infection (Ali 2022).
There are additional reasons why sitting toilets are favored in new toilet designs. According to Liang Ji (梁骥), vice-secretary of the Toilet Committee of the China Urban Environmental Sanitation Association (中国城市环境卫生协会厕所专业委员会), sitting toilets are also increasingly being introduced in public spaces due to practical concerns.
🚽📌 Squatting is not always easy, and can pose a safety risk, particularly for the elderly, pregnant women, and people with disabilities.
🚽📌 Then there are economic reasons: building squat toilets in malls (or elsewhere) requires a deeper floor design due to the sunken space needed below the fixture, which increases both construction time and cost.
🚽📌 Liang also points to an aesthetic factor: sitting toilets simply look more “high-end” and are easier to clean, which is why many consumer-oriented spaces prefer to install Western-style toilets.
So although there are plenty of reasons why sitting toilets are becoming a norm in newly built public spaces and trendy malls, they also lead to footprints on toilet seats — and all the problems that come with it.
The Catch 22 of Sitting vs Squad Toilets
This week, the issue became a trending topic on Weibo after Beijing News published an investigative report on it. The report suggested that most shopping malls in Beijing now have restrooms with sitting toilets, which should, in theory, be cleaner than the squat toilets of the past — but in reality, they’re often dirtier because people stand on them. This issue is more common in women’s restrooms, as men’s restrooms typically include urinals.
In researching the issue, a reporter visited several Beijing malls. In one women’s restroom, the reporter observed 23 people entering within five minutes. Although the restroom had only three squat toilets versus seven sitting ones, around 70% of the users opted for the squat toilets.
Upon inspection, most of the seven sitting toilets were dirty — despite being equipped with disposable seat covers — showing clear signs of urine stains and footprints. They found that sitting toilets being used as squat toilets is extremely common.
It’s a bit of a Catch-22. People generally prefer clean toilets, and there’s also a widespread preference for squat toilets. This leads to sitting toilets being used as squat toilets, which makes them dirty — reinforcing the preference for squat toilets, since the sitting toilets, though meant to be cleaner, end up dirtier.
In interviews with 20 women, nearly 80% said they either hover in a squat or directly squat on the toilet seat. One woman said, “I won’t sit unless I absolutely have to.” While some of those quoted in the article said that sitting toilets are more comfortable, especially for elderly people, they are still not preferred when the seats are not clean.
In the Beijing News article, the Toilet Committee’s Liang Ji suggested that while a balanced ratio of squat and sitting toilets is necessary, a gradual shift toward sitting toilets is likely the future for public restrooms in China.

How NOT to use the sitting toilet. Sign photographed by Xiaohongshu user @FREAK.00.com.
Liang also highlighted the importance of correct toilet use and the need to consider public habits in toilet design.
In Squatting We Trust
On Chinese social media, however, the majority of commenters support squatting toilets. One popular comment said:
💬 “Please make all public toilets squat toilets, with just one sitting toilet reserved for people with disabilities.”

Squatting toilets in a public toilet in a Beijing hutong area, image by Xiaohongshu user @00后饭桶.
The preference for squatting, however, doesn’t always come down to bowel movements or tradition. Many cite a lack of trust in how others use public toilets:
💬 “When it comes to things for public use, it’s best to reduce touching them directly. Honestly, I don’t trust other people…”
💬 “Squatting is the most hygienic. At least I don’t have to worry about touching something others touched with their skin.”
💬 “I hate it when all the toilets in the women’s restroom at the mall are sitting toilets. I’m almost mastering the art of doing the martial-arts squat (蹲马步).”
Others view the gradual shift toward sitting toilets as a result of Westernization:
💬 “Sitting toilets are a product of widespread ‘Westernization’ back in the day — the further south you go, the worse it gets.”
But some come to the defense of sitting toilets:
💬 “Are there really still people who think squat toilets are cleaner? The chances of stepping in poop with squat toilets are way higher than with sitting ones. Sitting toilet seats can be wiped with disinfectant or covered with paper. Some people only care about keeping themselves ‘clean’ without thinking about whether the next person might end up stepping in their mess.”
💬 One reply bluntly said: “I don’t use sitting toilets. If that’s all there is, I’ll just squat on top of it. Not even gonna bother wiping it.”
It’s clear this debate is far from over, and the issue of people standing on toilet seats isn’t going away anytime soon. As China’s toilet revolution continues, various Toilet Committees across the country may need to rethink their strategies — especially if they continue leaning toward installing more sitting toilets in public spaces.
As always, Taobao has a solution. For just 50 RMB (~$6.70), you can order an anti-slip sitting-to-squatting toilet aid through the popular e-commerce platform.
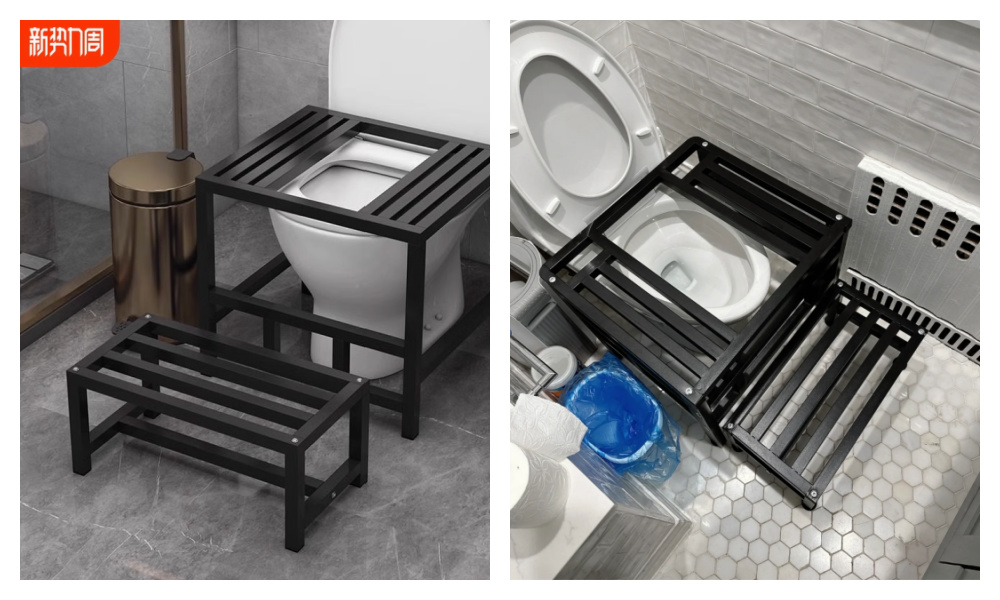

The Taobao solution.
For Chinese malls, offering these might be cheaper than dealing with broken toilets and the never-ending battle against footprints on toilet seats…
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
References:
Ali, Wajid, Dong-zi An, Ya-fei Yang, Bei-bei Cui, Jia-xin Ma, Hao Zhu, Ming Li, Xiao-Jun Ai, and Cheng Yan. 2022. “Comparing Bioaerosol Emission after Flushing in Squat and Bidet Toilets: Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment for Defecation and Hand Washing Postures.” Building and Environment 221: 109284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109284.
Bhattacharya, Sudip, Vijay Kumar Chattu, and Amarjeet Singh. 2019. “Health Promotion and Prevention of Bowel Disorders Through Toilet Designs: A Myth or Reality?” Journal of Education and Health Promotion 8 (40). https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_198_18.
Cao, Jingrui 曹晶瑞, and Tian Jiexiong 田杰雄. 2025. “城市微调查|商场女卫生间,坐厕为何频频变“蹲坑”? [In Shopping Mall Women’s Restrooms, Why Do Sitting Toilets Frequently Turn into ‘Squat Toilets’?]” Beijing News, March 20. https://weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309405146044773302810. Accessed March 19, 2025.
Cheng, Shikun, Zifu Li, Sayed Mohammad Nazim Uddin, Heinz-Peter Mang, Xiaoqin Zhou, Jian Zhang, Lei Zheng, and Lingling Zhang. 2018. “Toilet Revolution in China.” Journal of Environmental Management 216: 347–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.043.
Dai, Wangyun. 2018. “Seats, Squats, and Leaves: A Brief History of Chinese Toilets.” Sixth Tone, January 13. https://www.sixthtone.com/news/1001550. Accessed March 22, 2025.
Li, Jinzao. 2015. “Toilet Revolution for Tourism Evolution.” China Daily, April 7. https://europe.chinadaily.com.cn/opinion/2015-04/07/content_20012249_2.htm. Accessed March 22, 2025.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Insight
US-Russia Rapprochement and “Saint Zelensky”: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Shake-Up
From shifting sentiments on Zelensky to a renewed focus on Taiwan, recent geopolitical developments have sparked noteworthy takes from Chinese online commentators.
Published
3 weeks agoon
March 9, 2025
As the Russia-Ukraine war enters its fourth year, Chinese social media is once again flooded with discussions about the geopolitical shifts triggered by Trump’s policies. From the Oval Office clash to Trump’s ‘pivot’ to Russia, this article explores how Chinese netizens are interpreting the rapidly changing geopolitical landscape.
Three years ago, when the Russia-Ukraine war first broke out, one particular word went trending on Chinese social media: wūxīn gōngzuò (乌心工作). The term was a wordplay on the term wúxīn gōngzuò (无心工作), meaning not being in the mood to work, and it basically meant that people were too focused on Ukraine to concentrate on work.
Although that word has since faded from use online, recent geopolitical developments surrounding the Russia-Ukraine war have once again drawn considerable attention on Chinese social media, where trending word data tools show that “Trump” and “Zelensky” are among the hottest buzzwords of the moment.

Trump Zelensky, Ne Zha, Lei Jun; biggest words of interest on, among others, Weibo, on March 4, 2025.
Trump’s recent rhetoric toward Russia, his remarks about Ukraine, and his attitude toward NATO not only mark a shift from Biden and decades of US policy, but also reshuffle the geopolitical cards and raise questions about the future of the postwar international order.
Where does China stand in all this?
➜ Although China’s online environment is tightly controlled, particularly regarding political discussions, what stands out in conversations around the recent developments involving Trump, Putin, and Zelensky is a widespread sentiment that — at its core — it’s all about China.
Many believe that China’s rise on the global stage, and the resulting US-China rivalry, are key forces shaping US strategy toward Russia as well.
Woven into these discussions are US-China trade tensions, with Trump increasing tariffs by 10% on February 1, and then doubling the tariff on all Chinese imports to 20% from 10% on March 4. This immediately prompted China to retaliate with 10-15% tariffs on US agricultural products, effective March 10.
Currently, developments are unfolding so rapidly that one hashtag after another is appearing on Chinese social media. “It’s not that I don’t understand, it’s just that the world is changing so quickly,” one Weibo blogger commented, referencing a famous song by Cui Jian (“不是我不明白,是这世界变化快”).
Amid this whirlwind of events, let’s take a closer look at the current Chinese online discourse surrounding the Russia-Ukraine war, with a focus on shifting attitudes toward Zelensky and US-Russian relations.
THE OVAL OFFICE INCIDENT
“Saint Zelensky is a real man!”
One major moment in the recent developments has been the clash between Zelensky, Trump, and US Vice President JD Vance in the White House Oval Office on February 28.
Zelensky had come to the White House to discuss the US’s continued support against Russia and a potential deal involving Ukraine’s rare earth minerals, but it ended in a heated confrontation during which, among others, Zelensky questioned Vance’s notion of “diplomacy” with Putin, and Trump and Vance expressing frustration with what they perceived as Zelensky’s ingratitude for US support.
On Chinese social media, the clash between Zelensky, Trump, and Vance in the Oval Office seemingly caused a shift in public views towards Zelensky and the position of Ukraine. Some commentators who are known to usually take a pro-Russian stance were suddenly positive about Zelensky.
“Zelensky is really awesome, he had a confrontation with Putin’s two top negotiators in the Oval Office and still managed to hold his own,” historian Zhang Hongjie (@张宏杰) jokingly wrote on Weibo.
Others compared compared Trump and Vance to “two dogs barking” at Zelensky, and saw the meeting as one that was meant to humiliate Zelensky.
Nationalist blogging account “A Bad Potato” (一个坏土豆, 335k+ followers) admitted: “I’ll lay my cards on the table: I fully support Zelensky.”
He further wrote:
💬 “Let’s not make any illusions. Trump’s ultimate target is China. (..). He’s already added two rounds of 10% tariffs on China. Isn’t it obvious? Did you think he is pulling closer to Russia for some big China-Russia-America unification? Once he’s done dealing with his internal problems, he’ll inevitably come at China with full force. There are some people here who are hoping for Zelensky to kneel before the US, and I’d like to ask these people: Whose side are you on? Are you on the Russian or American side? When Zelensky’s firm towards the US, of course I’ll support him. His performance was so perfect that I’d like to call him Saint Zelensky!
(..) Some say Zelensky’s betraying his country. So what if he is? As long as he’s not selling out China, he can sell out the whole world for all I care. Just look at the stupid and bad Macron, or Starmer who’s full of sneaky tricks, they’re getting humiliated by Trump in all kinds of ways. Then look at Zelensky again and let me shout: Saint Zelensky is a real man! He’s a tough guy! Of course, I’m keeping it balanced here—I support Russia too. Both sides must make an effort.”
➜ Although there is some pragmatism in this ‘pro-Zelensky’ shift, which is Sino-centric and mostly based on which actors in the political game are considered antagonists of China, there is also another level of sympathy towards Zelensky as the underdog in this situation — facing a 2-against-1 dynamic on unfamiliar terrain, while speaking a language that is not his.
Weibo user “Uncle Bull” (@牛叔, 820k followers) wrote:
💬 “The arguing scene in the Oval Office should be a reminder for every politician that it doesn’t matter how well you speak English, when it’s a formal occasion, you should always speak your native language and have a translator with you— it helps avoid a lot of direct confrontations.”
In his analysis of the situation, well-known political commentator Chairman Rabbit (兔主席) took a far more critical stance towards Zelensky, suggesting that his confrontational attitude in the Oval Office was misplaced and driven by personal pride, and that his actions in the White House caused it to be “the most disastrous trip in history.”
Chairman Rabbit also commented:
💬 “There is an ancient Chinese saying: “A man of character can bow or stand tall as required [大丈夫能屈能伸].” When it comes to major issues like the survival of the nation, things like some dignity and righteousness and principles all are meaningless. When facing Trump, you just have to flatter and appease him. If Zelensky is unable to humble himself, then he’s probably not suited for this job. It’s just as the most pro-Ukraine Republican senator, Senator Lindsey Graham, said – he suggests that Zelensky should step down, and Ukraine should find someone else to negotiate.”
But there are many netizens who do not agree with him, like this popular comment saying: “Whatever you do, don’t kneel [to Trump] — you’re a spiritual totem (精神图腾) for so many people on Weibo.”
TRUMP’S ‘PIVOT’ TO RUSSIA
“The US-Russia honeymoon has begun”
When US and Russian delegates sat down in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, on February 18 to discuss improving Russia-US relations and ending the war in Ukraine—without Europe or Ukraine at the table—Chinese netizens pointed out that there were no plates on the table, joking that “Europe and Ukraine are what’s on the menu.”
They referred to a comment previously made by US Secretary of State Antony Blinken when replying to a question about US-China tensions leading to greater fragmentation: “If you’re not at the table in the international system, you’re going to be on the menu.”
The official Chinese response to the developments, as stated by Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Guo Jiakun (郭嘉昆), is that China is glad to see any efforts that contribute to peace, including any consensus reached between the US and Russia through negotiations (#中方回应俄美代表团举行会晤#).
Among social media users, there was banter about the sudden US-Russia rapprochement, after news came out that the two countries intend to cooperate on various matters concerning their shared geopolitical interests (#俄美决定未来将在多领域合作#).
“The US-Russian honeymoon has begun [美俄蜜月开始]!” some commenters concluded.
“It won’t last more than four years,” others predicted.
Some suggested it might be an opportunity for China and Europe to draw closer: “China and Europe will also cooperate on various matters.”
Regarding Putin agreeing to assist in US-Iran talks (#美媒爆普京同意协助美促成与伊朗核谈判#), reactions were cautiously optimistic: “It’s hard to find an American president seeking peace as much as Trump is,” one Weibo user wrote. Another added: “He might be pursuing ‘America First,’ but his efforts for peace deserve some acknowledgement. I hope it’s true.”
➜ Outside of China, analysts and commentators have argued that a US-Russia rapprochement could be bad for China, suggesting it might undermine the close strategic partnership between China and Russia. However, this sentiment seems less pronounced on Chinese social media, where many argue US-Russian relations are bound to be fickle, while others echo the official stance.
The official response to such concerns, as stated by Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson Lin Jian (林剑), is that the China-Russia bilateral relationship “will not be affected by any third party”:
💬 “Both China and Russia have long-term development strategies and foreign policies. No matter how the international landscape changes, our relationship will move forward at its own pace. The US attempt to sow discord between China and Russia is doomed to fail.”
Another perspective comes from Chinese political scientist and commentator Zheng Yongnian (郑永年), in a recent interview with Xiakedao (@侠客岛), a popular commentary account from People’s Daily Overseas Edition.
Zheng noted that the US-Russia shift is not surprising—considering, among other things, Trump’s previous comments about his good relationship with Putin—but that it places Ukraine and Europe in an unfavorable position.
➜ Like other commentators, Zheng suggests that Trump’s strategy to improve ties with Russia is also linked to gaining leverage over China. However, he does not necessarily view it as a direct revival of Kissinger’s famous Cold War-era strategy, which aimed to align with China to counter the Soviet Union. In this case, it would be reversed: allying with Russia to counter China (“联俄抗中”). In Trump’s view, Zheng argues, Europe doesn’t matter, and Ukraine is insignificant. Russia is the key to maximizing US interests.
➜ Like others—and in contrast to some foreign analyses—Zheng does not see the U.S.-Russia rapprochement as necessarily harmful to China. Instead, he suggests that right-wing, pragmatic partners may ultimately be more beneficial to China than left-wing ideological ones, stating:
💬 “When it comes to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the previous Biden administration continuously tried to frame China, attempting to shift the blame onto China. So now, after the US and Russian leaders spoke, the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs responded by saying they are ‘pleased to see all efforts working for peace, including Russia and the US coming to a common understanding that will lead to peace.’ China won’t meddle in another country’s internal affairs. No matter who’s in power, we will engage with them. China can indeed take a relatively neutral stance.
In the past, we said, ‘It’s easier to deal with the right-wing in the West.’ Why? Because the political right is less hypocritical; they value interests, and interests can be exchanged. Some Western left-wing factions, however, cling to ideological patterns, labeling and defining you, making exchange and interaction impossible.”
SHARPENED FOCUS ON TAIWAN
“Ever since Trump came to power and betrayed Ukraine, the rhetoric towards Taiwan has become increasingly tough”
Although there may be mixed views and different analyses, one thing is certain: Trump’s strategies are shaking things up from how they used to be.
➜ One thing that doesn’t change in rapidly changing times, is an overall anti-American sentiment on Chinese social media.
Even though some commenters appreciate Trump’s pragmatism or are entertained by the spectacle of US politics from the sidelines, there remains a strong belief that US strategies are ultimately aimed against China. This reinforces anti-American sentiments and fuels discussions about a potential US-China conflict.
This is especially tangible at a time when the US government has once again raised tariffs on Chinese imports.
“If war is what the U.S. wants—be it a tariff war, a trade war, or any other type of war—we’re ready to fight till the end,” China’s embassy in Washington posted on X, reiterating a government statement from Tuesday.
During the Two Sessions on March 7, Foreign Minister Wang Yi (王毅) also commented on US-China relations, stating:
💬 “No country should harbor the illusion that it can suppress and contain China on one hand while seeking to develop a good relationships with China on the other. Such two-faced behavior [两面人] is not only detrimental to the stability of bilateral relations and cannot build mutual trust.”
➜ Against this backdrop, the Taiwan issue has once again come into sharp focus.
This is partly driven by the two Two Sessions (March 5-11), China’s annual gathering of the National People’s Congress (NPC) and the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC). This is not just a major political event but also a key moment for propaganda and political messaging.
But it is mostly linked to the broader, rapidly changing geopolitical sphere and Trump’s shifting stance on Russia and Ukraine. The narrative of US power politics failing to change the course of a China-Taiwan “reunification” is surfacing again precisely because of Trump’s reshuffling of alliances.
Since the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, Chinese social media users have frequently drawn comparisons between Taiwan and Ukraine. The phrase “Today’s Ukraine, tomorrow’s Taiwan?” gained traction at the time, as online commenters saw Ukraine’s rapid invasion as a cautionary tale for Taiwan, highlighting how quickly the situation could change. A viral meme from that period depicted a pig labeled “Taiwan” watching another pig, “Ukraine,” being slaughtered.
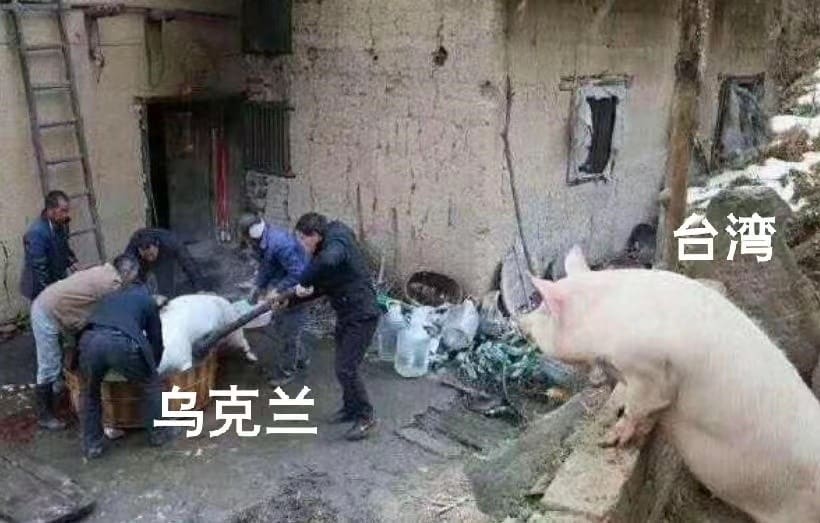

A meme circulating on social media in 2022 showing a pig “Taiwan” watching the slaughtering of another pig “Ukraine.”
This week, Chinese state media launched a large-scale social media propaganda campaign using strong language and clear visuals to reinforce the narrative that Taiwan is not a country, that it is part of China, and that reunification is inevitable.

Such rhetoric has appeared before, with similar peaks in Taiwan propaganda dating back to at least 2022. The topic of Taiwan has often been amplified during key political events, such as the 20th Party Congress and Xi Jinping’s speech in October 2022.
“Have you noticed?,” Weibo author Yangeisaibei (@雁归塞北) wrote: “Ever since Trump came to power and sold out Ukraine, the rhetoric towards Taiwan has become increasingly tough, the tones become more stern, and the words more straightforward.”
According to prominent Weibo blogger @前HR本人, who has over two million followers, the Taiwan issue is now more important than before.
💬 “When it comes to foreign struggles, resolving the Taiwan issue is China’s top priority. Judging from the Chinese Embassy in Washington declaring “We are not afraid of any kind of war with the US”, it seems we are already preparing to reunify Taiwan at any moment.”
Another Weibo blogger (@王江雨Law, 419k fans) wrote:
💬 “Now that all kinds of big and smaller developments are changing the [political] climate, especially if America’s strong territorial expansion claims turn into concrete actions, this could trigger synchronous reactions, greatly increasing the possibility of resolving the Taiwan issue within a few years. We need to rethink the previous view that the mainland is not in a hurry on this matter.”
What emerges from these discussions is that Chinese online discourse on the Russia-Ukraine war and US foreign policy is primarily centered around two key ideas:
🔸 The belief that China is ultimately at the core of US geopolitical strategies in its dealings with Russia.
🔸 A pragmatic, Sino-centric view in which support or opposition to leaders like Trump, Putin, or Zelensky shifts depending on what serves China’s interests best.
Rather than seeing the conflict in black-and-white terms, many Chinese netizens approach it as a dynamic political chess game, one in which China should play a smart and confident strategy.
Politics-focused blogger Mingshuzhatan (@明叔杂谈, 137k followers) wrote:
💬 “In the process of this game against US, we must respect them in tactics, and contempt them in strategy [战术上重视、战略上藐视] – stay patient and confident. Trump is currently going against the tide, he’s being destructive. But actually, this recklessness is damaging US credibility and its global influence, it will accelerate the decline of American hegemony. A silent majority of countries in the international community harbor growing resentment and disappointment toward the US, and when these sentiments reach a tipping point, America will truly experience the pain of “un unjust cause draws little support” [失道寡助]. China, on the other hand, although also facing some challenges, focuses on science and technological and industrial innovation. That’s the right path for China’s long-term stability, prosperity, and security. In the China-US competition, it is becoming increasingly evident that time is on China’s side.”
This perspective reflects a dominant theme across Chinese online discussions: No matter how intense the geopolitical shifts may be, or how much the US reshuffles its global strategy, China remains on its course and is playing the long game.🔚
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

How K-pop Fans and the 13-Year-Old Daughter of Baidu VP Sparked a Debate on Online Privacy

Squat or Sit? China’s Great Toilet Debate and the Problem of Footprints on the Seat

Weibo Watch: The Great Squat vs Sitting Toilet Debate in China🧻
Chinese Netizens Turn to Tim Cook Over Battery Factory’s Illegal Overtime

Revisiting China’s Most Viral Resignation Letter: “The World Is So Big, I Want to Go and See It”

Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: Christmas in China Is Everywhere and Nowhere

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua

“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music12 months ago
China Music12 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments







