Weiblog
About China’s ‘Completely Racist’ Washing Powder Commercial
A Chinese ad campaign for washing detergent brand Qiaobi (俏比) that recently aired on TV and in cinemas has caused big controversy for being “completely racist”. Watch our Weivlog update on this issue here.
Published
8 years agoon

A Chinese ad campaign for washing detergent brand Qiaobi (俏比) that recently aired on TV and in cinemas has caused big controversy for being “completely racist”. Watch our Weivlog update on this issue here. Read more about the Qiaobi controversy here.
©2016 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Manya is the founder and editor-in-chief of What's on Weibo, offering independent analysis of social trends, online media, and digital culture in China for over a decade. Subscribe to gain access to content, including the Weibo Watch newsletter, which provides deeper insights into the China trends that matter. More about Manya at manyakoetse.com or follow on X.

China Memes & Viral
The ‘Cycling to Kaifeng’ Trend: How It Started, How It’s Going
The Kaifeng cycling craze revealed more than just the adventurous spirit of Chinese students.
Published
3 days agoon
November 12, 2024
PREMIUM CONTENT
From city marketing to the spirit of China’s new generation, there are many themes behind the recent Zhengzhou trend of thousands of students cycling to Kaifeng overnight.
The term ‘yè qí‘ (夜骑), meaning “night ride,” has recently become a buzzword on Chinese social media. Large groups of students from various schools and universities in Zhengzhou, the capital of Henan province with a population of over 12 million, have been cycling en masse on shared bikes to Kaifeng, a neighboring historic city of around 5 million residents. These journeys often begin in the evenings or around midnight.
Across multiple platforms, videos of swarms of cyclists heading to Kaifeng have gone viral. The footage is striking, capturing streams of students embarking on the 40-mile nighttime journey, some waving Chinese flags, filming on their phones, singing together, and clearly having a great time.
According to some reports, approximately 100,000 or even 200,000 students have participated in these rides, drawing significant media attention both in China and internationally—especially after authorities began imposing restrictions on the so-called ‘Night Riding Army.’
HOW IT STARTED
The true origins of this story seem a bit murky.
The first Chinese news reports and blogs about students cycling to Kaifeng began surfacing around November 2-3 this year, coinciding with the first large-scale group rides from Zhengzhou to Kaifeng. The trend seemed to emerge out of nowhere.
On November 3, numerous Chinese media outlets provided an explanation for the phenomenon. According to these reports, on June 18, 2024, four female friends allegedly decided, at 7 PM, to embark on a 40-mile journey from Zhengzhou to Kaifeng to try out the city’s renowned soup dumplings. It took them around five hours to ride there, and, when they shared their adventure online, they used the slogan: “Youth only comes once” (青春只有一次).

These four girls allegedly started the Kaifeng night ride trend in June of 2024 (The Paper).
Their posts were said to have inspired hundreds of other students to follow suit, organizing night rides in groups with the trend peaking during the first two weekends of November. This narrative of an organic trend of night riding to Kaifeng for dumplings was picked up by Western media outlets, including reports from the BBC and The Guardian.
Earlier in summer, some Henan media indeed reported about four girls doing a night ride to Kaifeng. This was followed by another video by a Douyin user (@去你的岛), dated June 23, documenting a ride from Zhengzhou to Kaifeng for breakfast. That video was later turned into a small news item (dated June 29, but showing footage of the June 23 ride). Aside from an October 6 video by another Douyin user (@小木同学) imitating the June 23 group by cycling to Kaifeng with friends, however, there is a notable lack of videos indicating a widespread cycling-to-Kaifeng trend before the large-scale group rides of November 2-3. Moreover, the original posts by the four girls are nowhere to be found.
This raises questions: How did the story of the four girls gain traction without leaving a significant digital footprint? Was the Zhengzhou-to-Kaifeng cycling trend a truly organic movement, or could it have been more orchestrated? Curiously, the Weibo hashtag “How did the college students’ night ride to Kaifeng initially start?” (#大学生夜骑开封最早是怎么开始的#), which had been used by multiple bloggers, was also taken offline at the time of writing.
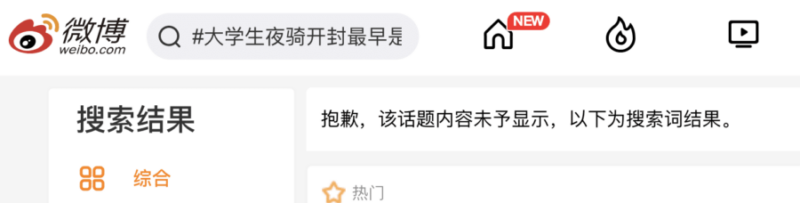
Screenshot of Weibo hashtag not being displayed.
The origins of the trend are particularly relevant as Chinese cities fiercely compete to become the next social media sensation. Since Zibo’s viral success, third- and second-tier cities across China have been striving to replicate its fame. While it’s ideal to become the next travel hit organically, cities often benefit from promoting local specialities and hyping up meme-worthy moments. Cities like Tianshui in Gansu and Harbin have enjoyed their moments in 2024, propelled by memes and viral content.
Kaifeng had already launched initiatives to boost tourism before the cycling trend. In March, a special shuttle service from Zhengzhou to Kaifeng was introduced to encourage day trips. In April, the city debuted its “Wang Po Matchmaking” show at Wansui Mountain Martial Arts City to attract tourists.
Tourist offices nationwide have become increasingly savvy in using social media for city marketing. Given the absence of a substantial social media trend from June to November, it seems plausible that the cycling phenomenon was a coordinated marketing effort. It likely began with a large group ride in early November, which sparked student interest, and snowballed. Kaifeng capitalized on the social media buzz starting November 2, but the scale of the phenomenon probably far exceeded what anyone had expected.
A CRAZY RIDE
As the ‘Zhengzhou to Kaifeng Night Ride’ was reported by local media and hit social media charts during the first weekend of November, it didn’t take long for students to catch on and join the ride. By the second weekend of November, Zhengkai Avenue, the main road from Zhengzhou to Kaifeng, was buzzing with activity, packed with thousands of university students participating in the night ride. Waving national flags, singing songs – including the national anthem -, taking group pictures, the moment was all that mattered.
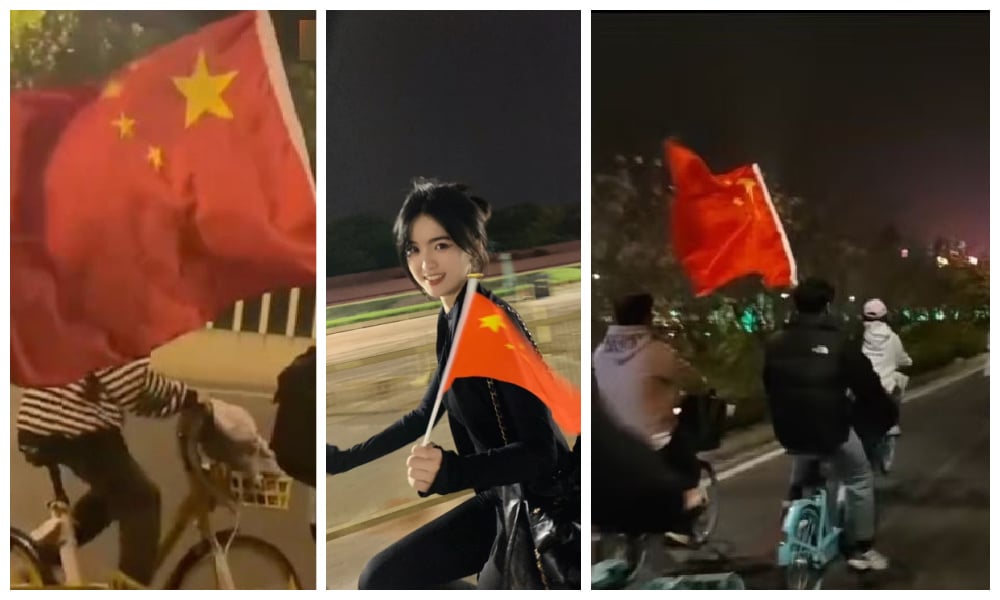

Night riding while waving the national flag.
While some foreign media speculated that the movement carried political undertones, citing at least one flag on the road advocating for the reunification of Taiwan with the motherland, it was likely more about patriotic youth waving non-controversial flags while channeling some nationalistic energy.
It was about “passion”—an English word that became synonymous with the nightly bike ride. It wasn’t about the soup dumplings or the exercise; it was about joy, freedom, and the pure, youthful energy of passion—an important theme for China’s Generation Z, the post-95 and post-00 generations, who often feel pushed and sometimes even paralyzed by the intense social pressures they face.

Night riders posing with a poster saying : You need passion in your life (source).
The trend was supported (or facilitated?) by Kaifeng authorities. On November 3, they set up shared bike stations along Zhengkai Avenue to manage the influx of cyclists. Police provided guidance at the scene and ensured safety throughout the night. Kaifeng’s Tourism Bureau issued a “cycling safety advisory” via its official WeChat account, encouraging visitors to adhere to traffic rules, travel sustainably, avoid peak times, and “enjoy the seasonal beauty of Kaifeng with a positive attitude.”
Starting on November 3, Kaifeng’s main tourist attractions, such as Millennium City Park, Wansui Mountain, and Daxiangguo Temple were specially opened to the ‘night riders’ in the middle of the night, even offering them free annual tourism passes (#开封多个景点为夜骑大学生免费#). At this time, the slogan “Youth is priceless, seize the night ride to Kaifeng” (“青春没有售价,夜骑开封拿下”) was actively promoted at Kaifeng tourist spots and in the media.

Historical cultural theme park Millennium City Park in Kaifeng on November 3, promoting free access to night riders and the slogan “Youth is priceless, seize the night ride to Kaifeng.”
The shuttle bus taking students back to Zhengzhou was provided for free.
On social apps like Xiaohongshu, students shared various ‘strategy guides’ for the best way to navigate the nightly ride to Kaifeng, including tips such as:
- Choose a comfortable shared bike and avoid unlocking it along the way. With a bike like HelloBike, the journey will only cost 19.5 RMB ($2.70). Starting from Zhengzhou Sports Center Station, head north on Jinshui Road and cycle east in a straight line to Kaifeng. The trip should take about 4 hours.
- From Zhengzhou University to Kaifeng Gulou, the total distance is 79.4 km, with an estimated travel time of 6 hours and 38 minutes. Including breaks and meal stops, the journey could take at least 8 hours.
- Bring a small flag for photo opportunities.
- Upon arrival, visit the Haidilao hotpot restaurant, where they provide blankets and snacks.
- Must-try local dishes: soup dumplings, egg casserole, and deep-fried dough with soy milk.
GOING DOWNHILL
During the weekend of November 8-9, numerous videos emerged showing thousands of students cycling from Zhengzhou to Kaifeng, revealing chaotic scenes (link, link). Some estimates suggested that over 30,000 students had arrived in Kaifeng in a single night.
The trend had a significant impact, raising several concerns. Safety issues loomed large as the sheer number of bicycles on the road created risks, especially given that many participants lacked experience with long-distance cycling. Traffic congestion reached such levels that some cars became trapped amid the cycling groups.

The shared bike system also faced severe challenges. While students eagerly undertook the 4-5 hour downhill journey to Kaifeng, they were unwilling to make the uphill return to Zhengzhou. This resulted in thousands of bikes being abandoned in Kaifeng or along the route, requiring retrieval by the bike companies.
Beyond logistical strain on the bike-sharing system, the abandoned bikes caused significant disruptions in Kaifeng, with entire roads blocked. In Zhengzhou, locals complained about a lack of available bikes for their commutes.
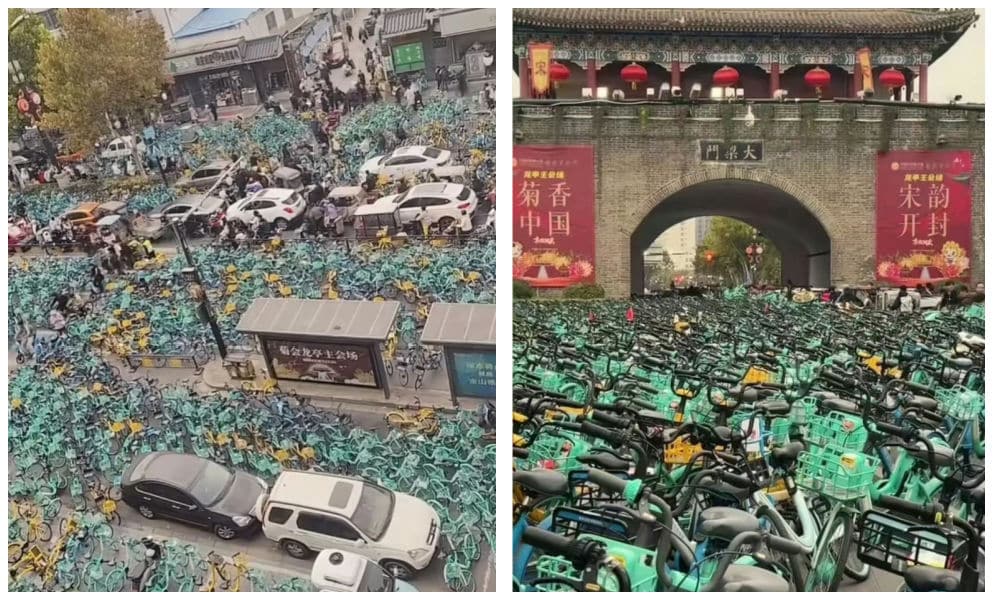

Shared bike chaos in Kaifeng.
While some praised the students’ adventurous spirit, others grew increasingly frustrated with the mounting problems.
By the afternoon of November 9, the official narrative shifted.
Initially, Chinese media celebrated the trend, but reports soon focused on its downsides. One widely shared story featured a 34-year-old man who had joined the ride with his daughter. Unaccustomed to cycling, he became exhausted after only 12-13 kilometers (about 8 miles) (#郑州34岁男子跟风夜骑开封后住院#). He was later hospitalized and diagnosed with hypokalemia (low potassium levels). The message? “Don’t blindly follow the trend.”
Authorities quickly stepped in to stop the night rides. Traffic police in Zhengzhou and Kaifeng issued a joint announcement banning the use of bike lanes on Zhengkai Avenue from 16:00 on November 9 to 12:00 on November 10.
Three major shared bike companies—Meituan, HelloBike, and Qingju—released statements reminding users that their bikes were not intended for cross-city travel. Bikes taken beyond designated zones would automatically lock and incur ‘relocation fees.’
Several universities implemented strict measures, ordering students back to campus and enforcing lockdowns. By Sunday night, some students took to Weibo to report that they were still not allowed to leave their campuses.
THE ROAD AHEAD
Despite the official crackdown on night rides to Kaifeng, some Zhengzhou students have now shifted to walking the entire route, a journey that can take up to 11 hours—equating to 70,000-100,000 steps on a smartwatch pedometer.

Unable to cycle, groups of students decided to walk to Kaifeng.
The crackdown on the nightly cycling craze has also prompted some reflection.
While many netizens praise the students for “truly embodying youth and vitality,” others see a deeper significance in the trend.
On Weibo, author Xu Kaizhen (许开祯) offers his perspective on what the Kaifeng phenomenon reveals about Chinese youth today. He writes:
“On the surface, the Kaifeng craze appears to be the latest trend in cultural tourism. But at its core, it has nothing to do with tourism. What is it really about? It’s about young people, about youth. And it’s not about youthful rebellion or hormones—modern youth have moved beyond that. It’s about escape. A collective, grand escape. An escape from a mediocre era, a mediocre life, and even a mediocre background. Every young person who joined the night ride was driven by a need to escape. Dissatisfied with reality yet powerless to change it, they turned to this collective unconscious act of performance art.”
Despite the criticism, it seems many hold a soft spot for China’s youth, understanding the challenges they face. As one popular comment puts it: “I dearly love this generation of Chinese youth. Their daytime has been drained by the previous generation, leaving only the night for them to carve out some space to unwind. ‘Escape’ describes it perfectly.”
For now, it seems the Kaifeng trend isn’t over. What began as an innocent, fun-loving initiative has turned into a mass mobilization that raises questions about hyped-up tourism, city marketing, and, most importantly, the boundless energy of China’s new generation. While the phenomenon has left many puzzled, some argue it’s crucial to grasp the youth’s yearning for these kinds of adventures.
As Xu Kaizhen concluded: “Perhaps by understanding this night ride, we can truly understand this generation. No—perhaps we can begin to understand the coming era.”
See our X thread with videos on this trend.
By Manya Koetse, with contributions by Miranda Barnes
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
China Media
Hu Xijin’s Comeback to Weibo
After 90 days of silence, Hu Xijin is back on Weibo—but not everyone’s thrilled.
Published
1 week agoon
November 7, 2024
A SHORTER VERSION OF THIS ARTICLE WAS PART OF THE MOST RECENT WEIBO WATCH NEWSLETTER.
For nearly 100 days, since July 27, the well-known social and political commentator Hu Xijin (胡锡进) remained silent on Chinese social media. This was highly unusual for the columnist and former Global Times editor-in-chief, who typically posts multiple Weibo updates daily, along with regular updates on his X account and video commentaries. His Weibo account boasts over 24.8 million followers.
Various foreign media outlets speculated that his silence might be related to comments he previously made about the Third Plenum and Chinese economics, especially regarding China’s shift to treating public and private enterprises equally. But without any official statement, Chinese netizens were left to speculate about his whereabouts.
Most assumed he had, in some way, taken a “wrong” stance in his commentary on the economy and stock market, or perhaps on politically sensitive topics like the Suzhou stabbing of a Japanese student, which might have led to his being sidelined for a while. He certainly wouldn’t be the first prominent influencer or celebrity to disappear from social media and public view—when Alibaba’s Jack Ma seemed to have fallen out of favor with authorities, he went missing, sparking public concern.
After 90 days of absence, the most-searched phrases on Weibo tied to Hu Xijin’s name included:
胡锡进解封 “Hu Xijin ban lifted”
胡锡进微博解禁 “Hu Xijin’s Weibo account unblocked”
胡锡进禁言 “Hu Xijin silenced”
胡锡进跳楼 “Hu Xijin jumped off a building”

On October 31, Hu suddenly reappeared on Weibo with a post praising the newly opened Chaobai River Bridge, which connects Beijing to Dachang in Hebei—where Hu owns a home—significantly reducing travel time and making the more affordable Dachang area attractive to people from Beijing. The post received over 9,000 comments and 25,000 likes, with many welcoming back the old journalist. “You’re back!” and “Old Hu, I didn’t see you on Weibo for so long. Although I regularly curse your posts, I missed you,” were among the replies.
When Hu wrote about Trump’s win, the top comment read: “Old Trump is back, just like you!”
Not everyone, however, is thrilled to see Hu’s return. Blogger Bad Potato (@一个坏土豆) criticized Hu, claiming that with his frequent posts and shifting views, he likes to jump on trends and gauge public opinion—but is actually not very skilled at it, allegedly contributing to a toxic online environment.
Other bloggers have also taken issue with Hu’s tendency to contradict himself or backtrack on stances he takes in his posts.
Some have noted that while Hu has returned, his posts seem to lack “soul.” For instance, his recent two posts about Trump’s win were just one sentence each. Perhaps, now that his return is fresh, Hu is carefully treading the line on what to comment on—or not.
Nevertheless, a post he made on November 3rd sparked plenty of discussion. In it, Hu addressed the story of math ‘genius’ Jiang Ping (姜萍), the 17-year-old vocational school student who made it to the top 12 of the Alibaba Global Mathematics Competition earlier this year. As covered in our recent newsletter, the final results revealed that both Jiang and her teacher were disqualified for violating rules about collaborating with others.
In his post, Hu criticized the “Jiang Ping fever” (姜萍热) that had flooded social media following her initial qualification, as well as Jiang’s teacher Wang Runqiu (王润秋), who allegedly misled the underage Jiang into breaking the rules.
The post was somewhat controversial because Hu himself had previously stated that those who doubted Jiang’s sudden rise as a math talent and presumed her guilty of cheating were coming from a place of “darkness.” That post, from June 23 of this year, has since been deleted.
Despite the criticism, some appreciate Hu’s consistency in being inconsistent: “Hu Xijin remains the same Hu Xijin, always shifting with the tide.”

Hu has not directly addressed his absence from Weibo. Instead, he shared a photo of himself from 1978, when he joined the military. In that post, he reflected on his journey of growth, learning, and commitment to the country. Judging by his renewed frequency of posting, it seems he’s also recommitted to Weibo.
By Manya Koetse
(follow on X, LinkedIn, or Instagram)
Spotted a mistake or want to add something? Please let us know in comments below or email us. First-time commenters, please be patient – we will have to manually approve your comment before it appears.
©2024 Whatsonweibo. All rights reserved. Do not reproduce our content without permission – you can contact us at info@whatsonweibo.com.
Subscribe

The ‘Cycling to Kaifeng’ Trend: How It Started, How It’s Going

Hu Xijin’s Comeback to Weibo

Weibo Watch: “Comrade Trump Returns to the Palace”

The Price of Writing Smut: Inside China’s Crackdown on Erotic Fiction

Controversial Wanghong Livestreamers Are Becoming a Weibo Staple in China

“Land Rover Woman” Sparks Outrage: Qingdao Road Rage Incident Goes Viral in China

China at Paris 2024 Olympics Trend File: Medals and Moments on Chinese Social Media

Weibo Watch: The Land Rover Woman Controversy Explained

Stolen Bodies, Censored Headlines: Shanxi Aorui’s Human Bone Scandal

Fired After Pregnancy Announcement: Court Case Involving Pregnant Employee Sparks Online Debate

Team China’s 10 Most Meme-Worthy Moments at the 2024 Paris Olympics

Weibo Watch: Going the Wrong Way

Weibo Watch: Shaping Olympic Narratives

The Rising Influence of Fandom Culture in Chinese Table Tennis

China at the 2024 Paralympics: Golds, Champions, and Trending Moments
Get in touch
Would you like to become a contributor, or do you have any tips or suggestions? Get in touch here!
Popular Reads
-

 China Insight6 months ago
China Insight6 months agoThe Tragic Story of “Fat Cat”: How a Chinese Gamer’s Suicide Went Viral
-

 China Music8 months ago
China Music8 months agoThe Chinese Viral TikTok Song Explained (No, It’s Not About Samsung)
-

 China Insight8 months ago
China Insight8 months agoThe ‘Two Sessions’ Suggestions: Six Proposals Raising Online Discussions
-

 China Insight12 months ago
China Insight12 months agoThe Story of Li Jun & Liang Liang: How the Challenges of an Ordinary Chinese Couple Captivated China’s Internet





