China Insight
Why Russia Is Nicknamed the “Weak Goose” on Chinese Social Media
Multiple Chinese (military) bloggers started using the ‘weak goose’ (菜鹅) term in light of Russia’s fading victory.
Published
3 years agoon

THIS IS A PREMIUM CONTENT ARTICLE
While the latest developments in the Russia-Ukraine war are closely watched by millions of Chinese social media users, the ‘Weak Goose’ meme is becoming more popular among military bloggers and Weibo users, signaling a shift in online sentiments regarding Russia’s position and its military competence.
Since the beginning of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the latest developments regarding the war in Ukraine are a big topic on Chinese social media, where military bloggers, academics, political commentators, and ordinary netizens have been sharing their views on the conflict over the past seven months.
Back in February of 2022, many Weibo commenters expressed anti-war sentiments and worries about the situation of the Ukrainian people and Ukraine-based Chinese compatriots.
At the same time, there was also a growing group of Chinese netizens who said they supported Russia. One top commenter at the time wrote: “I resolutely support the Russian military action! This is the evil result of Ukraine following the Yankees (美国佬). We should seize the opportunity to liberate Taiwan and to recover the Diaoyu Islands.”
Those speaking out in favor of Putin and the Russian military mainly focused on anti-Western sentiments, and this online discourse was only strengthened by media narratives that also framed the Russia-Ukraine war – commonly referred to as Russia’s “special military operation” – within a Chinese context that stressed the humiliation and injustice suffered by China at the hands of the very same Western powers that were now condemning Russia and were trying to get China on their side (read more in this article).
Others also saw the Russian military invasion of Ukraine as a warning to Taiwan, semi-jokingly writing that Chinese troops could arrive in the morning, that unification would be completed by noon, and that they would all be raising the flag and singing the national anthem together the next day.
But now, seven months and nine days later, it is clear that Russia’s “special military operation” in Ukraine is anything but a quick ‘victory.’
“We’re Witnessing History”
This week, after Russia proclaimed the annexation of four territories in Ukraine, the Russia-Ukraine war has reached a pivotal phase and this is receiving a lot of attention on Chinese social media.
After a series of so-called “referendums” which supposedly showed it was the “will of the millions of people,” Putin claimed that Luhansk, areas of Donetsk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia were now part of the Russian Federation. Using increasingly threatening rhetoric, Putin said in his September 30 speech that Russia would defend these areas with “all the means at our disposal.” On Weibo, the topic received over 220 million views (#普京签署顿涅茨克等四地入俄条约#).
That very same day, Ukraine applied for fast-track NATO accession, and Ukrainian President Zelensky said that they are ready for peace talks with Russia, but only with a different Russian president. The topic of Ukraine’s application to join NATO became a trending topic on Weibo, receiving over 190 million views on Saturday (#泽连斯基签署乌克兰加入北约申请#).
When Jake Sullivan, the U.S. President’s National Security Advisor, stated that it was “not the right time” for Ukraine’s admission to the alliance, China Daily initiated the hashtag “Ukraine’s Application to Join NATO Is Met with a Cold Shoulder by the U.S.” (#乌克兰申请加入北约遭美国冷遇#).
On Sunday, news of President Zelensky declaring the key eastern Ukrainian town of Lyman “fully cleared of Russian forces” also became trending. A Weibo hashtag dedicated to the topic of Russian forces retreating from Lyman (#俄军从红利曼撤退#) received over 150 million views.
“We’re witnessing history,” some Chinese netizens commented, with others replying: “We’ve been witnessing history for the past two years already.”
Shifting Online Sentiments
But the online sentiments regarding the war in Ukraine have shifted over the past months, and there is now more emphasis on the weakness of the Russian military strategy. There are also more voices criticizing those who cheer for Putin.
Qu Weiguo (@曲卫国), a professor at Shanghai’s Fudan College of Foreign Languages and Literatures, denounced fellow Chinese who seemed “happy and excited” about Putin signing the decree annexing four regions of eastern Ukraine and who called it a “checkmate move” that put the West in a difficult position.
According to Qu Weiguo, these “patriotic” fellow Chinese – “I am not sure whether they actually love China or Russia,” he wrote – were overseeing the fact that it is not just the West that is being affected by the annexation, of which the legality is more than questionable. Qu mentioned the 2013 PRC-Ukraine Treaty of Friendship & Cooperation, which conveys Chinese support for Ukraine’s “sovereignty, security, and territorial integrity.” Qu suggests that in this context, China could not possibly recognize the four annexed territories as being part of Russia; and Beijng would also be obliged to support Ukraine in case it would be attacked by Russian nuclear weapons.
Author Du Zijian (@杜子建) also spoke out on Weibo, saying the referendum regarding the four regions claimed by Russia cannot be recognized: “It’s Ukrainian territory, it can’t be stolen by anyone.”

Image posted by Littlepigpig
Military blogger ‘Littlepigpig’ (@用户littlepigpig1), who focuses on the war in Ukraine, provided another perspective on the recent developments, suggesting that Putin’s nuclear rhetoric is just bluff and likely stems from despair over Russia’s inability to defeat Ukraine: “What would be the point of sending hundreds of thousands of Russians to Ukraine to be brutally slaughtered before launching a nuclear strike!?”
The ‘Weak Goose’ Meme
There are more people who now express that they see little chance of Russia winning this war. One regular Weibo user wrote: “The soldiers have no morale, the country has no money, and their equipment technology lags behind NATO.” “They’re so disappointing,” others wrote.
One term that recurringly comes up in these discussions, from Weibo to Zhihu, is that of ‘Weak Goose’ or ‘Noob Goose’ (菜鹅 cài’é).
The term, that has been surfacing for a few months, is a wordplay on 菜俄 (also cài’é), which means ‘Weak Russia’ and is short for “the weak Russian army” or “the noob Russian army” (“俄军很菜”).
Although ‘菜’ (cài) actually means ‘vegetable,’ it is also slang for ‘poor’ or ‘weak’ when used as an adjective (see this video for explanation), also comparable to the ‘noob’ internet slang term (meaning “newbie”, “inexperienced player”).
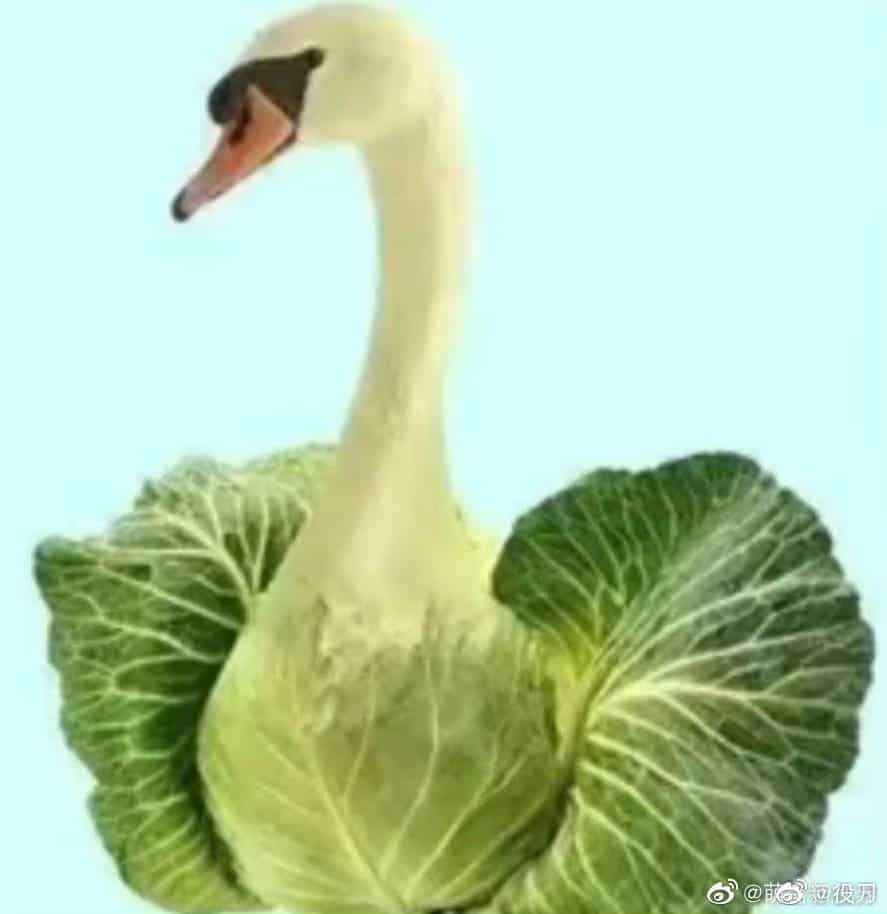

This image is another word play on ‘weak goose’, turning it into a ‘vegetable swan’ instead.
According to Jikipedia, ‘Weak Goose’ started to be used by Chinese political and military bloggers after they found that the Russian army advanced much slower than they had expected. They came up with the word to make fun of Russia struggling with basic military mistakes and low military capabilities.
Recently, instead of ‘weak goose,’ the term ‘weak Russia’ has also been used more often (so 菜俄 rather than 菜鹅; just for clarity, we’ll translate them both as ‘Weak Goose’ here). Russia is usually also nicknamed ‘big goose’ in China (大鹅) since the words for ‘goose’ and ‘Russia’ sound the same.
The past week, multiple Chinese (military) bloggers have started using this term again in light of Putin’s fading victory and the retreat from Lyman. Reports about Russian recruits allegedly being instructed to use tampons and pads on war wounds in light of a shortage of military supplies further strengthen the Weak Goose meme: “Who thought the ‘Weak Goose’ was so weak?”
Those using the ‘Weak Goose’ term are definitely not necessarily anti-Russian and also not pro-Ukrainian – they are just using the word as a joke and comic relief in a military conflict that has been dragging on for much longer than Chinese netizens had anticipated.
“The Russia-Ukraine conflict is not entertainment”
But not everyone on Weibo appreciates these kinds of jokes. “The Russia-Ukraine conflict is not some entertainment variety show,” one blogger (@Aglaia柒y) with over 220,000 fans wrote, criticizing those who are using the war as a source of drama and entertainment with Putin starring as the main “idol.”
Others also reminded people that the ‘Weak Goose’ is actually very resilient. Well-known finance blogger Liu Zhongling (刘忠岭), known under the alias of @笑看红绿, noted that there were many Chinese people cheering for the latest victory of the Ukrainian army recently. But according to Liu, it is not necessarily something to cheer about: “All the progress that the Ukrainian army is making now, comes at the cost of many injuries and military casualties. Considering that this war is going to take a long time, soldiers are far more important than weaponry.”
He added: “The ‘weak goose’ army is getting worn out (..) but by pulling back they are also preserving strength and that is not a bad choice. People who know their history already anticipated the Russians would get pulled down, but they also know the ‘Weak Goose’ is actually tough.”
Although the ‘Weak Goose’ meme is one that is just alive within particular online circles, it is telling of a shift in sentiments on Chinese social media regarding a conflict in which many initially believed Russia was like a strong brown bear fiercely attacking Ukraine, rather than a worn out goose nibbling on its neighboring country (reference post).
Chinese well-known political commentator Hu Xijin stirred away from any jokes. In his recent post on Weibo, he warned that “the world must be prepared for a further escalation of the war in Ukraine, even beyond Ukraine.”
By Manya Koetse
With contributions by Miranda Barnes.
Get the story behind the hashtag. Subscribe to What’s on Weibo here to receive our weekly newsletter and get access to our latest articles:
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2022 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China Insight
China Reacts: 3 Trending Hashtags Shaping the Tariff War Narrative
From historic speeches to trending slogans, this is China’s official media response to the US tariff escalation.
Published
2 days agoon
April 13, 2025
What do Mao’s 1953 Korean War speech and Yang Jiechi’s 2021 Alaska Summit remarks have to do with the escalating US–China trade war? In Chinese official media responses, history and emotionally charged rhetoric are used to clearly signal China’s stance and boost national confidence. Here, we explore three dominant narratives.
As you probably know by now, April 9 marked “D-Day” for Trump’s rollout of steep tariffs. On Chinese social media, the escalating trade war between China and the US dominated conversation, especially on that “D-Day Wednesday,” when nearly all of Weibo’s top 10 most-viewed hashtags were related to Trump’s tariffs and China’s retaliation.
Since developments are unfolding rapidly, here’s a quick recap:
- 🇺🇸💥 On Wednesday, April 2, President Trump announced steep new tariffs, including a universal 10% “minimum base tariff” on all imported goods, and an additional 34% reciprocal tariff specifically targeting China as part of the so-called “Liberation Day,” set to begin on April 9. Combined with pre-existing tariffs, this would bring the total tariff rate on Chinese goods entering the United States to over 54%.
- 🇨🇳⚔️On Friday, April 4, China’s State Council Customs Tariff Commission Office issued an announcement stating that, starting April 10, an additional 34% tariff would be levied on all imported goods originating from the United States, on top of existing tariff rates.
- 🇺🇸⚔️On Tuesday, April 8, Trump vowed to increase tariffs on Chinese exports by an additional 50% if Beijing would not withdraw its 34% counter-tariffs.
- 🇨🇳💥On Wednesday, April 9, China’s finance ministry announced it would further raise tariffs on US goods to 84% starting the following day, in retaliation for the newly imposed 104% tariff on Chinese goods.
- 🇺🇸💣On Wednesday, April 9, Trump then did a U-turn and halted the new steep tariffs for dozens of countries for 90 days, except for China, followed by yet another threat of an additional 21%, bringing those import taxes to 125%.
- 🇺🇸🚨On Thursday, April 10, it was clarified by the White House that tariffs on China would actually total 145%, combining the previously announced 125% with a 20% import tax levied for fentanyl smuggling.
- 🇨🇳💣On Friday, April 11, Chinese official channels reported that China would adjust its tariff measures on important goods from the US starting April 12, raising the rate from 84% to 125%. A related hashtag became no 1 trending topic on Weibo, where it received over 500 million views by Friday night (#对美所有进口商品加征125%关税#).
- 🇺🇸⬅️ On Friday, April 11, Trump’s administration announced that it will exempt smartphones, computers and some other electronic devices from the new tariffs, including the 125% levies imposed on Chinese imports (#特朗普政府再度退缩#; #美国免除智能手机电脑对等关税#).
There are hundreds of hashtags and trending topics circulating across Chinese platforms — from Weibo to Toutiao, from Kuaishou to Douyin — related to the latest developments in the US–China trade war. The topic is super popular, but censored comment sections and removed images also reveal just how sensitive it can be at times.
The biggest hashtags and slogans are those initiated and amplified by official channels. From press conferences to hashtags and visual propaganda, you can see a clear strategic media narrative that draws on history, national pride, and patriotism to frame recent developments, mobilize public sentiment domestically, and show China’s resilience to the rest of the world.
Here, I’ll highlight three hashtags that have recently become top trending, each representing a different kind of official narrative or rhetoric in response to the ongoing developments.
1. China Won’t Back Down
(China will see it through to the end #美方一意孤行中方必将奉陪到底#)
The message that China will not be intimidated by the US is one that echoes across Chinese social media these days, reinforced by official channels.
On April 9, the Weibo account of Chinese media outlet Guancha (@观察者网) and the state-run New Era China Foreign Affairs Think Tank (@新时代中国外交思想库) posted a video showing part of a speech given by Mao Zedong on February 7, 1953, during the final stages of the Korean War at the 4th Session of the 1st National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC).
In the short fragment, Mao Zedong says:
🇨🇳📢 “As to how long this war will last, we are not the ones who can decide. It used to depend on President Truman, and it will depend on President Eisenhower, or whoever becomes the next US President. It’s up to them. No matter how long this war is going to last, we’ll never yield. We’ll fight until we completely triumph.”

The 1953 speech by Mao was also posted on the US social media platform X by Mao Ning (@毛宁), spokesperson for China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The video was then also spread by blogging accounts and regular netizens. History blogger Zijin Gongzi (@紫禁公子), who has over 435k fans on Weibo, reposted the video, writing:
💬 “Our forefathers never bowed their heads to strong enemies. How could we easily accept defeat? (..) We must not lose this spirit, we must let everyone know that we have a strong backbone and will never bow down.”
Together with the Mao video, the hashtag used by the Think Tank and many other Chinese media accounts, such as People’s Daily (@人民日报), is “If the US obstinately clings to its course, China will fight to the end [lit. accompany them to the end]” (#美方一意孤行中方必将奉陪到底#) and “fight to the end” (#我们奉陪到底#).
These phrases in part come from a press conference given by Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson Lin Jian (林剑) on April 8. Here, he said:
🇨🇳📢 “I want to emphasize once again that there are no winners in trade wars and tariff wars, and protectionism is no way forward. The Chinese people do not provoke trouble, but they are also not afraid. Pressure, threats, and blackmail are not the proper ways to deal with China. China will inevitably take necessary measures and resolutely safeguard its legitimate rights and interests. If the American side disregards the interests of both countries and the international community and insists on waging a tariff war and trade war, China will fight to the end [lit. inevitably accompany them to the end 中方必将奉陪到底].”

The next day, these words had been turned into digital propaganda posters, with some slight variations in the phrases used. One People’s Daily graphic underlined: “We resolutely take countermeasures, and follow through until the end (坚决反制 奉陪到底),” accompanied by the line: “This is China’s attitude,” which was also turned into a hashtag (#这就是中国态度#).
2. This Is No Way to Deal with China
(Chinese people aren’t buying it #中国人从来不吃这一套#)
Another related yet somewhat different sentiment that dominates Chinese social media—led by official channels—is that China is not only rejecting the trade games played by the US, but is also distancing itself from the American playbook. The message is: this is no way to deal with China. This narrative, and the hashtag surrounding it, emerged slightly later than the first. While the earlier phrase about China not backing down trended as China matched the US in its tariff measures, this one took off with China’s final blow—raising the rate on US imports from 84% to 125% in response to the latest US tariff hikes.
The April 11 statement on the Ministry of Finance website (财政部网站), also posted on Weibo by Xinhua News (@新华社), announced that China would adjust its additional tariff measures on imports originating from the United States effective April 12. It also stated that China strongly condemns the US imposition of excessively high tariffs and will no longer engage in further tariff escalations:
🇨🇳📢 “Given that, at the current tariff level, US goods entering China effectively have no market viability, if the US continues to raise tariffs on Chinese exports to the US, China will no longer respond.”
The main hashtag used by Xinhua and many other media channels is “中国从来不吃这一套” (Zhōngguó cónglái bù chī zhè yī tào), which can be translated as: “The Chinese people have never accepted this,” or more colloquially, “We’re not buying it.”
The phrase initially became popular in 2021, after it was used by China’s top diplomat Yang Jiechi (杨洁篪) during the first major strategic talks of the Biden administration, held in Anchorage on March 19. Due to the occasionally heated exchanges between the two delegations, some called the Alaska talks a “diplomatic clash.”

Yang Jiechi during the Alaska Summit
At the time, Yang delivered a lengthy statement to US Secretary of State Antony Blinken and National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan, stressing that Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Xinjiang are “inseparable parts of China,” and that China strongly opposes US interference in its internal affairs. Suggesting the US should focus more on its own human rights issues and racial problems instead of lecturing China, he added the now-famous line: “The US is not qualified to speak to China from a position of strength. The Chinese people don’t buy that” (美国没有资格居高临下同中国说话,中国人不吃这一套).
The phrase quickly went viral—boosted by state media, celebrated by netizens, and turned into a marketing slogan. It now appears on t-shirts, teacups, phone cases, and other patriotic merchandise.

The translation of the phrase still triggers discussions. While merchandise typically translates it as “Stop interfering in China’s internal affairs,” that’s not an accurate translation. During the Alaska Summit, interpreter Zhang Jing (张京) (who gained viral fame at the time) translated it in real-time as “This is not the way to deal with the Chinese people.” However, some commentators and professional translators argued this was a missed opportunity to take a tougher stance, as the Chinese phrase is much sharper and could be loosely translated as: “We Chinese people don’t swallow this crap.”
In Alaska, Yang emphasized that dealing with China requires mutual respect, and that history will prove that trying to strangle China’s rise would ultimately hurt the US itself (“与中国打交道,就要在相互尊重的基础上进行。历史会证明,对中国采取卡脖子的办法,最后受损的是自己。”)
Similar sentiments now dominate online media discourse in China. The slogan has evolved from “The Chinese people don’t buy this” (中国人不吃这一套) to the more authoritative “China has never bought this” (#中国从来不吃这一套#)

Adding fuel to this message are hashtags like “America’s repeated imposition of excessively high tariffs on China has become a joke” (#美方对华轮番加征畸高关税已沦为笑话#).
Ridiculing America (especially Trump) has become a popular pastime on Chinese social media this past week, with a flood of Chinese and international memes circulating widely.

Especially popular are memes mocking the idea of America as a future “Made-in-America” manufacturing hub, the irony of iconic American products (like MAGA hats) being made in China, and how everyday essentials such as eggs have reached historic price highs in the US (a crisis partly caused by bird flu but now worsened by the tariffs).
On April 13, the hashtag “The 145% tariff makes one panda plush toy cost 80 dollars” (#145%关税让1只熊猫玩偶卖80美元#) also went trending, sparking jokes about how even the most trivial things could suddenly become luxuries in the US.
3. China is the Most Stabile Superpower
(Countering America’s madness with China’s stability #以中国稳应对美国疯#)
A third stance that has been dominant in Chinese official online discourse is that China’s development does not rely on anyone’s favors (#中国发展从不靠谁的恩赐#, derived from a quote by Xi Jinping), and that despite the US’s measures, China’s rise on the world stage cannot be stopped. In fact, the narrative suggests that these actions by the US are only accelerating China’s ascent.
A commentary piece published by state broadcaster CCTV (@央视新闻) on April 11 quoted Professor Li Haidong (李海东) of China Foreign Affairs University, who stated that the US’s increasingly aggressive behavior reinforces the notion that it is using tariffs as a tool of extreme pressure; as a weapon to serve its own interests. According to Li, this reflects America’s hegemonic mindset, aiming to assert superiority by intentionally creating crises.
But rather than strengthening the US, the commentary argues, these recent measures are backfiring and are damaging the US’s domestic economy and undermining its global credibility.
In contrast to the US’s presumed recklessness and “hysterical approach,” China is depicted as a “responsible world leader,” bringing certainty to an uncertain world by “responding with its own stability” and proving to be, supposedly, a more reliable engine of global growth. The commentary states:
🇨🇳📢 “As the tariff storm strikes, China is using its own ‘stability’ to resist the trials and tribulations, by upholding rules, defending justice, and steering the big ship of globalization through treacherous countercurrents, toward the right path of openness and cooperation.”
To promote the piece on social media, CCTV used the hashtag “Responding to America’s madness with China’s stability” (#以中国稳应对美国疯#).
This sentiment was echoed by nationalist bloggers, such as Tangzhe Tongxue (@唐哲同学), who posted on April 13:
💬 “In this world, besides China, the rest are all just a poorly equipped small-town theater troupe (草台班子).”
The phrase “草台班子” (cǎotái bānzi) literally refers to a makeshift opera troupe performing on a shabby rural stage, and is used to describe an incompetent group of amateurs.
The blogger’s comment indirectly responds to comments made by US Vice President JD Vance, who defended Trump’s tariffs in a Fox News interview by saying: “To make it a little more crystal clear, we borrow money from Chinese peasants to buy the things those Chinese peasants manufacture.”
That remark sparked controversy online, with many netizens calling it ignorant. Some pointed out that Chinese people were already wearing fine silks when Westerners were still wrapped in animal skins fishing in the sea, and flipping the narrative to portray Americans as the real “country bumpkins.”

Meme shared online.
This sentiment was reinforced by another hashtag trending on Weibo on April 13: “You think we’re scared, but we actually don’t care” (#你以为我们scared其实我们不care#).
That line comes from a Channel 4 interview with Gao Zhikai (Victor Gao/高志凯), Vice President of the Center for China & Globalization (CCG), who stated:
🇨🇳📢 “China is fully prepared to fight to the very end. Because the world is big enough that the United States is not the totality of the market in the world. So if the United States wants to go in that direction of completely shutting itself out of the Chinese market, be my guest. [Interviewer: Yes and China will lose the US market..] We don’t care. We don’t care. China has been here for 5000 years, and for most of the time there was no United States and we survived. If the United States wants to bully China, we will deal with the situation without the United States. And we except to survive for another 5000 years.”
While this reflects the official position and is widely echoed across social media, others stress the importance of remembering history; particularly China’s “Century of Humiliation” (百年国耻), which was marked by war, aggression, and unequal treaties imposed by foreign powers. Just like other historical anniversaries, some bloggers argue that Trump’s tariff “D-Day,” April 9, should not be forgotten (“今天是每个中国人难以释怀的日子”) and that it marks another reason for China’s renewed rise.
In a video posted by CCTV’s short video platform Xiaoyang Shipin (小央视频) on April 13 (link), the narrator states:
🇨🇳📢 “The so-called global “beacon” now puts “America first.” It slaps allies in the face, treats the world with predatory practices, and makes other countries pay for MAGA, pushing the fragile word economy over the edge, and pitching itself against the whole world. With China here, the sky won’t fall. With around 5% economic growth, China adds the output of a mid-sized European economy every year. China has hundreds of millions of skilled workers. The Chinese people are well known for their strong work ethic. China’s development over the past seven decades is a result of self-reliance and hard work, not favors from others, (..) Global businesses believe the next China is still China and the best is yet to come (..) Markets need to restore faith. Between the pond of closed markets, and the ocean of economic interconnectivity, which one would you choose?”
Overall, packaged across different media — from hashtags to short videos, from press conferences to news reports, and from digital slogan posters to Ministry of Foreign Affairs tweets — China’s strategic political media messaging is clear and quite powerful, despite the fragile and censored environment it operates in: China is not afraid to strike back, China will lead with calm, and eventually, China will emerge as the winner. Whatever happens next remains to be seen, but when it comes to turning crisis into opportunity, China’s official media channels have already done just that.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Insight
From Trade Crisis to Patriotic Push: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Tariffs
“This moment is the time to reflect on our unity. If we can choose domestic alternatives, we should.”
Published
1 week agoon
April 5, 2025
“China’s countermeasures are here” (#中方反制措施来了#). This hashtag, launched by Party newspaper People’s Daily, went top trending on Chinese social media on Friday, April 4, after President Trump announced steep new tariffs on Wednesday, including a universal 10 percent “minimum base tariff” on all imported goods and especially targeting China with an additional 34% reciprocal tariff as part of so-called “liberation day.”
Countermeasures were announced on Friday. China’s State Council Customs Tariff Commission Office (国务院关税税则委员会办公室) issued an announcement stating that, starting from April 10, an additional 34% tariff will be levied on all imported goods originating from the United States, on top of existing tariff rates.
Other countermeasures include immediate export restrictions on seven key medium to heavy rare earth elements, which are important for manufacturing critical products used in semiconductors, defense, aerospace, and green energy.
“This won’t make America great again”
The official response to the tariffs, both from state media and the government, has been twofold: on the one hand, it criticizes the U.S. for placing American interests above the good of the global community, arguing that the move only hurts the U.S., its people, and the world. On the other hand, the Chinese side stresses that although they do not believe tariff wars are the answer, China is not afraid of a trade war and will not sit idly by, but will respond with equal measures.
Chinese official media have condemned the new tariffs, which led to the largest single-day market drop in years. Describing the reactions of various experts, Xinhua News highlighted a comment by a Croatian professor, stating that the policy will only increase export prices and worsen inflation, ultimately hurting middle- and working-class Americans — and noting that the policy “won’t make America great again” (不会“让美国再次伟大”).
The official announcement by Chinese state media regarding China’s countermeasures received widespread support in its (highly controlled) comment sections, with both media outlets and netizens echoing the message that China will not be bullied by the U.S.
On Xiaohongshu, similar sentiments shnone through in popular posts, such as one person writing:
💬 “Congratulations to the U.S. on receiving a 34% tariff on all its goods! Luckily, very few of the things ordinary Chinese people eat or use come from the U.S. anyway.
#RMB purchasing power #China will inevitably be unified #Consumer confidence #Contemporary Chinese economy #Carrying forward the construction of a Beautiful China”

“Monday’s stock market will be a bloodbath,” another commenter wrote.
One Weibo blogger (@兰启昌) saw the recent developments as another sign of an ongoing trend of “de-globalization” (逆全球化).
But beyond global economics and geopolitics, many Chinese netizens — from Weibo to Xiaohongshu — seem more focused on how the new policies will affect everyday consumers.
Netizens have been actively discussing which goods will be hit hardest by the new tariffs. Based on 2023 trade data, here’s a breakdown of the top exports between China and the United States — and the sectors most likely to feel the impact.
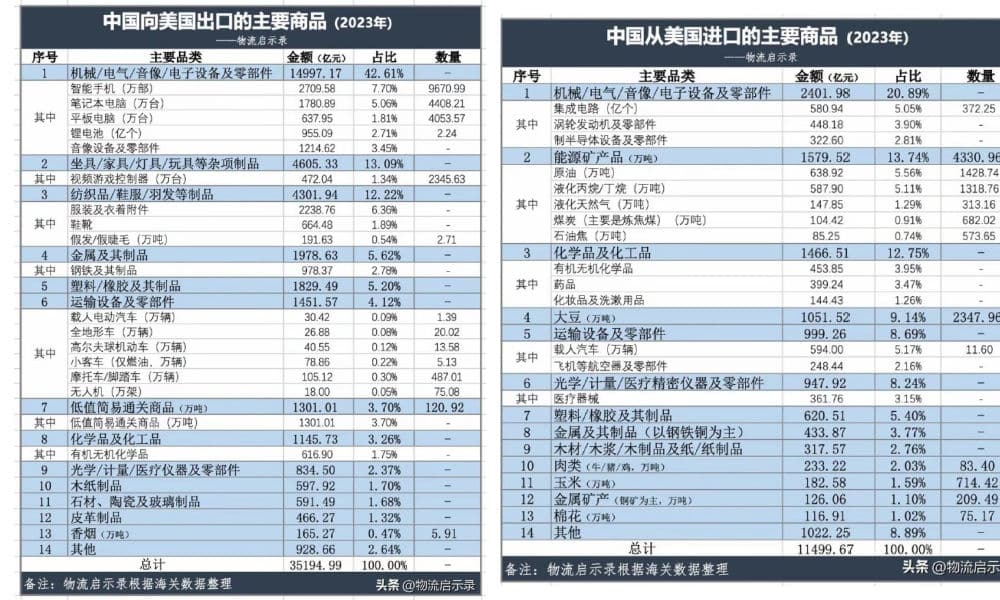
🔷🇺🇸🇨🇳Top 10 Chinese Exports to the U.S.
1. Electronics and Machinery
Includes smartphones, laptops, tablets, integrated circuits, and image processing equipment.
2. Furniture, Home Goods & Toys
Such as video game consoles, lamps, and much more.
3. Textiles and Apparel
Garments, footwear, and accessories like sunglasses.
4. Metals and Related Products
Especially steel and steel-based items.
5. Plastic and Rubber Products
Widely used in packaging, manufacturing, and consumer goods.
6. Transportation Equipment
Electric vehicles, passenger cars, motorcycles, scooters, and drones.
7. Low-Value Commodities
Bulk items used in general trade and low-cost manufacturing.
8. Chemicals
Industrial chemicals and related materials.
9. Medical and Optical Instruments
Includes medical devices and precision instruments.
10. Paper Products
Ranging from office supplies to industrial paper goods.
🔹🇨🇳🇺🇸Top 10 U.S. Exports to China
1. High-Tech Machinery and Electronics
Especially integrated circuits, turbine engine components, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
2. Energy Products
Crude oil, liquefied propane and butane, natural gas, and coking coal.
3. Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
Includes cosmetics, cleaning agents, and various medical drugs.
4. Soybeans
A key agricultural export widely used in food and animal feed in China.
5. Transportation Equipment
Such as automobiles and aircraft parts.
6. Medical and Optical Devices
Medical precision equipment, diagnostic tools, and lab instruments.
7. Plastic and Rubber Goods
Used in both consumer and industrial sectors.
8. Metal Products
Primarily iron and steel exports.
9. Wood and Pulp Products
Lumber, wood pulp, charcoal, and paper goods.
10. Meat
Including beef, pork, and poultry.
Those doing trade with the US, or otherwise involved in made-in-China products, like those working clothing and furniture factories, will inevitably be affected by the tariffs.
“Patriotism isn’t just a sentiment – it’s an action”
Much of the popular online conversation has focused on concrete examples of what kinds of things might get more expensive for Chinese consumers in their everyday lives.
Some bloggers noted that people might start to see price hikes in everyday groceries like dairy, meat, corn, and soybeans. With fewer soybeans coming in from the US, cooking oil prices may also rise.
China is the world’s largest consumer of soybeans, but because domestic production is relatively low, soybeans remain a key import.
Then there are popular American brands in the Chinese market that are expected to get pricier too — like beauty and health products, Starbucks coffee, or Häagen-Dazs ice cream.
Some also predicted a 30% to 40% increase in prices for iPhones and other Apple products.
Contrary to the earlier comment by the Xiaohongshu blogger, some netizens explain just how many American products are actually used by Chinese consumers, with many American companies operating in China — from McDonald’s and Coca-Cola, Walmart to Disney or Warner Brothers, Procter & Gamble to Colgate and Estée Lauder.
What’s noteworthy in these discussions, however, is a strong tendency to point to Chinese alternatives and encourage smart buying instead of following hypes (“理性替代,拒绝跟风”): No need to panic about soybeans — there are domestic alternatives, and China’s own soybean program is getting a boost. Who needs Starbucks when there’s Luckin Coffee? Why buy an iPhone when you can get a Huawei? Skip the Tesla, go for a BYD.
In these discussions, the ‘crisis’ is turned into an ‘opportunity’ for Chinese companies to focus even more on the Chinese market, and for Chinese consumers to, more than ever, actively embrace and celebrate local brands and made-in-China products.
One Chinese blogger (@O浅夏拾光O) wrote:
💬 “This moment is the time to reflect on our unity. If we can choose domestic alternatives, we should. For example, we can use rapeseed oil or peanut oil instead of imported soybean oil; we can buy cost-effective Chinese electronics instead of foreign brands. Support domestic products and respond to the nation’s call to expand domestic consumption.
We must have faith in our country. Only by uniting as one, young and old all together, the entire country working together, can we withstand all hazards. As Professor Ai Yuejin (艾跃进) once said, patriotism isn’t just a sentiment – it’s an action. As long as our core is stable and we are united in spirit, no hardship can defeat us.”
Despite the major happenings and the big words, some people just care about the small things: “As long as KFC and McDonald’s don’t raise their prices, it’s all fine by me.”
See the follow-up to this article here.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

China Reacts: 3 Trending Hashtags Shaping the Tariff War Narrative

No Quiet Qingming: From High-Tech Tomb-Sweeping to IShowSpeed & the Seven China Streams

From Trade Crisis to Patriotic Push: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Tariffs

China Trending Week 14: Gucci Fake Lipstick, Xiaomi SU7 Crash, Yoon’s Impeachment

Strange Encounter During IShowSpeed’s Chengdu Livestream

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Beyond the Box Office: What’s Behind Ne Zha 2’s Success?

Weibo Watch: A New Chapter

15 Years of Weibo: The Evolution of China’s Social Media Giant

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

IShowSpeed in China: Streaming China’s Stories Well

TikTok Refugees, Xiaohongshu, and the Letters from Li Hua

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?

US-Russia Rapprochement and “Saint Zelensky”: Chinese Online Reactions to Trump’s Shake-Up
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Digital10 months ago
China Digital10 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI
-

 China Arts & Entertainment11 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment11 months agoSinging Competition or Patriotic Fight? Hunan TV’s ‘Singer 2024’ Stirs Nationalistic Sentiments
-

 China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago
China Arts & Entertainment12 months ago“Old Bull Eating Young Grass”: 86-Year-Old Chinese Painter Fan Zeng Marries 36-Year-Old Xu Meng






an
October 4, 2022 at 7:11 am
In fact, weak goose is not proper. Using “noob goose” is more exact. 菜 have mean for noob(菜鸟 in Chinese)
from a Chinese netizen