Chinese Language
“Offensive to Chinese Language” – USC Controversy over Chinese Filler Word 那个 (Nèigè) Discussed on Weibo
Weibo users discuss how a professor at the University of Southern California was temporarily suspended for using Chinese filler word ‘nage.’
Published
5 years agoon
In English it’s “uuh”, in Dutch it’s “ehm”, the French say “euh”, in Japan it’s “eto”, and in Mandarin Chinese it’s “nàge” (or “nèige” 那个). Every language has different filler words and hesitation markers that are used as a natural pause or stalling in speech.
The Chinese nàge recently received much more attention in western media than filler words usually get, when an American professor was suspended by the Marshall School of Business (University of Southern California) for saying “nàge” while teaching an online communications class. Students took offense because they thought the Chinese word sounded like the English n-word.
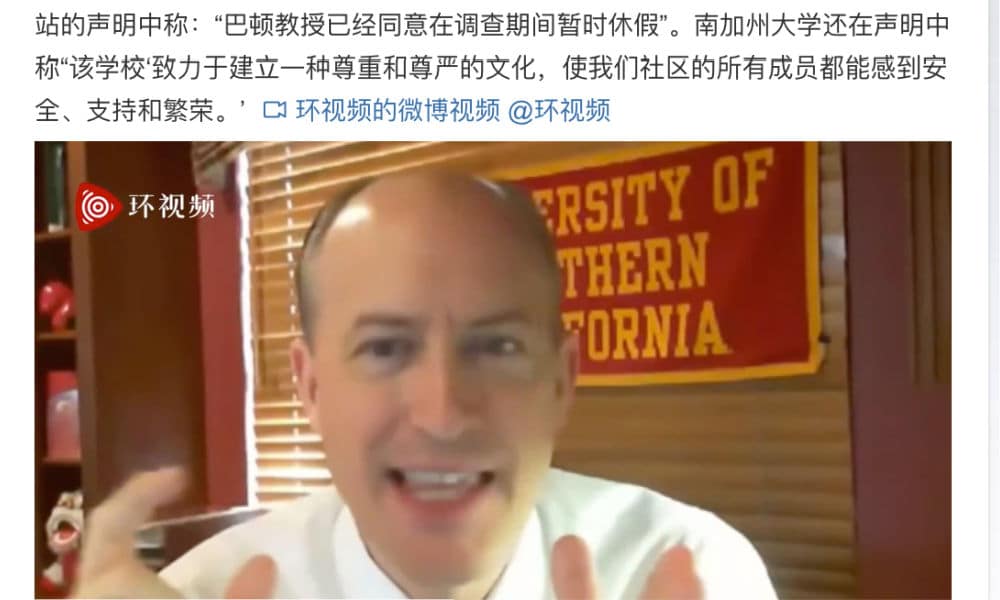
Greg Patton, a Professor of Clinical Business Communication, was teaching his online class via Zoom on August 20 when explaining the Chinese filler word nàge”/”nèige” (那个).
According to the Los Angeles Times, students complained that the words he used “sounded like a racial slur” and “harmed their mental health.”
I cannot believe this is real, but it is.
This USC Professor is on leave after students were offended that a Chinese word he used during a lecture on foreign languages sounded like an english racial slur.
Watch the video for yourself: pic.twitter.com/HkFPMEP5I2
— Cabot Phillips (@cabot_phillips) September 3, 2020
Following the class, Patton’s students wrote a letter to the USC Marshall dean in which they stated they blamed the incident for no longer being able to focus on their studies, saying their professor “lacks the tact, racial awareness and empathy to lead and teach an audience as diverse as ours” and that it would be “unacceptable” to expect the students to sit through two more weeks of his class.
In an email to all MBA students on August 24, the USC Marshall dean apologized that the class led to “great pain and upset among students,” also stating that Patton “agreed to take a short-term pause” from teaching the course while another instructor took over.
“These students are discriminating against the Chinese language“
News of the incident blew over to Chinese social media this week, where it was discussed under hashtags such as “US Professor Suspended for Saying Chinese Word Nage” (#美国教授课上说中文词那个被停课#, 1.4 million views) and “US Professor Saying the Chinese Nage Suspended over Racism” (#美国大学教授说中文词那个因种族歧视被停课#, 7.5 million views).
On Weibo, netizens had little sympathy for the students feeling offended over the Chinese words. Many called them “ignorant” or “uncultured” for mistaking the Chinese words for a racial slur.
Although there are many Weibo users who think the controversy is laughable, there are also some who are shocked and surprised that this incident actually took place, and some taking offense over the controversy – seeing it as an insult to the Chinese language.
“These students are discriminating against the Chinese language,” several people wrote, calling it “offensive to Chinese”, with others saying: “So English is higher in rank than Chinese? The pronunciation is similar, but why is it the English [meaning] that is superior here?”
“I can’t believe this is real life,” another popular comment said.
This is not the first time for ‘nèige‘ to receive attention. A well-known skit by comedian Russell Peters also mentions how ‘nèige’ sounds like the n-word, and there are many Quora posts dedicated to the word.
On Weibo, various commenters mention the song “Sunshine, Rainbow, White Pony” by Da Zhang Wei (大张伟), aka Wowkie Zhang, of which the catchy chorus also repeats a Chinese nèige word (meaning “in that”) (see video below).
The song from 2018, that has over four million views on Youtube, also has thousands of comments underneath suggesting that the singer is singing the n-word.
“Da Zhang Wei would be killed if he would sing this in the US,” one Weibo commenter wrote.
Also read: “Fake” and “Hypocritical” – Western Anti-Racism Movements Criticized on Weibo
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
Follow @WhatsOnWeibo
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2020 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China Memes & Viral
Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained
From quirky potatoes to low-key vibes, we uncover 10 buzzwords that shaped China’s cultural and social landscape in 2024.
Published
3 months agoon
December 31, 2024
From ‘Chillax’ to ‘Digital Ibuprofen,’ this compilation of ten Chinese buzzwords and catchphrases by What’s on Weibo reflects social trends and the changing times in China in 2024.
At the end of each year, Chinese media outlets compile lists of the most impactful buzzwords that shaped public discourse. The most popular new words and expressions are generally listed by the Chinese linguistics magazine Yǎowén Jiáozì (咬文嚼字), which selects ten noteworthy buzzwords (十大流行语).
If you want to know more about the buzzwords that made it to Chinese official media’s lists this year, check out this post by Andrew Methven at RealTime Mandarin which is a top ten compilation of Chinese buzzwords of 2024 based on these lists.
Here, we’ve curated a different list: a special What’s on Weibo top 10 of buzzwords and catchphrases from 2024. Each term reflects a broader trend, which we’ll explore in this article. Many of these words were previously featured in our premium Weibo Watch newsletter, where we highlight a word of the week in every issue. (Subscribe to get our newsletter).
These words are not in order of popularity, but rather in order of appearance throughout the year.
#1: SOUTHERN LITTLE POTATOES

Nánfāng xiǎo tǔdòu (南方小土豆)
The term “Southern Little Potatoes” (南方小土豆) became all the rage in early 2024 in the context of the travel hype surrounding Harbin, which saw a huge influx of tourists from the warmer southern regions who came to the snow-blanketed city or other destinations in the Three Northeastern Provinces (东北三省: Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning).
The southern tourists were soon nicknamed “Southern Little Potatoes.” While visiting China’s cold northeast, they tend to stand out due to their smaller stature, light-colored down jackets, and brand-new winter hats. Their appearance not only contrasts with that of the typically taller and darker-dressed locals, but some people also think it makes them look like “little potatoes.” After the endearing term “Southern Little Potato” became popular due to a viral video, some southern tourists, especially women, also adopted this term to humorously describe themselves.

Very soon after it caught on, locals started using “Southern Little Potatoes” as a humorous marketing strategy to attract more southern visitors. Harbin street vendors began selling plush keychains of “Southern Little Potatoes,” and even local taxis invited the “baby potatoes” to get on board (“土豆宝宝请上车”).
Through jokes, memes, and media stories about these “potatoes,” a narrative came to life about the city of Harbin taking care of and pampering these “naive,” “little” visitors. Although the term is meant to be affectionate, some took offense, suggesting that since it predominantly refers to smaller women, it is actually sexist and reinforces stereotypical perceptions of southern Chinese women. While some critical bloggers argue that the term is harmful and derogatory, the majority of netizens continue to use it for light-hearted banter about the enthusiasm of southern visitors and the hospitality of the northerners welcoming them.
#2: SPRING MOUNTAIN STUDIES

Chūn Shān Xué (春山学)
“Spring Mountain Studies,” or “Chunshan Studies” (春山学), became a viral phenomenon on the Chinese internet following the CMG Spring Festival Gala earlier this year. It was the buzz of the show, capturing widespread attention and sparking heated debates. The phrase “Chunshan Studies” arose from the controversy surrounding the performance by Bai Jingting (白敬亭), Wei Chen (魏晨), and Wei Daxun (魏大勋).
Popular actor and singer Bai Jingting, alongside co-performers Wei Chen and Wei Daxun, performed the song “Going Up Spring Mountain” (上春山). While the song itself wasn’t particularly remarkable at first glance, it quickly became the center of attention due to the staging arrangement: the three singers were positioned on a tiered platform representing a mountain, with Bai standing on the highest pedestal.

Controversy arose when Bai remained on the top pedestal after his part, seemingly blocking Wei Daxun from taking the higher position. As a result, Wei performed from a lower step, creating choreographic asymmetry and apparent confusion on stage. Speculation grew that Bai may have intentionally stayed in the prominent position to draw more attention.
Adding to the rumors was Bai’s choice of attire—he wore all black, while Wei Chen and Wei Daxun were dressed in white. Netizens suggested this made him stand out even more. Rehearsal footage posted online fueled these suspicions. In one rehearsal video, Bai stepped down after his part as expected and wore white like the others. This led to accusations that he deliberately changed his outfit and position during the live performance to ensure he stayed at the center of attention.
The timing of these changes also raised eyebrows. Since the Spring Festival Gala is a live event, but typically runs a recorded dress rehearsal alongside the live broadcast for contingency purposes, any significant alterations to staging or wardrobe would prevent producers from seamlessly switching to the pre-recorded version. Critics argued that Bai’s supposed changes sabotaged this fallback option, leaving producers unable to correct the perceived imbalance.
The controversy ignited widespread criticism of Bai Jingting, with detractors accusing him of selfishness and poor character. Social media erupted with debates, and the term “Chunshan Studies” was coined humorously to describe the detailed analysis and theories surrounding the incident.
Online communities, particularly on platforms like Douyin and Bilibili, became hubs of “Chunshan Studies,” as netizens scrutinized every detail of the performance. Videos dissecting wardrobe choices, body language, and stage movements frame by frame went viral. What began as speculation about Bai’s intent turned into a pseudo-academic field, blending elements of popular culture analysis, media discourse, and social studies.
Some commentators argued that the discussion reflected deeper issues about equity and ethical behavior in the entertainment industry, elevating the controversy beyond a simple song performance. Who would have thought that a single performance of “Going Up Spring Mountain” could spark such an intellectual and cultural phenomenon?
#3: MELLOW PEOPLE

Dàn rén (淡人)
“Mellow People” (淡人) is a term that emerged in 2024 to describe the mental state of young people in China today. The word dàn 淡, which I’ve translated as ‘mellow’ in this context, carries a range of meanings in Chinese: it can imply lightness, calmness, indifference, paleness, or even triviality.
To be a dàn individual, a dànrén 淡人, has become a way for young people to express how they navigate life. They might want to quit their uninspiring job, but it pays the bills—so it’s okay. They endure hours of commuting every day because the rent is cheaper—so it’s okay. They’re pushed into blind dates by their parents, even though they’d rather not go, but they lack the energy to resist—so it’s okay.
Being ‘mellow’ or ‘unperturbed’ means remaining indifferent in a calm, lighthearted way. Similar to earlier Chinese popular expressions like “lying flat” (躺平) or being “Buddha-like” (佛系), it’s a way of coping with the pressures and challenges of modern life. However, it’s slightly more optimistic than outright passivity (like lying flat): it reflects a passive acceptance of life as it is, embracing the monotony of daily routines and competitive work environments without resistance.
The concept of being a dànrén has even developed into its own pseudo-discipline, referred to as 淡人学 dànrén xué, which might be translated as ‘Mellowism’ or, perhaps more aptly, ‘Unperturbabilism.’
#4: “BACK TO THE ROOT”

Dāngguī (当归)
The term dāngguī 当归, freely translated as “back to the root,” came up this year in the context of the propaganda campaign surrounding reunification with Taiwan. Since earlier in 2024, dāngguī is used by Chinese state media in the slogan “Táiwān dāngguī” (#台湾当归#), which means “Taiwan must return [to the motherland].” Separately, the two characters in dāngguī 当归 literally mean “should return.”
However, the slogan is a play on words, as the term dāngguī (当归) as a noun actually means Angelica Sinensis, the Chinese Angelica root or ‘female ginseng,’ a medicinal herb commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine, native to China and cultivated in various East Asian countries.

Poster by People’s Daily. ‘Taiwan’ on the left side resembles a piece of ‘female ginseng’.
This play on words is also evident in the poster disseminated by People’s Daily, where Taiwan is depicted on the left and resembles a piece of the yellowish ‘female ginseng’ root. It is part of the character “归” (guī, to return, go back to). The remainder of the character consists of various slogans commonly used by Chinese official media to emphasize that Taiwan is part of China.
Because of this context, where dāngguī 当归 both refers to the discourse of Taiwan returning to China and to the female ginseng root, a creative translation would be “back to the root.” If you want to be less creative, you could also say it’s the Taiwan “should return” campaign.
#5: CHILLAX

Sōngchígǎn (松弛感)
In recent years, the pursuit of a certain “relaxed feeling” has gained popularity across the Chinese internet. Sōngchígǎn is a combination of the word for “relaxed,” “loose” or “lax” (松弛) and the word for “feeling” (感). Initially used to describe a particular female aesthetic, the term evolved to represent a lifestyle where individuals strive to maintain a relaxed demeanor, especially in the face of stressful situations.
The concept gained traction online in mid-2022 when a Weibo user shared a story of a family remaining composed when their travel plans were unexpectedly disrupted due to passport issues. Their calm and collected response inspired the adoption of the “relaxed feeling” term (also read here). Central to embodying this sense of relaxation is being unfazed by others’ opinions and avoiding unnecessary stress or haste out of fear of judgment. Nowadays, Chinese cities aim to foster this sense of sōngchígǎn. Not too long ago, there were many hot topics suggesting that Chengdu is the most sōngchí 松弛, the most relaxed city in China. This sentiment was further reinforced in 2024 when ‘Chengdu Disney’ emerged as a quirky new hotspot (read here).
As for individuals, the most sōngchígǎn person of the year was undoubtedly Olympic athlete Quan Hongchan (全红婵). The young springboard diver from Guangdong became a multi-medalist at the Paris Olympics, going viral for her quirkiness and authenticity. Chinese netizens describe her as “being Guangdong-style relaxed” (“广式”松弛感), not just for her unique sense of style (she loves her “ugly fish slippers”), but for her ability to remain chill while dozens of cameras focus on her.
#6: STRONG STEALTH VIBE

Tōugǎn hěn zhòng (偷感很重)
It’s that moment when you see someone you know and pretend to be busy on your phone to avoid social interaction. Or when someone takes a group picture and you’re unsure how to pose. Or when all eyes are on you and you wish for an invisible cloak.
In 2024, the term “tōugǎn” (偷感) emerged on Chinese social media. Tōugǎn (偷感) literally translates to “stealth sense” or “secret feeling,” but we can interpret it as an overall vibe of being “under-the-radar.” The phrase “tōugǎn hěn zhòng” (偷感很重) means “the stealth sense is strong,” and can be used to describe someone as being “very under-the-radar” or having “a strong stealth vibe.”
The exact origin of this term is unclear, but it likely first appeared on Xiaohongshu in response to a videoclip by the South Korean girl group Le Sserafim for their single “Easy,” where they sing and dance effortlessly with some low-key dance moves.
Tōugǎn (偷感) is used by and resonates with China’s Gen Z to express a common feeling in their daily lives, where they prefer to go about things quietly and low-key, avoiding too much attention. They can still be smooth and effortless, but out of fear of embarrassment or judgment, they do so in a subtle and low-profile manner. They won’t flaunt their achievements, but wait for others to notice them. Unlike earlier internet buzzwords where young people mock themselves, tōugǎn is not negative – it’s a bit tongue-in-cheek and a way for people to connect over their inner worlds that aren’t visible to others.
#7: CITY BU CITY

City不City啊
The phrase ‘City bu City a’ (City不City啊), translated as “City or not?”, took the Chinese internet by storm in the summer of 2024. The phrase became popular thanks to American influencer Paul Mike Ashton, nicknamed “Bao Bao Xiong” (保保熊, Baby Bear), who runs a Chinese-language account on Douyin. On his channel, Ashton shares humorous snippets about his life in China, where he works as an entertainer and tour guide.
In one video from April this year, Ashton posted a clip in which he cycles through the city like a Shanghai ‘city girl’ who often mixes Chinese and English words, calling himself “very city” (“我是好city”). He says: “I’m so city, a city girl. It’s so cool, breezy. Life in the city is so good, I feel so free.” Ashton later began incorporating this phrase more frequently in his humorous videos, sometimes also involving his sister.

Walking on the Shanghai Bund, the brother and sister describe Shanghai as “so city” (“好city啊”). While walking on the Great Wall, Bao Bao asks his sister if it’s “city or not” (it’s not). In other videos in which the two are traveling throug China, Ashton repeatedly asks his younger sister if certain things are “city or not,” to which she usually responds humorously: “It’s very city.” In this context, “city” has evolved from a noun into a quirky adjective, describing something that embodies the essence of urban life; something that is ‘city’ is metropolitan, lively, and modern. It’s very tongue-in-cheek and also serves as a playful commentary on how young Chinese people often mix Chinese and English words to sound more sophisticated and trendy.
This phenomenon sparked the ‘city or not’ meme, which even reached the Foreign Ministry this week when spokesperson Mao Ning was asked about it. She responded that she had heard about the new use of the phrase and that it is a positive sign of foreigners enjoying life in China. Chinese authorities and state media have also jumped on this trend to promote tourism. The meme has been imitated and adapted by various local tourism departments. Ashton himself has encouraged foreigners to come and experience Chinese culture (and its very ‘city’ city life), further boosting its popularity. By now, the phrase has become ingrained in China’s digital culture.
#8: FAN CULTURED

Fànquānhuà (饭圈化)
Around the time of the Olympics and the skyrocketing popularity of Chinese table tennis players, the word ‘fan-cultured’ or ‘fandom-ization’ (fànquānhuà 饭圈化) became increasingly popular in 2024. While fànquān 饭圈 literally means “fan circle,” the suffix huà 化 is generally used to indicate a process of transformation or turning into something, similar to the “-ization” suffix in English.
The term fànquānhuà 饭圈化 refers to the recently much-discussed phenomenon where something—often outside the realms of entertainment—receives passionate support from people who begin to form online fan circles around it, changing the dynamics in ways that resemble the relationships between celebrity idols and their fans.
This year, it became clear how Chinese fans started to form extremely strong communities around China’s table tennis stars, defending them as if they were idols. This fan behavior was harshly criticized by Chinese authorities this year, as they see it as toxic fan culture that goes against the Olympic spirit (read more).
However, “fandom-ization” extends beyond sports. For instance, Chinese pandas have similarly strong fan club dynamics. Even inanimate objects can become “fan-cultured.” A notable example is the Little Forklift Truck (小叉车) that played a role in constructing the Huoshenshan emergency specialty field hospital during the early days of the Covid crisis.

The construction process was live-streamed, and millions of viewers found the hardworking little truck so cute and brave that it too became “fan-cultured.”
#9: RUSHING TO COUNTY-LEVEL TOWNS

Bèn xiàn (奔县)
The term “rushing to the county,” bèn xiàn (奔县), surged in Chinese media after the 2024 National Day holiday. This time, the peak travel period saw increased popularity for lesser-known county-level towns instead of large cities or famous tourist destinations. According to travel industry reports following the week-long holiday, bookings significantly increased compared to 2023, which was already a notably crowded year.
In 2024, 765 million trips were taken nationwide, marking a 10.2% increase compared to pre-pandemic 2019. In 2023, ‘domestic travel’ was the key trend, with the so-called “special forces travel” (tè zhǒng bīng lǚxíng 特种兵旅游) becoming popular among Chinese youth. That trend focused on visiting as many places as possible at the lowest cost within a limited time, often involving incredibly tight schedules and 12-hour travel days.
In 2024, the focus shifted to a more relaxed and cost-effective approach, turning county-level tourism (bèn xiàn yóu 奔县游) into a new trend. People are no longer just visiting county-level towns to see family; more young travelers from China’s major cities are exploring nearby smaller towns for “micro-holidays” (wēi dùjià 微度假).
County-level towns in China are smaller than major cities like Beijing or Shanghai but are still large enough to offer plenty to do, as they serve as important hubs for the surrounding rural areas. In these county-level destinations, the cost of hotels and meals tends to be much cheaper than in popular tourist hotspots. Staying closer to home also reduces travel time and expenses while offering the chance to visit lesser-known locations and avoid peak tourist crowds.
According to The Observer, during the 2024 National Holiday, places like Jiuzhaigou, Anji, Shangri-La, Pingtan, Dujiangyan, and Jinghong saw booking increases of 109%, 86%, 74%, 67%, 51%, and 50%, respectively.
#10: DIGITAL IBUPROFEN

Diànzǐ bùluòfēn (电子布洛芬)
The term “Digital Ibuprofen” or “Electronic Ibuprofen” came up this year when fans told Chinese actor and singer Tan Jianci (檀健次) that he is their “digital ibuprofen.” Tan, with a puzzled look, asked what that meant. A fan explained, “It means we feel better when we see you” (or, essentially, “our bodies feel no pain”). Since then, Tan Jianci has become associated with the term “digital ibuprofen.”
The term has been around for some time, gaining popularity in 2022-2023 among fans of entertainment shows. It refers to content that provides relief from stress or discomfort, much like how ibuprofen alleviates physical pain. For instance, the Hunan TV show Go for Happiness (快乐再出发) is often called “digital ibuprofen.”
The term saw a surge in popularity alongside the Japanese animated series Chiikawa, which became a viral hit among young people. The anime’s portrayal of its cute character staying optimistic despite life’s stresses earned Chiikawa the nickname “digital ibuprofen,” as fans found comfort in its stories (read more in this story by Sixth Tone).
“Digital ibuprofen” applies to more than just shows—it can be any content, such as videos, memes, or idols, that provides comfort, distraction, and relief to fans. In the same category, there’s also “digital pickled mustard” or “electronic pickled mustard” (电子榨菜, diànzǐ zhàcài), which refers to a binge-worthy or comforting show. *The term 电子 (diànzǐ) means “electronic” and is commonly used in modern Chinese terms, much like the English “e-” prefix in ebook (电子书) or email (电子邮件). It’s also used for digital transactions, like digital payments (电子支付) or digital wallets (电子钱包).
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Memes & Viral
“Bye Bye Biden”: Biden’s Many Nicknames in Chinese
Throughout the years, Biden has received many nicknames on Chinese social media.
Published
9 months agoon
July 22, 2024
Our Weibo phrase of the week is Bye Bye Biden (bài bài Bàidēng 拜拜拜登). As news of Biden dropping out of the presidential race went viral on Weibo early Monday local time, it’s time to reflect on some of the popular nicknames and phrases given to US President Joe Biden on Chinese social media.
🔹 Biden in Chinese: Bàidēng 拜登
Biden in Chinese is generally written pronounced and written as Bàidēng 拜登. Although the character 拜 (bài) means “to pay respect, to worship” and 登 (dēng) means “to ascend, to climb,” they’re used here primarily for their phonetic similarity. The characters chosen are neutral to avoid any negative implications in the official translation of Biden’s name.
Why are non-Chinese names translated into Chinese at all? With English and Chinese being vastly different languages with entirely different phonetics and scripts, most Chinese people find it difficult to pronounce a foreign name written in English. Writing foreign names in Chinese not only standardizes them but also makes pronunciation and memorization easier for Chinese speakers.
🔹 Bye Biden: Bài Bài Bàidēng 拜拜拜登
Because Biden is Bàidēng, and the Chinese for ‘bye bye’ is written as bài bài 拜拜, some netizens quickly created the wordplay “bài bài Bàidēng” 拜拜拜登 (“bye bye Biden”) upon hearing that Biden would not seek reelection. Try saying it out loud—it almost sounds like you’re stammering.
🔹 Old Joe: Lǎo Dēng Dēng 老登登
Another common farewell greeting to Biden seen online is “bài bài lǎo dēng dēng” 拜拜老登登, which sounds cute due to the repetition of sounds.
“Old Biden” or “lǎo dēng dēng” 老登登 is a common online nickname for Biden in Chinese. The reduplication of the 登 (dēng) makes it sound playful and affectionate, while the “old” prefix is commonly used when referring to someone older. It’s similar to calling someone “Old Joe” in English.
🔹 Biden Variations: 拜灯, 白等, 败蹬
Let’s look at some other ways Biden is nicknamed online:
Besides the official way of writing Biden with the 拜登 Bàidēng characters, there are also other variations:
拜灯: bài dēng
白等: bái děng
败蹬: bài dèng
These alternative ways of writing Biden’s name are not neutral. Although the first variation is not necessarily negative (using the formal Biden 拜 bài character but with ‘Light’ 灯 dēng instead of the other 登 ‘dēng’), the other two variations are usually used in more negative contexts.
In 白等 (bái děng), the first character 白 (bái) means “white,” which can evoke associations with old age due to white hair (白发). The character 等 (děng) means “to wait,” and the combination can imply being old and sluggish.
败蹬 (bài dèng) is typically used by netizens to reflect negative sentiments towards the American president. The characters separately mean 败 (bài): “to be defeated,” “to fail,” and 蹬 (dèng): “to step on,” “to kick.” This would never be used by official media and is also often used by netizens to circumvent censorship around a Biden-related topic.
🔹 Revive the Country Biden: Bài Zhènhuá 拜振华
Then there is 拜振华 Bài Zhènhuá: revive the country Biden
In recent years, Biden has come to be referred to with the Chinese nickname “Revive the Country Biden,” also translatable as ‘Thriving China Biden’. This nickname has circulated online since 2020 and matches one previously given to former President Trump, namely “Build the Country Trump” (Chuān Jiànguó 川建国).
The idea behind these humorous monikers is that both Trump and Biden are seen as benefitting China by doing a poor job in running the United States and dealing with China.
🔹 Sleepy King: Shuì wáng 睡王
Shuì wáng 睡王, Sleepy King, is another common nickname, similar to the English “Sleepy Joe.” During and after the 2020 American presidential elections, there were numerous discussions on Chinese social media about ‘Trump versus Biden.’ Many saw it as a contest between the ‘King of Knowing’ (懂王) and the ‘Sleepy King’ (睡王).
These nicknames were attributed to Trump, who frequently boasted about his unparalleled understanding of various matters, and Biden, who gained notoriety for being older and tired. Viral videos, some manipulated, showed him nodding off or seemingly disoriented. The name ‘Sleepy King’ then stuck.
🔹 Grandpa Biden: Bài Yéyé 拜爷爷
Throughout the years, Biden has also been nicknamed Bài yéyé 拜爷爷, “Grandpa Biden.” This is usually more affectionate, though it emphasizes his age—Trump is not much younger than Biden and is not nicknamed ‘Grandpa Trump.’
Another similar nickname is lǎo bái 老白, “Old White,” referring to Biden’s age and white hair. 白 (bái, white) can also be a surname in Chinese. This nickname makes it seem like Biden is an old, familiar friend.
On Weibo, many speculate that American Vice President Kamala Harris will be the new candidate for the Democrats, especially since she’s been endorsed by Biden. Many have little confidence that she can compete against Trump. Her Chinese name is Kǎmǎlā Hālǐsī 卡玛拉·哈里斯, commonly referred to as ‘Harris’ (Hālǐsī).
In light of the latest developments, some netizens jokingly write: “Bye bye Biden, Ha ha ha, Harris.” (Bài bài, Bàidēng. Hā hā hā, Hālǐsī 拜拜,拜登。 哈哈哈,哈里斯). With a new Democratic candidate entering the presidential race, we can expect a fresh batch of creative nicknames to join the mix on Chinese social media.
Want to read more? Also read: Why Trump has Two Different Names in Chinese.
By Manya Koetse
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

No Quiet Qingming: From High-Tech Tomb-Sweeping to IShowSpeed & the Seven China Streams

From Trade Crisis to Patriotic Push: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Tariffs

China Trending Week 14: Gucci Fake Lipstick, Xiaomi SU7 Crash, Yoon’s Impeachment

Strange Encounter During IShowSpeed’s Chengdu Livestream

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng






Jörg
October 1, 2020 at 8:05 am
When i was in China, i also wonder about this word, and when asking for the meaning, they said “there is no meaning”. That gives me another mystery, because the answer could mean “there is no meaning” or “it has a strong meaning we do not want to tell you”
But now its solved.
Thanks for this article.
By the way, when chinease people around, i try to say “Auf Wiedersehen” and not “Tschüss” to avoid confusion 🙂
Diandian Guo
October 23, 2020 at 1:11 pm
Maybe interesting to know: the official pronunciation of 那个 is nàge. This is also the pronunciation you would learn at school. However, in colloquial use, people tend to say nèige. The most common explanation is that nèige is 那&一 pronounced together.
Diandian Guo
October 23, 2020 at 1:15 pm
And talking about “sounds-alikes”: if taken seriously, China probably have a valid cultural reason to ban Facebook. It sounds just like 非死不可(feisibuke), “one has no other choice but to die”. That could sound both unlucky and offensive for a mandarin speaker, I guess.
Hello
November 17, 2020 at 2:04 pm
Nage, neige, means “that”, i.e. that one. It’s not a filler word!! A filler word would be “en”. Which is essentially the same sound in English, it is an affirmative sound.