China Arts & Entertainment
Why the Gay Kisses in ‘Bohemian Rhapsody’ Won’t Make It to Chinese Cinemas
Fresh off its Oscar wins, “Bohemian Rhapsody” will hit theaters in China, but some scenes won’t make it to the Mainland.
Published
6 years agoon

First published
The award-winning movie Bohemian Rhapsody is set to debut in mainland China later this month but foreign media reports on censorship of gay scenes within the movie have prompted animated discussion on Chinese social media. Why are these scenes being cut at all? What’s on Weibo explains.
In March 2019, Bohemian Rhapsody, a biopic on the life and career of Freddie Mercury, will be released in theatres across mainland China, with various Chinese news outlets identifying the Chinese National Alliance of Arthouse Cinema (全国艺术电影联盟) as the movie’s distributor.
The National Alliance of Arthouse Cinema is a non-profit film distribution organization established in 2016. According to QDaily, the organization cooperates with major Chinese cinemas in distributing films throughout the country and has some 1500 member cinemas – about 3% of the country’s total number of movie theatres.
Various foreign media outlets, including The Guardian and The Hollywood Reporter, report that portrayals of drug use and several intimate kisses between Mercury and other male characters will be cut from the Chinese version of the film, a decision that has been regarded as controversial by social media users both inside and outside of China.
Film Censorship in China
The Chinese movie industry is an area that has always been subjected to strict control and censorship. The first movie censorship laws in China were implemented as early as the 1930s, carried out by the Central Film Inspection Committee since 1931, with the purpose of legally prohibiting movies deemed “offensive to the Chinese public” (Pang 2011, 463; Zhu 2003, 202).
Theatrical releases in China are controlled by the SARFT (State Administration for Radio, Film, and Television), which is overseen by the Propaganda Department of the Communist Party (Grimm 162-163).
Throughout the years, China’s censorship apparatus has affected the screening of hundreds of foreign films in the PRC in a multitude of ways. The famous Titanic scene in which Rose (Kate Winslet) poses naked for Jack (Leonardo DiCaprio), for instance, was cut from the Chinese version. In Mission: Impossible III a scene in which Ethan Hunt (Tom Cruise) distracts two Chinese henchmen and kills one was also eliminated in China.
In March 2017, a new film censorship law came into force in mainland China, officially titled the ‘Film Industry Promotion Law of the People’s Republic of China’ (中华人民共和国电影产业促进法), laying out the regulations for prohibited content and content that must be cut. The law applies to the various pre-shooting and pre-screening stages, and is meant to “promote the healthy and prosperous development of the film industry.”

The law, as outlined here, stipulates that, among other things, movies cannot contain any elements that, for example:
- violate, resist, or undermine the basic principles of the constitution
- “harm national unity, sovereignty, or territorial integrity” or “damage the national dignity”
- “slander ethnic cultural traditions” or “instigate hostility towards ethnic groups”
- damage the “mental health of minors”
- harm China’s “social morality” or disturb the “order of society”
- promote “obscenities,” “gambling,” “drug abuse,” or “violence”
Although some of the stipulations in the law are straightforward, there are also many parts that are vague. How does one determine what is harmful to the “mental health of minors”? Is there an objective way to judge whether a film is “hurting the feelings of ethnic groups”? What is the censors’ definition of “obscene”?
In the end, these regulations leave ample room for the main censorship body, the SARFT, to determine case-by-case how and if foreign films that have been allowed to be screened in mainland China should be altered to stay ‘in line’ with the country’s strict censorship policies.
Banning Gay Content?
Homosexuality is no longer illegal in mainland China since 1997, and has been removed from a list of mental illnesses since 2001, but bans on content displaying homosexuality have made headlines over the years, highlighting the general discomfort of Chinese regulators towards gay-themed dramas and films.
In early 2016, Chinese State Administration released new regulations banning “homosexuality” in filmography for conveying “unnatural” values of love (Guangming Online). That same year, China’s popular gay-themed web series Addiction (上瘾) was yanked by censors due to disapproval at the plot’s lengthy exploration of homosexuality. A year later, Chinese regulators laid out rules stating that online videos showing “displays of homosexuality” were no longer allowed. In 2018, gay romance Call Me by Your Name was suddenly pulled from the Beijing film festival.
At the same time, there is no shortage of examples that show homosexuality has some leeway in China’s (online) film and media landscape. Last year, 2018, saw the mainland release of gay movie Seek McCartney (Looking for Rohmer) (寻找罗麦). Thai gay-themed film Fathers was released on popular video platform Bilibili in 2017.

Chinese version of Thai gay-themed film “Fathers” or “Two Fathers”
An online video showing a young Chinese man coming out to his parents as gay became an online hit in 2015. And now, in 2019, Bohemian Rhapsody, centered around one of the LGBT community’s most global cultural icons, is set to hit the big screen in China – albeit censored.
Mixed signals? Confused censors? Not necessarily. According to renowned Chinese sexologist Li Yinhe, the Chinese government is not against homosexuality per se. At an Amsterdam symposium in 2014, the LGBT rights activist stated that “the government is not against homosexuality, but against sex in general.”
Such a stance was made explicit with the March 2017 Film Industry Promotion Law, which, in the words of a Beijing-based film director, has since forced many in the industry to “prioritize education over art” so that their work can get past the censors. Any scenes including (explicit) portrayals of prostitution, LGBT relations, extramarital affairs, polyamory, or pornography, will generally not be permitted to reach a large Chinese audience, wrapped in conservative rhetoric that accuses such scenes of “promoting obscenities” or being “harmful to the healthy development of Chinese minors.”
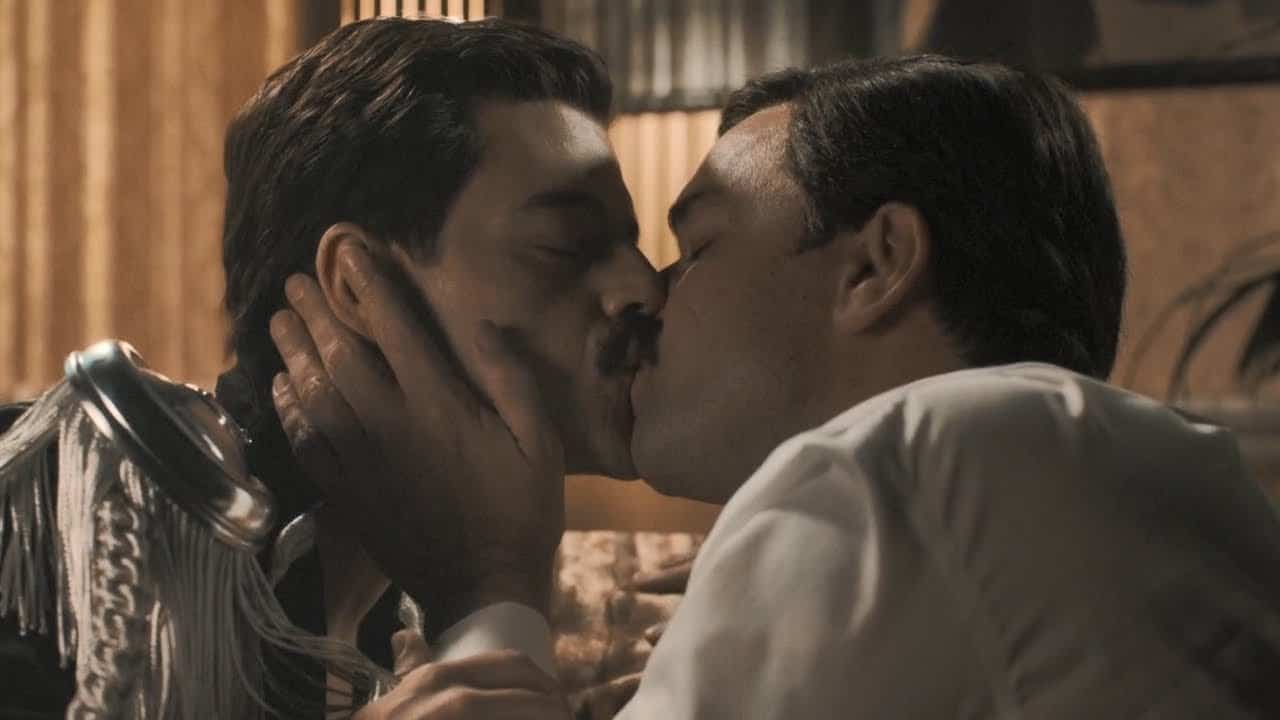

At a time of a rapidly transforming (and aging) China, “healthy content” is mostly the kind of content that depicts the conventional family – marriage and children – as the cornerstone of a stable Chinese society. Depictions of Freddy Mercury kissing other men, apparently, does not fit the ideal family model propagated by Chinese authorities; with the government’s ongoing trumpeting of the two-child policy, homosexuality’s refusal to be dictated by the laws of biological fertility may also be one of the many reasons motivating the censors’ decision to tone down the ‘gayness’ of Bohemian Rhapsody.
Weibo Responses
On Weibo, news about censorship of the Chinese release of Bohemian Rhapsody became a trending topic.
Although a large number of netizens are happy that the movie will be released in China, there are also many dissatisfied with the censorship that comes with it.

Some people argue that the selective cutting of scenes will be detrimental to the overall quality of the movie. Popular Weibo user ‘Gongyuan 1874’ (@公元1874), a self-proclaimed ‘author’ and ‘cultural critic’ with more than 3 million online followers, wrote a lengthy post on February 28 in which he describes Freddie Mercury as a “rebel fighter” whose life was defined by freedom. The author argues that the “artistic value of the movie is “greatly reduced” by censoring those parts that show Mercury letting himself go.
Some commenters are so disgruntled at the movie’s censorship that they are boycotting it. One Weibo user wrote: “Because I want to protest against the unfair treatment of LGBT by authorities, I will not go and see the edited version of Bohemian Rhapsody.”
“I’d advise everyone to go and get a pirated version of the movie,” another commenter writes: “Homosexuality and drugs were a part of Freddie Mercury’s life, to ‘castrate’ this movie is disrespectful [to his memory].”
There are also some more moderate netizens, well aware of the current restrictions placed on the film and TV industry, who argue that cutting some scenes – total scene time cut from the Chinese release is alleged to be no longer than two minutes – will leave the message conveyed by the movie unharmed, and that viewers should be grateful such a film is being screened in China at all.
“I have been watching the comments about Bohemian Rhapsody and the deleted gay scenes,” one music blogger writes: “Some people think it’s an insult to Freddie Mercury, and say we should boycott the movie. I think this kind of reasoning doesn’t show much goodwill.”
The blogger argues: “I think Freddie Mercury is a great singer, a well-respected artist, and an icon of his time – not just a representative for gays. The exploration of his own identity was a major influence in his life and artistic work, but if you insist on discussing the content of the film, the legendary experiences of the band…their artistic achievements and rock ‘n roll spirit are all relevant – all in all, don’t hold on to sexual orientation [as the most crucial theme].”
There are some who might agree, asking “is it necessary to screen those deleted gay scenes in China?”
Amid hundreds of comments on the issue, there is no clear consensus. While some point out that the Chinese release of a movie such as Bohemian Rhapsody is a sign of ‘progress’ in a strictly controlled media environment, others see its censorship as doing a disservice to the film’s main themes of artistic freedom and LGBT emancipation.
However, in an age where censors even go after heterosexual, ancient Chinese dramas, the mere entry of Bohemian Rhapsody into the Mainland perhaps suggests an atypical loosening of the stranglehold being placed on China’s TV and film industry. Any way the wind blows, apparently, does really matter to Chinese netizens.
By Manya Koetse , edited by Eduardo Baptista
References [online sources via in-text hyperlinks]
Grimm, Jessica. 2015. “The Import of Hollywood Films in China: Censorship and Quotas.” Syracuse J. Int’l L. & Com. 43 (1): 155-190.
Pang, Laikwan. 2011. “The State Against Ghosts: A Genealogy of China’s Film Censorship Policy.” Screen 52 (4): 461-476.
Zhu, Ying. 2003. Chinese Cinema During the Era of Reform: The Ingenuity of the System. Westport, Connecticut, London: Prager.
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please email us.
©2019 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China ACG Culture
“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?
Published
2 weeks agoon
January 21, 2025
FROM THE WEIBO WATCH PREMIUM NEWSLETTER
Is Chinese game sensation ‘Black Myth Wukong’ making a jump from gaming screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala? There’s already some online excitement over a potential performance at the biggest liveshow of the year.
The countdown to the most-watched show of the year has begun. On January 29, the Year of the Snake will be celebrated across China, and as always, the CMG Spring Festival Gala, broadcast on CCTV1, will air on the night leading up to midnight on January 28.
Rehearsals for the show began last week, sparking rumors and discussions about the must-watch performances this year. Soon, the hashtag “Black Myth: Wukong – From New Year’s Gala to Spring Festival Gala” (#黑神话悟空从跨晚到春晚#) became a topic of discussion on Weibo, following rumors that the Gala will feature a performance based on the hugely popular game Black Myth: Wukong.
Three weeks ago, a 16-minute-long Black Myth: Wukong performance already was a major highlight of Bilibili’s 2024 New Year’s Gala (B站跨年晚会). The show featured stunning visuals from the game, anime-inspired elements, special effects, spectacular stage design, and live song-and-dance performances. It was such a hit that many viewers said it brought them to tears. You can watch that show on YouTube here.
While it’s unlikely that the entire 16-minute performance will be included in the Spring Festival Gala (it’s a long 4-hour show but maintains a very fast pace), it seems highly possible that a highlight segment of the performance could make its way to the show.
Recently, Black Myth: Wukong was crowned 2024’s Game of the Year at the Steam Awards. The game is nothing short of a sensation. Officially released on August 20, 2024, it topped the international gaming platform Steam’s “Most Played” list within hours of its launch. Developed by Game Science, a studio founded by former Tencent employees, Black Myth: Wukong draws inspiration from the classic Chinese novel Journey to the West. This legendary tale of heroes and demons follows the supernatural monkey Sun Wukong as he accompanies the Tang Dynasty monk Xuanzang on a pilgrimage to India to retrieve Buddhist scriptures. The game, however, focuses on Sun Wukong’s story after this iconic journey.
The success of Black Myth: Wukong cannot be overstated—I’ve also not seen a Chinese video game be this hugely popular on social media over the past decade. Beyond being a blockbuster game it is now widely regarded as an impactful Chinese pop cultural export that showcases Chinese culture, history, and traditions. Its massive success has made anything associated with it go viral—for example, a merchandise collaboration with Luckin Coffee sold out instantly.
If Black Myth: Wukong does indeed become part of the Spring Festival Gala, it will likely be one of the most talked-about and celebrated segments of the show. If it does not come on, which we would be a shame, we can still see a Black Myth performance at the pre-recorded Fujian Spring Festival Gala, which will air on January 29.

Lastly, if you’re not into video games and not that interested in watching the show, I still highly recommend that you check out the game’s music. You can find it on Spotify (link to album). It will also give you a sense of the unique beauty of Black Myth: Wukong that you might appreciate—I certainly do.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2025 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Chinese Movies
Why Chinese Hit Movie “Her Story” is ‘Good Stuff’: Stirring Controversy and Celebrating Female Perspectives
China’s end-of-year movie hit, Her Story, is sparking debates and highlighting the rising influence of Chinese female directors.
Published
2 months agoon
December 7, 2024
The Chinese comedy-drama Her Story (好东西, literally “Good Stuff”), directed by Shao Yihui (邵艺辉), has been gaining attention and sparking discussions on Weibo since its late November release in mainland China.
The film features an all-star cast including Song Jia (宋佳), Zhong Chuxi (钟楚曦), Zeng Mumei (曾慕梅), Zhao Youting (赵又廷), and Zhang Yu (章宇). It tells a quirky yet heartfelt story about two women: Wang Tiemei (王铁梅), a self-reliant single mom juggling life and work, and Xiao Ye (小叶), a free-spirited young woman navigating her chaotic relationships.
Their friendship begins when Xiao Ye starts babysitting Tiemei’s nine-year-old daughter, Wang Moli (王茉莉). Xiao Ye introduces her drummer friend, Xiao Ma (小马), to teach Moli how to play the drums, but Xiao Ma’s presence stirs jealousy in Tiemei’s unemployed ex-husband, who schemes to regain his place in the family. Blending humor with poignant insights, the film explores themes of imperfect love, friendship, and the messy process of rebuilding lives.

(“Her Story” poster and the director Shao Yihui)
The film also addresses a range of hot societal issues through dialogues woven into everyday interactions, touching on topics like menstruation stigma, sexual consent, feminism, and how family dynamics can impact personal development.
In just eight days, Her Story surpassed 300 million RMB ($41 million) at the Chinese box office (#好东西票房破3亿#). Two days later, on December 2, it exceeded 400 million RMB (#好东西票房破4亿#), and on December 7 news came out that it had surpassed the 500 million RMB ($68.7 million) mark at the box office.
The film also achieved an impressive 9.1/10 rating on Douban, a Chinese platform similar to IMDb, making it the highest-rated domestic film on Douban in 2024.
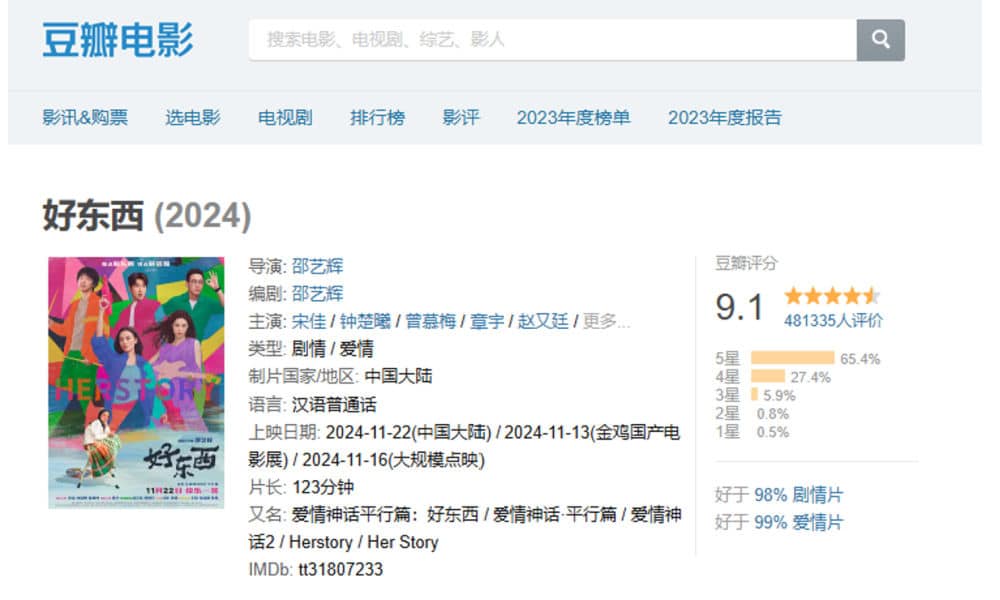
(“Her Story” on Douban)
Notably, 65.4% of voters awarded it five stars, while only 0.5% gave it one star.
Conflicting Views: From Feminist Film to Chick Flick
Despite its huge success, it is almost unavoidable for a movie this big to come without controversy. The film sparked debate on Hupu (虎扑), a platform focused on sports and men’s lifestyle, where it received a lower score of 5/10. While 33.1% of users gave it five stars, 58.4% rated it one star, reflecting divided opinions.
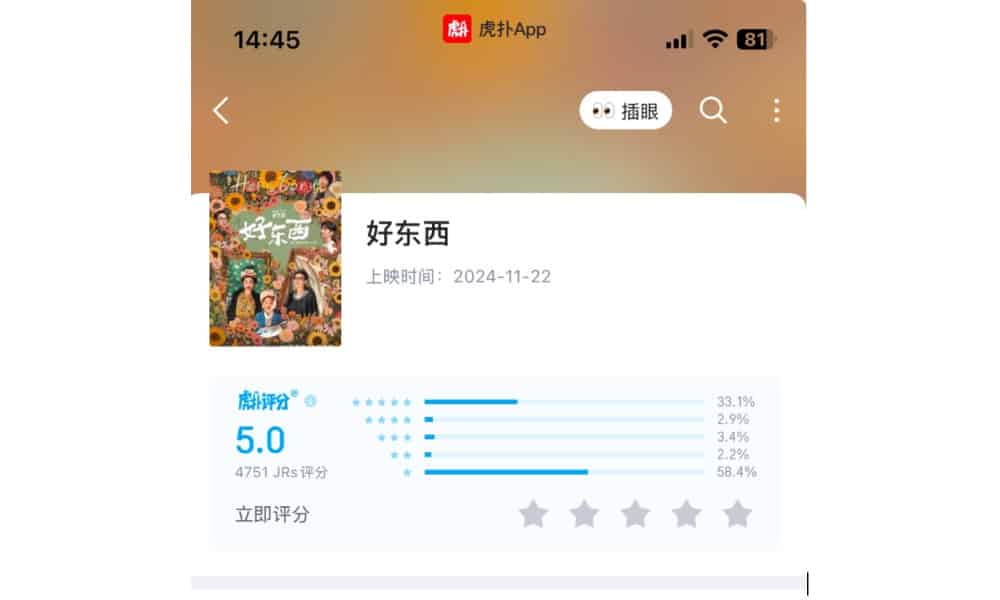
(“Her Story” on Hupu)
Much of the criticism comes from male viewers who feel the film undermines men by portraying them in non-traditional ways and omitting proper names for male characters, such as referring to the ex-husband only as “the ex-husband” (前夫). On the other hand, many female viewers resonate with the film’s female-centered perspective, with one scene blending household sounds and Xiao Ye’s recordings praised as a standout cinematic moment of 2024.
Interestingly, not all women appreciated the film either. A Weibo user, identified as a female scriptwriter for two Chinese TV dramas, emphasized that most of the producers of the film are male. She accused the director of hypocrisy, claiming Shao accepts money and resources from privileged men to create films that encourage female audiences to look down on average men.
She wrote, “I hope that everyone who believes in the ‘ghg’ [girl help girl] myth and supports female idols will also congratulate the male producers who will earn a lot of money from the film.”
Zhou Liming (周黎明), one of China’s most influential film critics, noted two extreme perspectives in film reviews. Some critics label the film as a “boxer film” (拳师电影) or an “extreme feminist film.”
However, the film itself suggests otherwise, as reflected in Moli’s line, “I don’t want to box,” when her father tries to convince her to take up boxing. Some audiences interpreted the line as rejecting extreme feminist messages.
In China, the term “boxer” (拳师) is used to critique certain feminists. The second character in the word for feminists (“权” [quán] in 女权主义者) is pronounced the same as the first character in “boxer” (“拳” [quán] in 拳师). This term often mocks behaviors seen as overly aggressive or lacking nuance in feminist discourse, such as avoiding dialogue or oversimplifying social issues.
Some also dismissed the film as a “chick flick,” a casual term for romantic comedies, which Zhou argued unfairly minimizes its significance. He likened the film to Woody Allen’s Annie Hall, suggesting that, much like Allen’s work, Her Story transcends gender differences and reflects the cultural zeitgeist of its time.
Despite the controversy, the film has been praised by notable figures like actor Zhang Ruoyun (张若昀), who called it “super good, super awesome, and super cute” (“超级好、超级牛、超级可爱的东西”). Zhang described the movie as tackling absurd yet realistic issues from a female perspective with humor and depth.
The Increasing Influence of Female Directors in China
At the end of Her Story, Tiemei’s daughter, Moli, nervously prepares for her first drum performance. Despite her hesitation, she gathers her courage and steps on stage. This moment reminded some viewers of a similar scene in another female-directed film this year, YOLO (麻辣滚烫), where the protagonist gears up for a boxing match.
YOLO is a 2024 comedy-drama directed by Jia Ling (贾玲), starring Jia Ling and Lei Jiayin (雷佳音). A comedic adaptation of the Japanese film 100 Yen Love (2014), it tells the story of Du Leying (杜乐莹), a woman facing personal struggles who turns to boxing after meeting coach Hao Kun (昊坤). Through her journey, she finds a new direction in life after their breakup. Grossing USD 496 million worldwide, YOLO became the highest-grossing Chinese film of 2024.
These parallels between Her Story and YOLO highlight a broader trend: the growing prominence of female directors in Chinese cinema. Beyond the discussions of plot and central themes, Her Story reflects the increasing success and influence of women filmmakers in the industry.
In 2024, female directors have made a notable impact on Chinese cinema, with their films achieving both critical acclaim and box office success. Their works also spark conversations about the need for more diverse perspectives in the industry.

(“The Last Frenzy” poster and the director Wu Rina)
The Last Frenzy (末路狂花钱), directed by Wu Rina (乌日娜), premiered on May 1. This comedy follows Jia Youwei (贾有为), a man diagnosed with a terminal illness, who decides to sell his assets and live fully with his friends. Despite mixed reviews and a Douban score of 5.9, the film grossed over 700 million RMB ($96 million) by May 31, becoming a major box office hit.

(“Stand By Me” poster and the director Yin Ruoxin)
Stand By Me (野孩子, literally “Wild Kids”), directed by Yin Ruoxin (殷若昕), premiered on September 13. Starring Wang Junkai (王俊凯), it tells the story of two neglected children, Ma Liang (马亮) and Xuan Xuan (轩轩), who form a makeshift family while facing life’s challenges. With a Douban rating of 6.7, the film grossed 241 million RMB by October 9.

(“Like A Rolling Stone” poster and the director Yin Lichuan)
Like A Rolling Stone (出走的决心, literally “The Determination to Leave”), directed by Yin Lichuan (尹丽川), premiered the same week as Stand By Me. Inspired by Su Min (苏敏), a 50-year-old woman who embarked on a solo road trip, the film explores themes of self-discovery and the struggles of neglected women. Featuring Yong Mei (咏梅), the film earned praise for its authenticity, achieving a Douban score of 8.8 and grossing over 123 million RMB.
To the Wonder (我的阿勒泰, literally “My Altay”), a film-like TV drama directed by Teng Congcong (滕丛丛), adapts Li Juan’s (李娟) memoir. Starring Ma Yili (马伊琍), it tells the story of Li Wenxiu (李文秀), a young woman finding her place in her hometown of Altay after setbacks in the big city. Known for its poetic storytelling and portrayal of ethnic harmony, the series has a Douban score of 8.9 from over 300,000 ratings, ranking among the top dramas of 2024.
“An Era Where Women Are Being Seen”
The growing influence of female directors has sparked discussions about how women’s perspectives are challenging traditional storytelling.
Some Weibo users compared a scene from Her Story, where Tiemei scolds a man for urinating roadside, to a similar moments in YOLO. In YOLO, Hao Kun’s attempt to urinate roadside is humorously interrupted by car headlights. Such scenes highlight how female directors reinterpret everyday behaviors, inviting audiences to question societal norms.
Her Story has already been released in several countries, including the United States, Australia, Germany, and the United Kingdom, with more international releases to follow.
The success of Her Story, the conversations it inspires, and its contribution to highlighting female perspectives in film reflect the evolving dynamics of contemporary cinema and the strengthening of female voices in traditionally male-dominated industries.
On Weibo, many view this as a positive development. One commenter wrote:
“Her Story [好东西/”Good Stuff”] is truly ‘good stuff.’ (..) At the start of this year, I watched YOLO, and at the end of this year, I watched Her Story. Suddenly, I feel very grateful to live in this era—the era where women are gradually being ‘seen.’ Both films hold very special meaning for me. It feels like everything has come together perfectly. I hope to see more outstanding works from female directors in the future, and I look forward to an era where there’s no gender opposition, only mutual equality.”
By Wendy Huang
Follow @whatsonweibo
Edited for clarity by Manya Koetse
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. Please note that your comment below will need to be manually approved if you’re a first-time poster here.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com
What’s on Weibo Chapters
Subscribe

Tuning Into the Year of the Snake

The ‘China-chic Girl’ Image and the Realities of China’s Competitive Food Delivery Market

From “Public Megaphone” to “National Watercooler”: Casper Wichmann on Weibo’s Role in Digital China

“Black Myth: Wukong”: From Gaming Screens to the CMG Spring Festival Gala?

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

The Price of Writing Smut: Inside China’s Crackdown on Erotic Fiction

Our Picks: Top 10 Chinese Buzzwords and Phrases of 2024 Explained

Weibo Watch: “Comrade Trump Returns to the Palace”

The ‘Cycling to Kaifeng’ Trend: How It Started, How It’s Going

Hu Xijin’s Comeback to Weibo

“Dear Li Hua”: The TikTok/Xiaohongshu Honeymoon Explained

Why Chinese Hit Movie “Her Story” is ‘Good Stuff’: Stirring Controversy and Celebrating Female Perspectives

Chiung Yao’s Suicide Farewell Letter: An English Translation
12-Year-Old Girl from Shandong Gets Infected with HPV: Viral Case Exposes Failures in Protecting Minors

Breaking the Taboo: China’s Sanitary Pad Controversy Sparks Demand for Change
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight9 months ago
China Insight9 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music10 months ago
China Music10 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Insight11 months ago
China Insight11 months agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Digital8 months ago
China Digital8 months agoChina’s 2024 Gaokao Triggers Online Discussions on AI






