China and Covid19
Trending on Weibo: “Why Can’t Shanghai Residents with Covid-19 Recover at Home?”
While Chinese top experts stress that Covid patients can not recover at home, Shanghai’s centralized quarantine locations are anything but a home away from home.
Published
3 years agoon
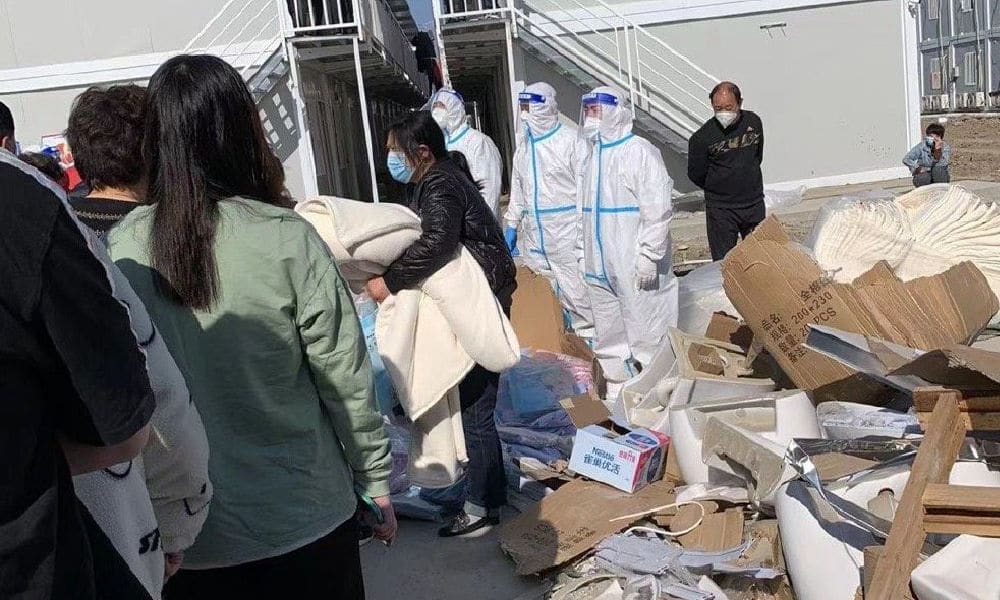

According to China’s strict Covid measures, everyone testing positive during Shanghai’s current outbreak needs to go to a centralized quarantine location. While Chinese top experts say home isolation is not an option, Shanghai residents complain about the deplorable conditions at the isolation centers.
While Shanghai is battling the worst Covid outbreak the city has ever seen and infection numbers continue to rise, today’s number one hashtag on social media platform Weibo is: “Why Can’t People Infected with Covid-19 Isolate at Home?” (#新冠感染者为什么不能居家隔离#).

Trending topic list of Weibo, April 11 2022.
Since Shanghai’s current outbreak started on March 1, the city’s 26 million residents have been seeing stringent anti-epidemic measures, including a citywide lockdown and mass testing campaigns. This month, frustrations have been building among residents who struggle to get food, medications, and urgent medical care amid China’s dynamic zero-infection policy.
China’s so-called ‘zero-Covid policy’ is all about rapidly responding to new Covid cases, precise prevention measures, and controlling and extinguishing local outbreaks as fast as possible to avoid further spread of the virus and drastically reduce the number of people getting sick and dying. As part of this strategy, people who test positive for Covid-19 are sent to centralized facilities for a mandatory quarantine.
It’s not just people at home who have been struggling during this lockdown – many also face difficulties in getting basic medical care or adequate supplies at these centralized quarantine centers. Videos circulating on Chinese social media expose how people at some isolation facilities are fighting over food or are facing unhygienic living conditions.
The situation is Shanghai is difficult and messy, for those at quarantine sites, and for those at home. So many videos circulating online these days. This video was posted on Weibo to show the chaotic situation a quarantine location in Pudong. pic.twitter.com/E82tLCmVZ9
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) April 9, 2022
The apparent disorganization at some quarantine facilities has triggered discussions on Chinese social media, where many are wondering why people who barely show any Covid symptoms should still be quarantined at centralized locations. Besides the fact that many of these quarantine facilities are far less comfortable than people’s own home environment (there are usually no private rooms, no showers, etc), people also fear cross-infection or re-infection due to the crowded and sometimes chaotic living conditions.
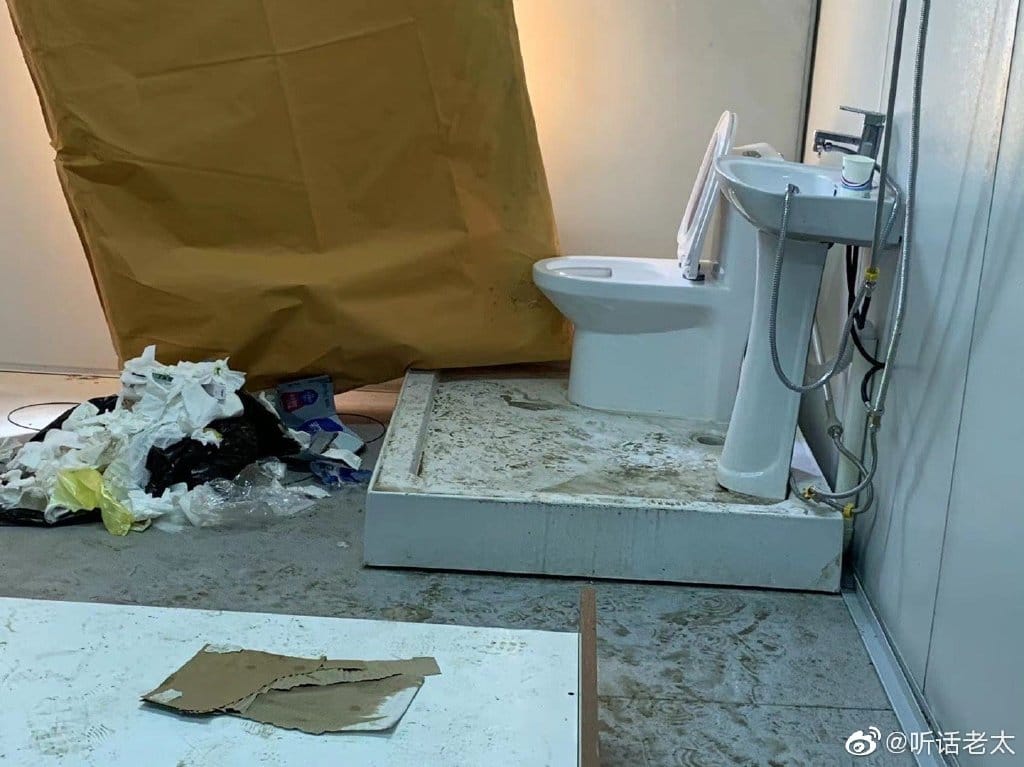

The state of the toilets at one Pudong quarantine location.
Due to a lack of medical staff, many of these facilities cannot offer adequate medical care to Covid patients who need it. Additionally, people who test positive for Covid-19 and are required to go to a quarantine location also cannot take care of pets or vulnerable family members who test negative and are left at home by themselves.
Last week, two dog owners who were taken away to a quarantine location left their Corgi dog on the streets because they feared it would starve to death if they would leave it inside their home. The dog was killed by an anti-epidemic worker shortly after. This incident also triggered massive outrage online and fuelled discussions on the need to be quarantined at a designated location rather than being allowed to stay at home.
On Weibo, the hashtag “Why Can’t People Infected with Covid-19 Isolate at Home?” received over 160 million views on Monday. The topic was initiated by the Daily Economic News (@每日经济新闻) account, which posted a video showing the renowned Chinese top epidemiologist Liang Wannian (梁万年) stressing the importance of China’s zero-Covid strategy and centralized isolation policy in light of the rapid growth in Omicron infections.
According to Liang, isolating asymptomatic or mildly ill Covid patients at home may cause further spread of the virus, especially because Omicron spreads so quickly. Even though they have mild symptoms, these Covid patients are still contagious and could spread the virus to their families and beyond. Liang also argued that patients need to be isolated at a centralized location because they can be easily monitored and treated that way.
Liang also addressed the problem of ‘people waiting for beds’ (“人等床”). Some people from Shanghai sharing their Covid journey online have expressed their frustration with being taken away for quarantine days or even weeks after they tested positive. The Shanghai-based Italian producer Alessandro Pavanello detailed his Covid experience on Instagram, where he wrote that he tested positive on March 26 but was not taken away for quarantine until April 9th. By that time, two entire weeks after his positive test, he already tested negative again but still needed to go to a centralized isolation site.
Alessandro's Shanghai Covid journey is baffling. This Italian DJ tested positive on March 26, QR code turned red on 3-28. Was told he'd get picked up for quarantine at 4-3, but wasn't picked up until 4-9 (!) – which is when he actually tested negative again. Still needed to go. pic.twitter.com/vDgnfhFpQF
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) April 11, 2022
Liang Wannian called Shanghai’s fight against the virus an issue of systematic project management, where the problems within the process of screening, diagnosing and a rapid transfer and treatment need to be solved in order to stop continuous transmission of the virus: patients should not wait for beds, beds should be waiting for patients (“床等人”).
On Saturday, China’s largest-ever makeshift hospital opened its doors in Shanghai. The hospital at the National Exhibition Convention Center has a capacity of 50,000 beds for Covid-19 patients, and there are more than 5000 members of medical staff and 10,000 people doing logistics and supporting work (Xing & Cao 2022).
Meanwhile, more Chinese officials and experts are emphasizing the importance of sticking to the “dynamic zero-COVID strategy” as the best way forward for China. Zhang Wenhong (张文宏), head of the infectious disease department at Fudan’s Huashan Hospital, was also quoted by China Daily on Monday as saying that the pressing task for China now is to contain the epidemic in Shanghai and to cut off the transmission in communities so that normal life and production in the city can resume.
China Daily also reported that prominent Chinese pulmonologist Zhong Nanshan (钟南山) gave a lecture on Friday in which he suggested that co-existing with the virus and lifting the restrictions does not fit China’s situation since it would allegedly lead to many deaths: “In China, we should stick to the dynamic zero-COVID strategy and ease policies gradually in the future,” he said (Wang 2022, 3).
Shanghai’s mandatory quarantine implementation: lacking logic
On Weibo, thousands of people have commented on the “Why Can’t People Infected with Covid-19 Isolate at Home?” hashtag. Many agree with the centralized quarantine measures, as they fear that the virus would otherwise quickly spread in Shanghai’s densely populated areas and high-rise buildings through, for example, ventilation systems or shared facilities.
But there is also a lot of criticism. Although the Weibo post by Daily Economic News had received over 3300 replies on Monday, only a handful of comments were viewable at the time of writing. Another post containing the video received 222 replies, but none of them were displayed. “The comment section just shows ten comments, does it mean that the other 3000 people didn’t agree?”, one Weibo user wondered.
Another Weibo user described her experiences at an isolation site, posting photos of the conditions there. She writes:
“Up to now, I’ve always supported Shanghai’s active disease prevention. We have been isolated at home since early March. Ten tests we did all came up normal, but the last one unexpectedly came up positive. They took us to an isolation site. If the conditions had just been a bit better, we’d be okay with it, but this is just unimaginable. These are the facts. Over 800 people have entered this facility since April 9, their ages varying from seventy or eighty years old to babies just a few months old.
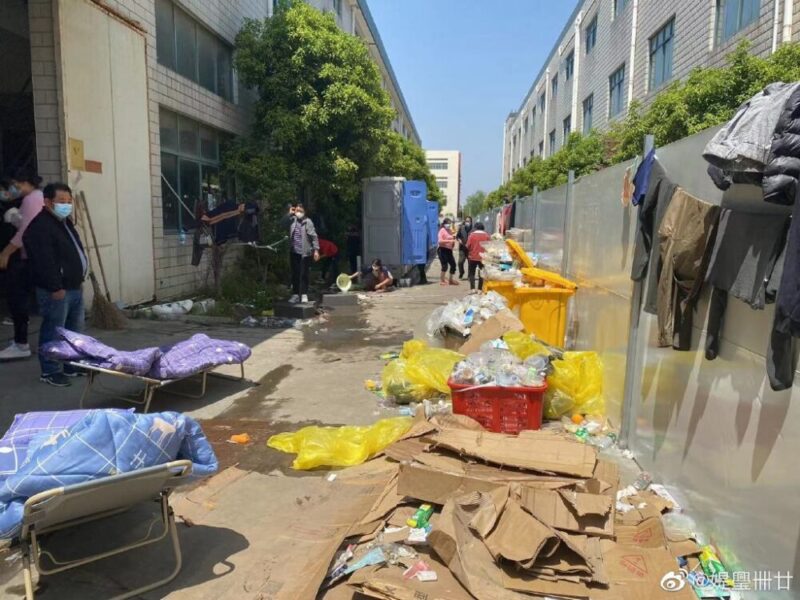

1. Inside the factory building, there are plank beds without mattresses, there are no people to clean.
2. There is no supervisor, we need to fight over our food.
3. There are not enough supplies, not even enough toiletpaper.
4. 80% of the toilets are clogged, there’s nobody to clean them.
5. There are no doctors and nobody to take care of patients with a fever.
6. There is no one to dispose of the garbage.
7. The weather’s hot, but there’s no place to shower or change clothes.
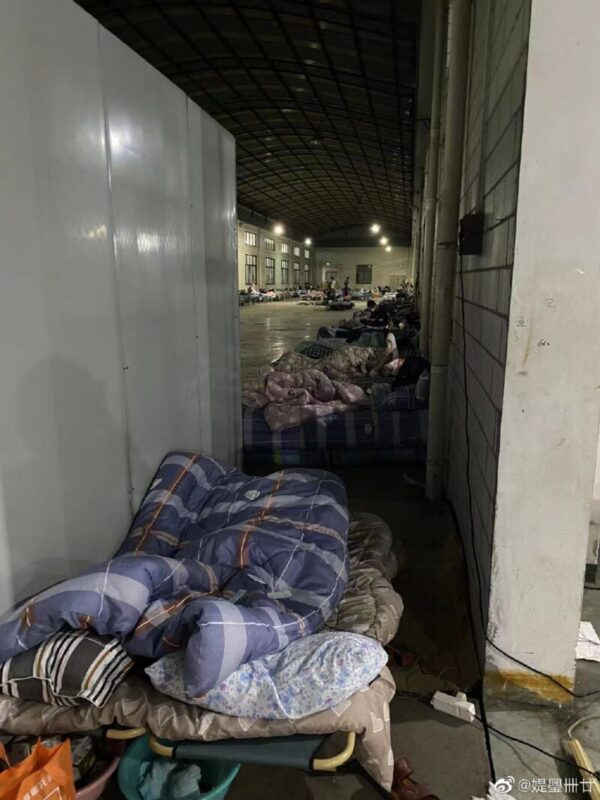
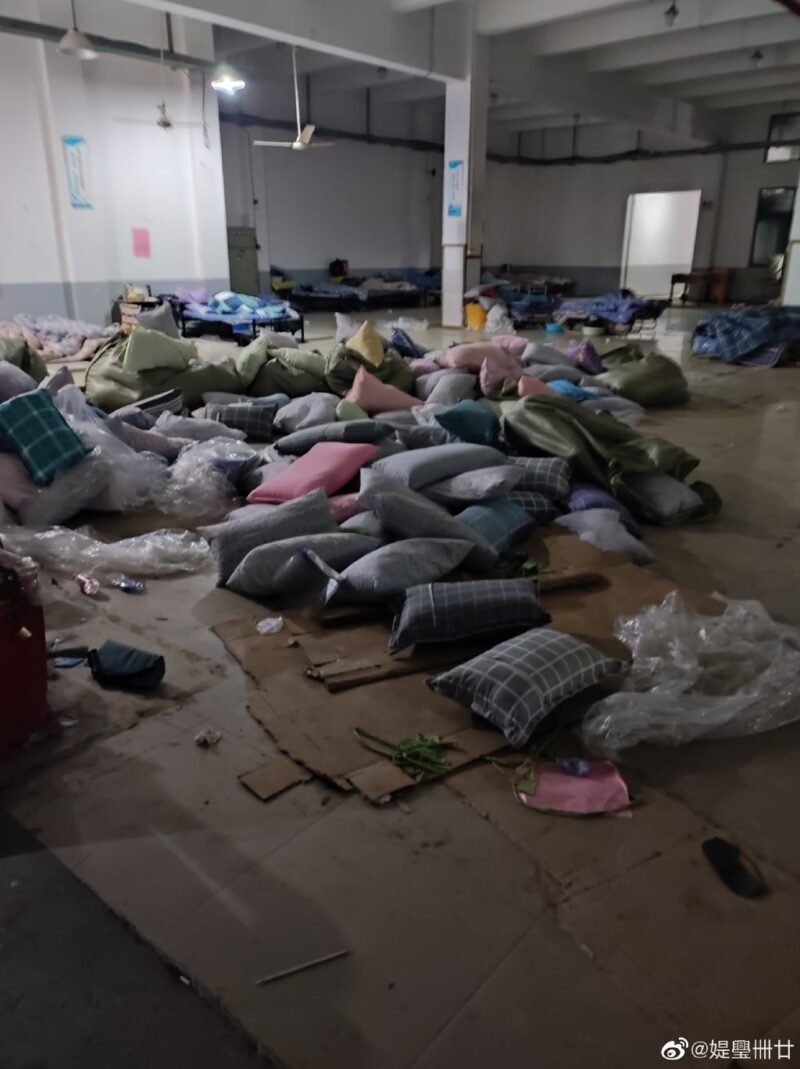


I really hope the relevant departments will pay attention to the fact that the dirty environment may cause other diseases and lead to more serious secondary hazards.”
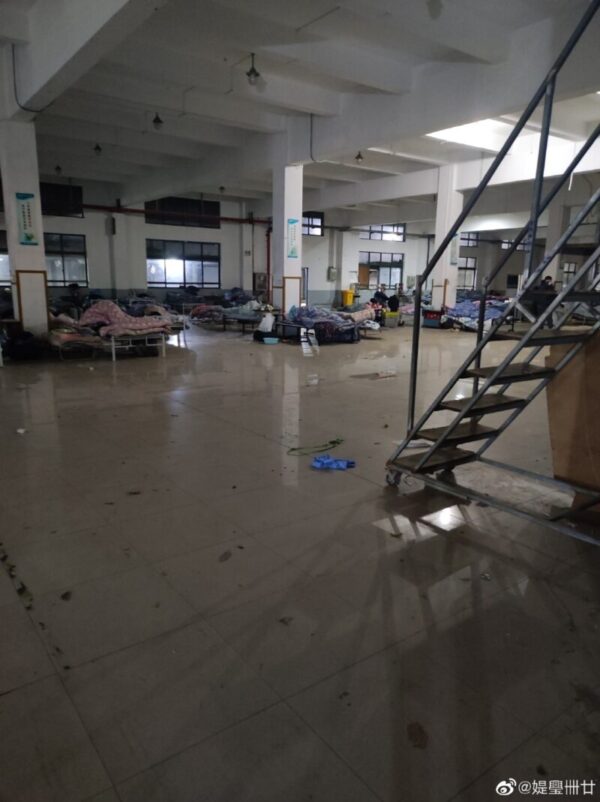

“The conditions at home are definitely much better than at the makeshift hospitals,” one Weibo blogger wrote.
There are also posts commenting on how Shanghai’s mandatory quarantine strategy implementation is devoid of logic, making people isolate who have already recovered from Covid (like the aforementioned example of the Italian man). One netizen wrote about her friend who tested positive, recovered at home by herself, tested negative multiple times, and only received a call from the Center of Disease Control days later that she had to go to a quarantine location. She asked them to come to her house to do a test, so she could show them she had recovered, but the CDC refused due to “lack of staff” and still made her go to the facility for 14 days, stuck in between Covid positive people without enough medical staff and a lack of supplies. “This is Shanghai,” the blogger wrote.
Another Weibo user also published a lengthy post about their experiences getting to a Shanghai quarantine location. Like many others, this Weibo user also tested negative again and was still required to go to a centralized isolation site without getting any information on where he would be taken or how long he would be gone.

Together with many people who tested positive for Covid, he was inside a bus for hours without any access to water or toilets. When he finally reached the isolation site, he found that people who tested negative and positive were all mixed together – and that there was not a single doctor at the entire facility. Angry and frustrated, he wrote on Weibo:
“Before I put pen to paper, I hesitated if I should write down the facts of what is happening to us and if it would only bring more worry and stress to my friends and family, but after thinking twice I still think that all the people outside, no matter where you are, need to understand what we are going through and realize how different the reality is from the reports.”
For more articles on the Covid-19 topics on Chinese social media, check here.
By Manya Koetse
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our weekly newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
References (online sources are linked to in text)
Wang, Xiaoyu. 2022. “Virus Highly Infectious, But Unlike Flu.” China Daily (Hong Kong), April 11, page 3.
Xing, Yi and Cao Yin. 2022. “Giant Makeshift Hospital to Ease Treatment Burden.” China Daily (Hong Kong), April 9, page 1.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2022 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China and Covid19
Weibo Watch: Small Earthquakes in Wuhan
How Wuhan is shaking off its past with a new wave of innovation, the hot topics to know, and the Weibo catchphrase of the week: ‘the Three Questions of Patriotism.’
Published
6 months agoon
September 27, 2024
PREMIUM NEWSLETTER | ISSUE #37
Dear Reader,
“Wuhan Earthquake” (#武汉地震#) momentarily became the number one trending topic on Weibo this Friday night, after residents of Jiangxia District reported feeling their homes and buildings shake. “Was there an earthquake, or am I drunk?” some wondered.
I also felt a bit tipsy in Wuhan this month. Neon signs, dancing livestreamers, flying drones, bustling night markets, and holographic lights. On my first night in Wuhan, the lights made me dizzy and I discovered that the city was nothing like I had imagined.
Until now, I couldn’t help but associate Wuhan with the wet market, crowded fever clinics, and China’s first Covid hospitals. As the world watched the pandemic unfold in 2020, Wuhan became instantly famous as an early epicenter of the Covid-19 crisis. It became known as the quarantined city, the city of Dr. Li Wenliang, and the city of the “invincible Wuhan man.” At the time, it seemed like such a monumental event that Wuhan would not recover anytime soon, even after enduring the worst peak of Covid.
Now, over four years later, everything feels different. I felt a rush of energy as I strolled through the lively streets. It was evident that Wuhan is much more than the city that gained global notoriety as the pandemic hotspot. Beyond its vibrant atmosphere, it is making international headlines for its leadership in autonomous driving, having emerged as the world’s largest testing ground for self-driving cars, particularly in unmanned ride-hailing services.
Baidu’s Apollo Go, referred to as Luobo Kuaipao (萝卜快跑) in Chinese, is the driving force behind the robotaxi revolution in Wuhan. Since their arrival earlier this year, they have become a hot topic on Chinese social media, and I was eager to experience it for myself.
(Brief explainer: Luóbo (萝卜) means radish or turnip in Chinese, but when pronounced, it sounds similar to “robo.” Kuàipǎo (快跑) translates to “run fast.” Combined, it creates a playful name that can be interpreted as “Radish Runs Fast” or “Robo Go.” I’ll use ‘Luobo’ here, as it is the most common way to refer to Apollo Go in China and has a cute sound.)
In the areas where the robotaxis operate, people already seem to have become accustomed to the driverless ‘Luobo.’ During a 1.5-hour ride in the unmanned taxi—I took a long journey and then needed to return again—I was surprised to see so many of them on the road. Other drivers, motorcyclists, and passengers didn’t even bat an eye anymore when encountering the new AI taxi.
Currently, there is an active fleet of 400 cars in Wuhan, and Baidu plans to expand this to 1,000 in the fourth quarter of this year. Although these taxis still comprise only a fraction of the city’s entire taxi industry, their impact is noticeable on the roads, where you will inevitably encounter them. I stood at one drop-off point near an urban shopping center for at least forty minutes and witnessed passengers being dropped off continually, with some proceeding their journeys into areas where Luobo doesn’t operate by calling the ride-hailing service Didi from there.
As for the experience itself, it was thrilling to see the steering wheel move with no driver in the front seat. I was surprised at how quickly I adapted to something so unfamiliar. It’s incredibly comfortable to have a car to yourself—no driver, no worries—while you choose your own music (and sing along), set the air conditioning, and relax as the Luobo navigates the traffic.
Even inside the vehicle, Baidu emphasizes the safety of their self-driving cars, providing information about how Apollo Go has accumulated over 100 million kilometers of autonomous driving testing without any major accidents, thanks to a strict safety management system.
If you close your eyes, the experience feels like riding with a regular driver. Luobo speeds up, slows down, and occasionally makes unexpected maneuvers when a car or bike suddenly approaches. It ensures there’s enough space between itself and the car in front. While I can’t say that merging onto the highway or encountering unexpected traffic situations didn’t feel a bit scary, I soon felt at ease and came to rely on the technology.
That said, there are still bumps in the road. Luobo has often been ridiculed on Chinese social media for getting stuck at a green light, stopping for a garbage bag, or struggling to make a U-turn. While riding and observing the robotaxis in Wuhan, I noticed plenty of honking and road rage as Luobo chooses safety first, often appearing sluggish, earning them the nickname ‘Sháo Luóbo’ (勺萝卜/苕萝卜, “silly radish”).
While Luobo might still have its silly moments, it is a serious part of the future. Already, it is popular among commuters for its low cost, privacy, and convenience.
After spending an entire morning riding and watching the Luobos, I excitedly felt like I had experienced a glimpse of the future. Right now, Luobo Kuaipao operates in various cities across China, including Beijing, but it’s still in the testing phase there—none of my friends from Beijing have ever seen or taken one yet. However, this will likely change soon, heavily relying on policy support.
That night, I spoke to a young local in a busy commercial area near my hotel. Like many residents, he was curious about where I came from and what I was doing in Wuhan. (During the four days I spent there, I noticed very few foreign tourists.) We briefly discussed the pandemic; he reflected on the difficulties it brought but treated it as something from the past—just another bump in the road in the city’s long history.
Instead of dwelling on the pandemic, our conversation focused on the future: Wuhan’s robotaxis, his confidence in China’s technology, and the rising importance of his country on the geopolitical stage. He was just one of several young people I spoke to, from shopkeepers to students, who seemed very focused on China’s growth and development and how its technological advancements reflect its position in a world where the U.S. is no longer leading.
When it comes to China’s driverless innovations, they are shaking the foundations of transportation like an earthquake. Besides Apollo Go, companies like Pony.ai (小马智行), WeRide (文远知行), SAIC Motor (上汽集团), AutoX (安途), FAW (一汽), Changan Automobile (长安汽车), BYD (比亚迪), Yutong (宇通), and many other industry players are also working to realize driverless passenger cars, shuttle services, freight trucks, delivery vehicles, public transport buses, and much more.
What we’re witnessing in Wuhan is merely a glimpse into a future under construction, actively promoted by Chinese state media. Over the past week alone, CCTV featured Luobo Kuaipao in three segments as a key example of China’s new technological advancements and the national strategy to build a strong tech-driven economy.
As I left Wuhan in a traditional taxi, I suddenly felt like a time traveler. Wuhan was the birthplace of the 1911 revolution and will also appear in foreign history books as the initial epicenter of the Covid-19 pandemic. Now, it is at the center of an international robotaxi revolution, and it won’t be the same the next time I return.
While my friendly elderly driver—I estimated him to be in his late 50s—honked at other cars, I realized he had witnessed many other revolutions, including the Cultural Revolution as a young boy, the economic reforms, and the major social changes of the 1980s, as well as the digital revolution of the 2000s. With the growth of Wuhan’s robotaxi fleet, his job might be affected, adding another tremor to his city and his life—though he may already be retired by then.
As he helped me with my luggage and wished me a safe trip home at the Wuhan Hankou Station, I couldn’t help but feel nostalgic about how everything always changes and gets shaken up as we move forward into a future driven by technology.
As for Friday’s earthquake in Wuhan—it turns out it was a 1.6. Despite the online interest in the topic, it means virtually nothing in a city where things of much greater magnitude are happening.
If you’d like to know more about my experiences and the slight setback I encountered while searching for Wuhan’s robotaxis, check out the short videos I made here:
Part 1 (also on Instagram)
Part 2 (also on Instagram).
Best,
Manya Koetse
(@manyapan)
What To Know
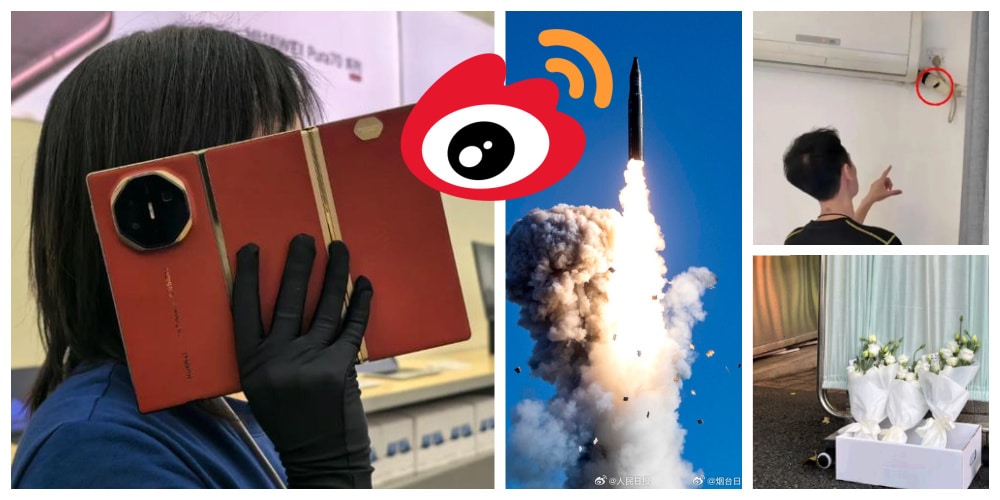

🚀 China’s First Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Test-Launch Since 1980
On the morning of September 25, China announced a successful test launch of an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) carrying a ‘dummy warhead’ into the Pacific Ocean. This marked the first ICBM launch in decades, described by official media as part of routine annual training.
The People’s Daily Weibo account of the Communist Party shared a video of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) announcing the successful test launch, accompanied by suspenseful and patriotic music, specifically the “March of the Steel Torrent” (钢铁洪流进行曲) (see video). This launch quickly became a trending topic (#我军向太平洋发射洲际弹道导弹#). While Chinese state media claimed that Beijing informed relevant countries in advance, Japan stated that it did not receive any prior notice, further heightening tensions between China and Japan.
🇯🇵 Aftermath of Japanese Schoolboy Stabbing
The incident in which a Chinese man fatally stabbed a ten-year-old Japanese schoolboy near the Shenzhen Japanese School on September 18 has become a widely discussed topic this month. The attacker, a 44-year-old Chinese national, was immediately arrested. However, discussions about the stabbing are ongoing, as it has sparked a wave of anger in Japan, where critics argue that anti-Japanese sentiments in China are fueled by official media and national education.
Meanwhile, China and Japan have effectively resolved their diplomatic dispute regarding the Fukushima water discharge, with some suggesting a connection between the two events. China’s Foreign Ministry spokesperson Mao Ning (毛宁) stated on September 20 that the issues are not related (#中日共识与日本男童遇袭无关#). Beyond the geopolitical implications, the international media coverage of the stabbing incident has also provoked anger on Chinese social media, where many netizens reject the supposed negative portrayal of China. The topic is quite sensitive and continues to face significant censorship online.
📱 Huawei Trifold Phone
The launch of Huawei’s ‘trifold’ phone earlier this month generated significant excitement in China, with many believing that Huawei—and, by extension, China—is now at the forefront of innovation in the folding screen smartphone race. The Mate XT is the first triple-folding screen phone, leading some top commenters to proclaim, “Huawei’s innovation capability is truly the best in the world. While other manufacturers are still researching foldable phones, Huawei has already released the trifold.”
During my travels in China over the past few weeks, I visited several Huawei stores, but unfortunately, the trifold was never on display; it’s available only by reservation and has allegedly garnered millions of pre-orders, despite its hefty price tag of CNY 19,999 (USD 2,850). There’s also been some lighthearted banter surrounding the phone, including a viral post that humorously depicts what it looks like when you make a phone call with the screen unfolded (it looks ridiculous), and a user who taped two phones together to create a sixfold.
👴 Retirement Age Discussions
News came out last week that China will raise its retirement age for the first time since the 1950s. China’s current retirement ages are among the world’s lowest. Facing an aging society and declining birth rates, the ages will now be increased in a step-by-step implementation process: 50 to 55 for women in blue-collar jobs, 55 to 58 for females in white-collar jobs, and 60 to 63 for male workers.
This change, set to take effect on January 1, 2025, has already sparked considerable discussion this year after experts proposed the adjustment. A related hashtag has garnered over 870 million views on Weibo (#延迟法定退休年龄改革#), where many users expressed their dissatisfaction with the change. “Great, I’ll get to retire in September of 2051 now,” one young worker wrote. “We start studying earlier and retire later; how can we keep up with this?”
📷 Hidden Hotel Cameras
After a Chinese blogger known as “Shadows Don’t Lie” (@影子不会说谎) recently discovered and exposed hidden cameras in the rooms of two guesthouses in Shijiazhuang, he faced significant intimidation and threats from the owners and employees, who accused him of staging the situation for attention.
However, the situation turned out to be real, and local police arrested multiple suspects responsible for installing these cameras inside these hotel rooms, which are often rented by young couples for romantic short stays. The suspects reportedly did not know the guesthouse owners and had secretly set up the cameras to profit illegally. This incident, which continues to generate discussion online, has heightened public concern over privacy protection and the integrity of the guesthouse industry, particularly as this is not the first time such issues have been revealed.
Weibo Word of the Week

The Three Questions of Patriotism
Our Weibo word of the week is 爱国三问 (àiguó sān wèn), which translates to “The Three Questions of Patriotism.” This phrase has recently gained attention on Chinese social media as it was highlighted and propagated by official media channels.
The three questions are:
1. Are you Chinese? (你是中国人吗)
2. Do you love China? (你爱中国吗)
3. Do you wish China well? (你愿意中国好吗)
These questions were originally posed in 1935 by Zhang Boling (张伯苓), the first president of the renowned Nankai University (南开大学) in Tianjin.
Today, they are being revived on Chinese social media through various videos released by official channels.
One notable video is part of a new online series produced by state media titled “Great Educators” (大教育家), which features reenactments of speeches by prominent Chinese educators. In this series, Zhang Boling’s speech, portrayed by actor Wang Ban (王斑), emphasizes the importance of unity in tumultuous times.
Rather than dwelling on differences, Zhang urged people to recognize their shared identity: they are all Chinese, they love China, and they all aspire for the country’s prosperity.
Another video features Nankai University’s current president, Chen Yulu (陈雨露), addressing students during a large event on September 21st. In his speech, Chen reiterates the three famous questions, prompting the hundreds of students in attendance to respond enthusiastically: “We are [Chinese]!” “We love [China]!” “We wish [China well]! We want China to be strong and prosperous!” This response is followed by enthusiastic applause.
Additionally, another video from the same day features a meeting between Chen Yulu and an AI version of Zhang Boling, digitally resurrected to address the students and celebrate the start of the new school year. During this ‘virtual dialogue,’ Chen informs Zhang that his ‘Three Questions of Patriotism’ have become a cherished tradition at Nankai’s annual opening ceremony.
According to Chinese state media, the students’ responses to these three questions illustrate how contemporary Chinese youth are aligning their personal aspirations with national progress. This alignment is seen as a revival of the patriotic spirit that Zhang Boling instilled in students during wartime. However, the current ‘revival’ of this sentiment appears to be largely reflected across various official channels, with limited engagement from ordinary netizens.
This is an on-site version of the Weibo Watch newsletter by What’s on Weibo. Missed last week’s newsletter? Find it here. If you are already subscribed to What’s on Weibo but are not yet receiving this newsletter in your inbox, please contact us directly to let us know.
China and Covid19
Sick Kids, Worried Parents, Overcrowded Hospitals: China’s Peak Flu Season on the Way
“Besides Mycoplasma infections, cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
Published
1 year agoon
November 22, 2023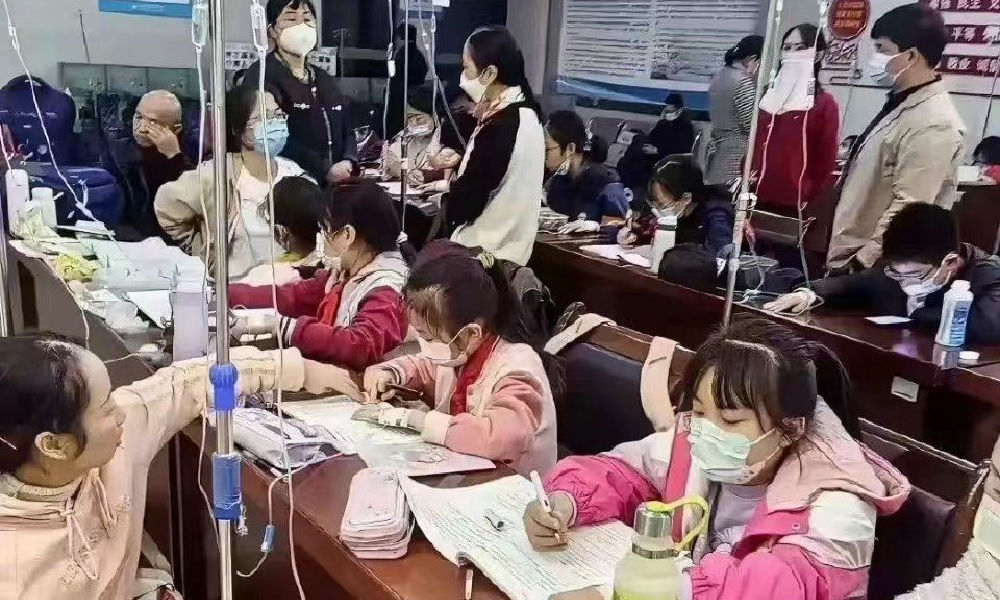
In the early morning of November 21, parents are already queuing up at Xi’an Children’s Hospital with their sons and daughters. It’s not even the line for a doctor’s appointment, but rather for the removal of IV needles.
The scene was captured in a recent video, only one among many videos and images that have been making their rounds on Chinese social media these days (#凌晨的儿童医院拔针也要排队#).

One photo shows a bulletin board at a local hospital warning parents that over 700 patients are waiting in line, estimating a waiting time of more than 13 hours to see a doctor.

Another image shows children doing their homework while hooked up on an IV.
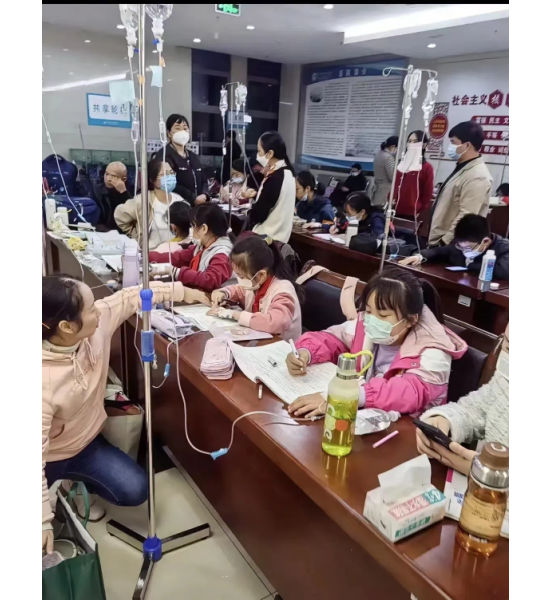

Recent discussions on Chinese social media platforms have highlighted a notable surge in flu cases. The ongoing flu season is particularly impacting children, with multiple viruses concurrently circulating and contributing to a high incidence of respiratory infections.
Among the prevalent respiratory infections affecting children are Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections, influenza, and Adenovirus infection.
The spike in flu cases has resulted in overcrowded children’s hospitals in Beijing and other Chinese cities. Parents sometimes have to wait in line for hours to get an appointment or pick up medication.
According to one reporter at Haibao News (海报新闻), there were so many patients at the Children’s Hospital of Capital Institute of Pediatrics (首都儿科研究所) on November 21st that the outpatient desk stopped accepting new patients by the afternoon. Meanwhile, 628 people were waiting in line to see a doctor at the emergency department.
Reflecting on the past few years, the current flu season marks China’s first ‘normal’ flu peak season since the outbreak of Covid-19 in late 2019 / early 2020 and the end of its stringent zero-Covid policies in December 2022. Compared to many other countries, wearing masks was also commonplace for much longer following the relaxation of Covid policies.
Hu Xijin, the well-known political commentator, noted on Weibo that this year’s flu season seems to be far worse than that of the years before. He also shared that his own granddaughter was suffering from a 40 degrees fever.
“We’re all running a fever in our home. But I didn’t dare to go to the hospital today, although I want my child to go to the hospital tomorrow. I heard waiting times are up to five hours now,” one Weibo user wrote.
“Half of the kids in my child’s class are sick now. The hospital is overflowing with people,” another person commented.
One mother described how her 7-year-old child had been running a fever for eight days already. Seeking medical attention on the first day, the initial diagnosis was a cold. As the fever persisted, daily visits to the hospital ensued, involving multiple hours for IV fluid administration.
While this account stems from a single Weibo post within a fever-advice community, it highlights a broader trend: many parents swiftly resort to hospital visits at the first signs of flu or fever. Several factors contribute to this, including a lack of General Practitioners in China, making hospitals the primary choice for medical consultations also in non-urgent cases.
There is also a strong belief in the efficacy of IV infusion therapy, whether fluid-based or containing medication, as the quickest path to recovery. Multiple factors contribute to the widespread and sometimes irrational use of IV infusions in China. Some clinics are profit-driven and see IV infusions as a way to make more money. Widespread expectations among Chinese patients that IV infusions will make them feel better also play a role, along with some physicians’ lacking knowledge of IV therapy or their uncertainty to distinguish bacterial from viral infections (read more here)
To prevent an overwhelming influx of patients to hospitals, Chinese state media, citing specialists, advise parents to seek medical attention at the hospital only for sick infants under three months old displaying clear signs of fever (with or without cough). For older children, it is recommended to consult a doctor if a high fever persists for 3 to 5 days or if there is a deterioration in respiratory symptoms. Children dealing with fever and (mild) respiratory symptoms can otherwise recover at home.
One Weibo blogger (@奶霸知道) warned parents that taking their child straight to the hospital on the first day of them getting sick could actually be a bad idea. They write:
“(..) pediatric departments are already packed with patients, and it’s not just Mycoplasma infections anymore. Cases include influenza, Covid-19, Norovirus, and Adenovirus. And then, of course, those with bad luck are cross-infected with multiple viruses at the same time, leading to endless cycles. Therefore, if your child experiences mild coughing or a slight fever, consider observing at home first. Heading straight to the hospital could mean entering a cesspool of viruses.”
The hashtag for “fever” saw over 350 million clicks on Weibo within one day on November 22.
Meanwhile, there are also other ongoing discussions on Weibo surrounding the current flu season. One topic revolves around whether children should continue doing their homework while receiving IV fluids in the hospital. Some hospitals have designated special desks and study areas for children.
Although some commenters commend the hospitals for being so considerate, others also remind the parents not to pressure their kids too much and to let them rest when they are not feeling well.
Opinions vary: although some on Chinese social media say it's very thoughtful for hospitals to set up areas where kids can study and read, others blame parents for pressuring their kids to do homework at the hospital instead of resting when not feeling well. pic.twitter.com/gnQD9tFW2c
— Manya Koetse (@manyapan) November 22, 2023
By Manya Koetse, with contributions from Miranda Barnes
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2023 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

No Quiet Qingming: From High-Tech Tomb-Sweeping to IShowSpeed & the Seven China Streams

From Trade Crisis to Patriotic Push: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Tariffs

China Trending Week 14: Gucci Fake Lipstick, Xiaomi SU7 Crash, Yoon’s Impeachment

Strange Encounter During IShowSpeed’s Chengdu Livestream

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng